Operation of a dns proxy, Configuring dns, Configuration overview – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 228
27-3
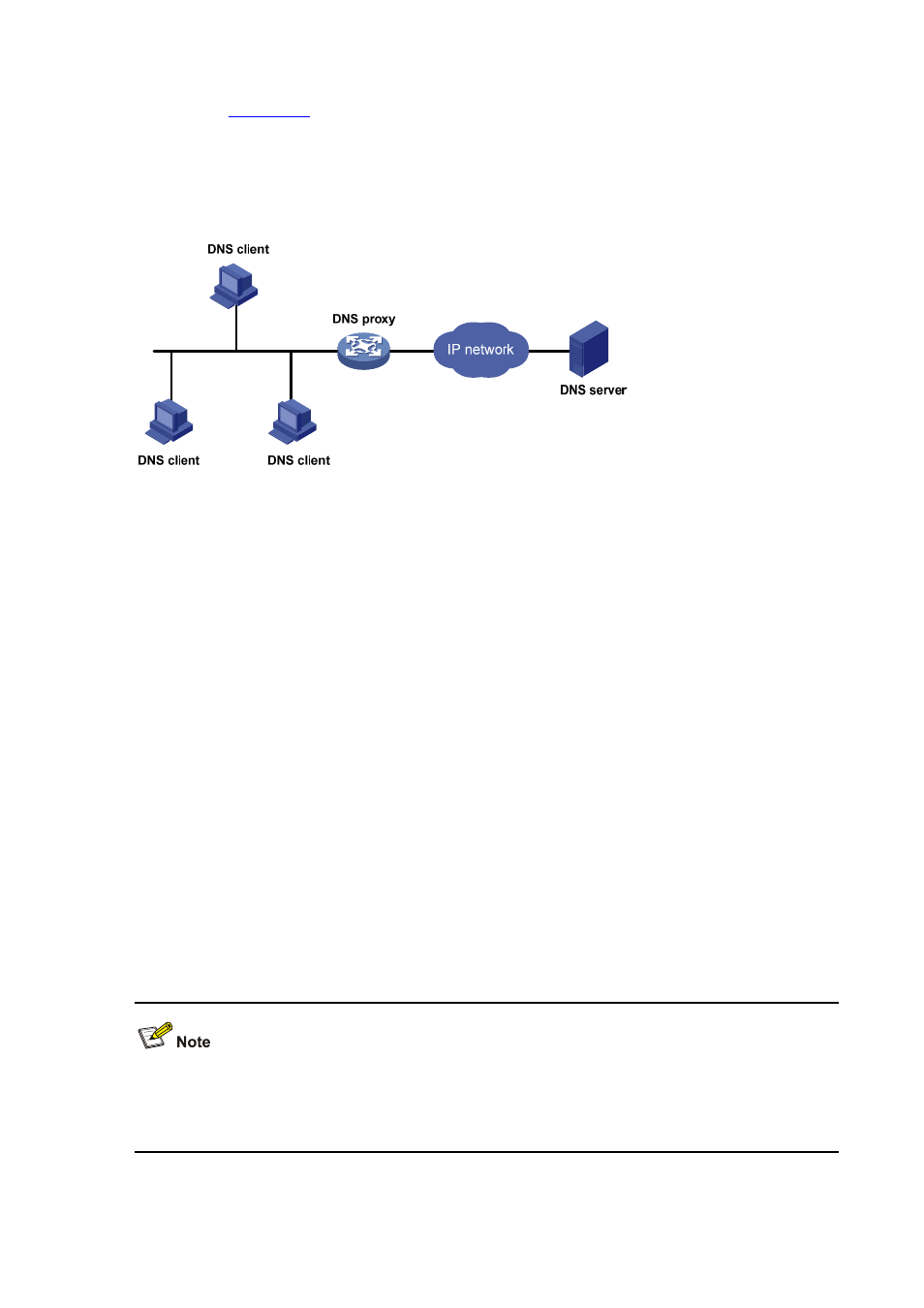
As shown in
, a DNS client sends a DNS request to the DNS proxy, which forwards the
request to the designated DNS server, and conveys the reply from the DNS server to the client.
The DNS proxy simplifies network management. When the DNS server address is changed, you only
need to change the configuration on the DNS proxy instead of on each DNS client.
Figure 27-2 DNS proxy networking application
Operation of a DNS proxy
1) A DNS client considers the DNS proxy as the DNS server, and sends a DNS request to the DNS
proxy, that is, the destination address of the request is the IP address of the DNS proxy.
2) The DNS proxy searches the local static domain name resolution table after receiving the request.
If the requested information exists in the table, the DNS proxy returns a DNS reply to the client.
3) If the requested information does not exist in the static domain name resolution table, the DNS
proxy sends the request to the designated DNS server for domain name resolution.
4) After receiving a reply from the DNS server, the DNS proxy forwards the reply to the DNS client.
Configuring DNS
Configuration Overview
DNS provides three functions, static name resolution, dynamic domain name resolution, and DNS
proxy.
Static name resolution: Name resolution is carried out through manually configured name
resolution entries.
Dynamic name resolution: A device resolves domain names through the DNS server.
DNS proxy: You can configure a device as a DNS proxy.
If both static domain name resolution and dynamic domain name resolution are configured, the device
first checks the static name resolution table for an IP address. If no IP address is available, it then
contacts the DNS server for dynamic name resolution.