Ipv4 acl match order, Fragments filtering with ipv4 acl – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 514
45-2
IPv4 ACL Match Order
An ACL may consist of multiple rules, which specify different matching criteria. These criteria may have
overlapping or conflicting parts. The match order is for determining how packets should be matched
against the rules.
There are two types of IPv4 ACL match orders:
config: Packets are compared against ACL rules in the order that the rules are configured.
auto: Packets are compared against ACL rules in the depth-first match order.
The term depth-first match has different meanings for different types of IPv4 ACLs, as shown in
.
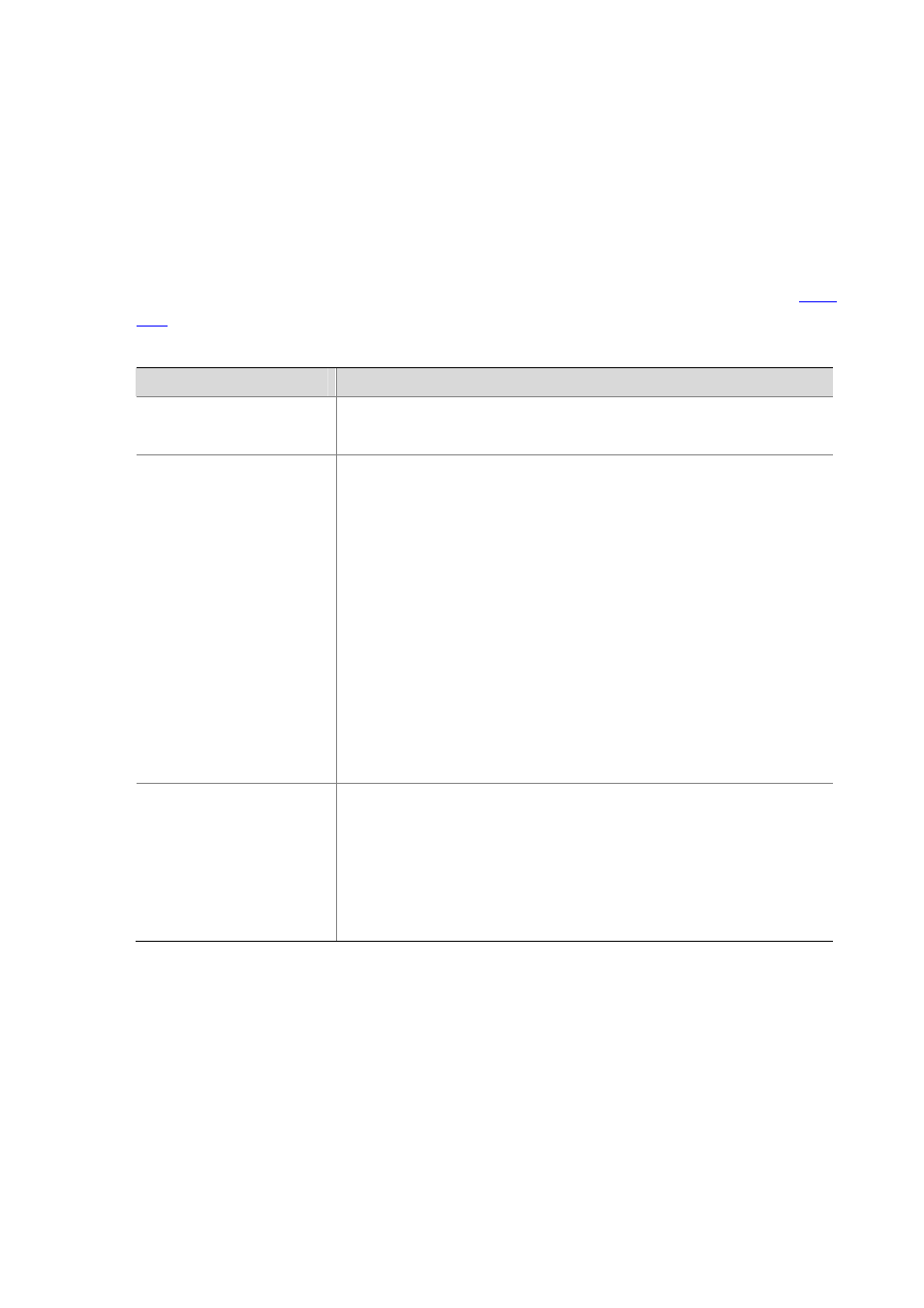
Table 45-2 Depth-first match for IPv4 ACLs
IPv4 ACL category
Depth-first match procedure
Basic IPv4 ACL
1)
Sort rules by source IP address wildcard and compare packets against
the rule configured with more zeros in the source IP address wildcard.
2)
In case of a tie, compare packets against the rule configured first.
Advanced IPv4 ACL
1) Sort rules by VPN instance first and compare packets against the rule
configured with a VPN instance.
2)
In case of a tie, look at the protocol carried over IP. A rule with no limit to
the protocol type (that is, configured with the ip keyword) has the lowest
precedence. Rules each of which has a single specified protocol type are
of the same precedence level.
3) If the protocol types have the same precedence, look at the source IP
address wildcards. Then, compare packets against the rule configured
with more zeros in the source IP address wildcard.
4)
If the numbers of zeros in the source IP address wildcards are the same,
look at the destination IP address wildcards. Then, compare packets
against the rule configured with more zeros in the destination IP address
wildcard.
5)
If the numbers of zeros in the destination IP address wildcards are the
same, look at the Layer 4 port number ranges, namely the TCP/UDP port
number ranges. Then compare packets against the rule configured with
the smaller port number range.
6)
If the port number ranges are the same, compare packets against the rule
configured first.
Ethernet frame header ACL
1) Sort rules by source MAC address mask first and compare packets
against the rule configured with more ones in the source MAC address
mask.
2)
If two rules are present with the same number of ones in their source MAC
address masks, look at the destination MAC address masks. Then,
compare packets against the rule configured with more ones in the
destination MAC address mask.
3) If the numbers of ones in the destination MAC address masks are the
same, compare packets against the one configured first.
The comparison of a packet against ACL rules stops immediately after a match is found. The packet is
then processed as per the rule.
Fragments Filtering with IPv4 ACL
Traditional packet filtering performs match operation on only the first fragments. All subsequent non-first
fragments are handled in the way the first fragments are handled. As attackers may fabricate non-first
fragments to attack your network, this results in security risks.
To address the risks, the device implements the following packet filtering functions:
IP-based filtering on all fragments.