Guest access management (gam) – H3C Technologies H3C Intelligent Management Center User Manual
Page 1020
1006
Guest Access Management (GAM)
An enterprise or organization usually has temporary, external users. These users access the network for
a short time, and are assigned restricted network access privileges. These users are called "guests." The
key factors of guest management are guaranteeing that the guests can quickly access the network and
guaranteeing the network access security.
Based on the characteristics of guests, IMC provides the Guest Access Manager (GAM) component. The
GAM provides two parts: guest access management module and guest access self-service system. After
an IMC operator logs in to IMC, the operator can use the guest access management module to manage
guest access operators and guest access user groups. After a guest access operator logs in to the guest
access self-service system, the guest access operator can create and manage guest accounts.
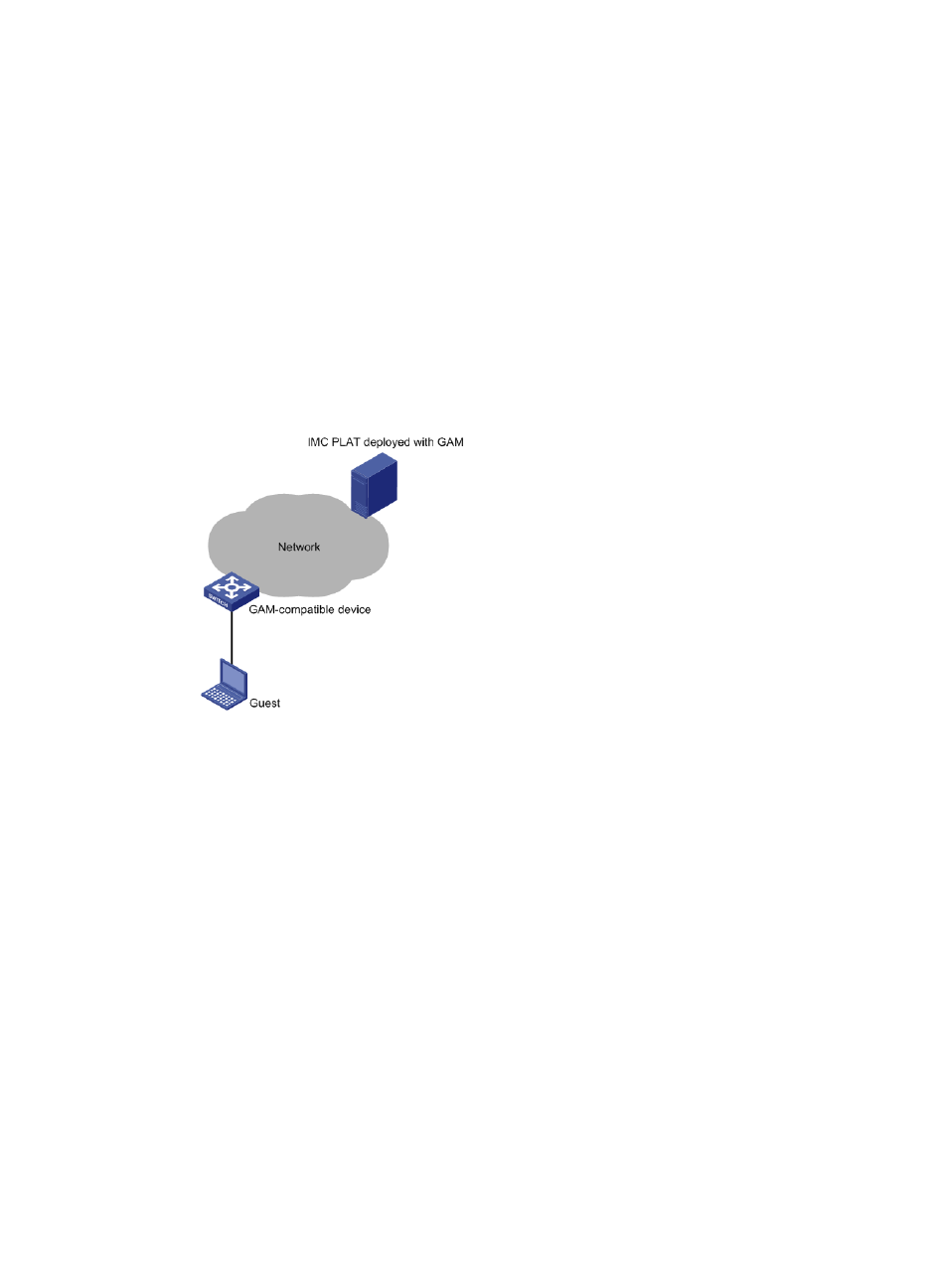
GAM is deployed in the following position of a network, as shown in
Figure 99 Position of GAM in a network
To implement GAM, follow these steps:
1.
An IMC operator (network administrator) creates a guest access user group based on the guest
characteristics, and specifies the access devices and the corresponding device user groups in the
guest access user group.
A guest can access the network through only the access devices specified in the guest access user
group to which the guest belongs. When an access device receives a network access request from
the guest, the access device adds the guest to the user group specified for the access device. After
the guest passes the authentication, the guest can access network resources.
Because the authentication requires the access device to support user groups, the software version
of the access device must be Comware Platform Software Version COMWAREV500R002B56 or
higher.
2.
The IMC operator creates guest access operators, and specifies the guest access user groups that
each guest access operator can manage.
3.
A guest access operator logs in to the guest access self-service system and creates guest users.
4.
The guest access operator prints the guest user information in the guest access self-service system
and gives it to the guest users.