Ip core architecture, Chapter 6. ip core architecture – Altera Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express User Manual
Page 75
December 2013
Altera Corporation
Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express
User Guide
6. IP Core Architecture
This chapter describes the architecture of the Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express. The
Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express implements the complete PCI Express protocol stack
as defined
The protocol stack includes the
following layers:
■
Transaction Layer—The Transaction Layer contains the Configuration Space, the RX
and TX channels, the RX buffer, and flow control credits.
■
Data Link Layer—The Data Link Layer, located between the Physical Layer and the
Transaction Layer, manages packet transmission and maintains data integrity at
the link level. Specifically, the Data Link Layer performs the following tasks:
■
Manages transmission and reception of Data Link Layer Packets (DLLPs)
■
Generates all transmission cyclical redundancy code (CRC) values and checks
all CRCs during reception
■
Manages the retry buffer and retry mechanism according to received
ACK/NAK Data Link Layer packets
■
Initializes the flow control mechanism for DLLPs and routes flow control
credits to and from the Transaction Layer
■
Physical Layer—The Physical Layer initializes the speed, lane numbering, and lane
width of the PCI Express link according to packets received from the link and
directives received from higher layers.
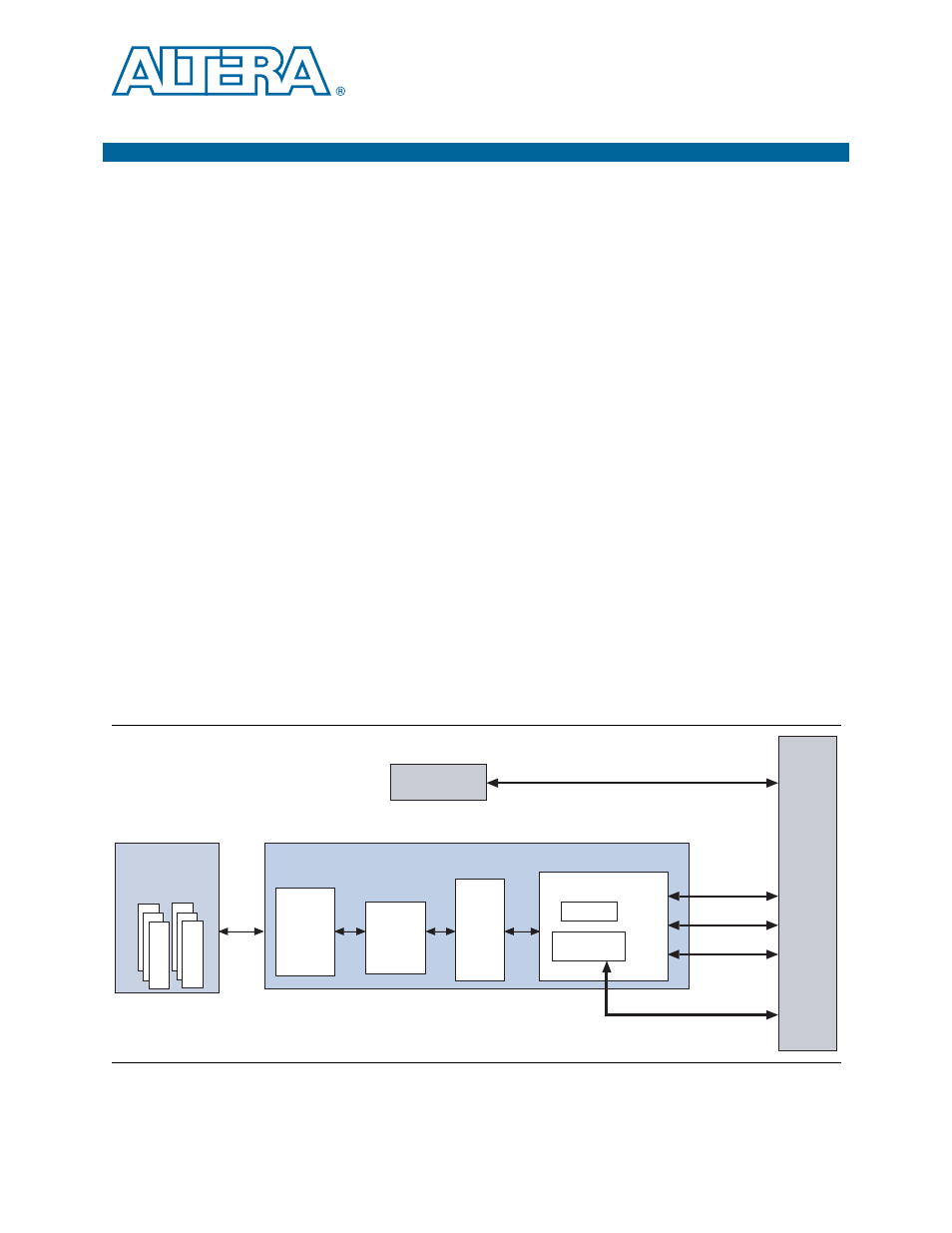
Figure 6–1
provides a high-level block diagram of the Arria V Hard IP for PCI
Express.
Figure 6–1. Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express with Avalon-ST Interface
Clock
Domain
Crossing
(CDC)
Data
Link
Layer
(DLL)
Transaction Layer (TL)
PHYMAC
Hard IP for PCI Express
Avalon-ST TX
Avalon-ST RX
Side Band
Local
Management
Interface (LMI)
PIPE
Application
Layer
Clock & Reset
Selection
Configuration
Space
PCS
PMA
Physical Layer
(Transceivers)
RX Buffer
PHY IP Core for
PCI Express (PIPE)
December 2013
UG-01110-1.5