Miscellaneous logic settings, Application tips, Trip circuit continuity and voltage monitor – Basler Electric BE1-851 User Manual
Page 217: Miscellaneous logic settings -61, Application tips -61, Trip circuit continuity and voltage monitor -61, Table 8-29. miscellaneous logic expressions -61
Miscellaneous Logic Settings
There are five logic variables that are classified as miscellaneous logic expressions. These expressions
are: SG-TARG, SG-TRIGGER, SB-DUTY, SB-LOGIC, and SA-RESET. The equations associated with
these variables determine how the BE1-851 responds to conditions such as when to target what triggers
fault reporting, defining breaker status monitoring, and setup for remote alarm/target reset provisions.
These variables aren’t included in any of the BESTlogic preprogrammed schemes. However, the factory
default equations are compatible with each scheme.
The default miscellaneous expressions are common among the preprogrammed and custom schemes.
When a preprogrammed scheme is modified or a new scheme is created, the miscellaneous logic
expressions should be reviewed to ensure desired performance.
The default expressions for the miscellaneous logic settings are as follows:
SB-LOGIC=/IN1
SG-TRIGGER=BFT+VO11,BFPU+VO12,0
SP-79ZONE=0
SG-TARG=50TA/50TB/50TC/50TN/50TQ/62/162/BF/150TA/150TB/150TC/150TN/150TQ/51A/51B/51C/51N/51Q,0
SA-RESET=0
SB-DUTY=0,0.000e+00,0
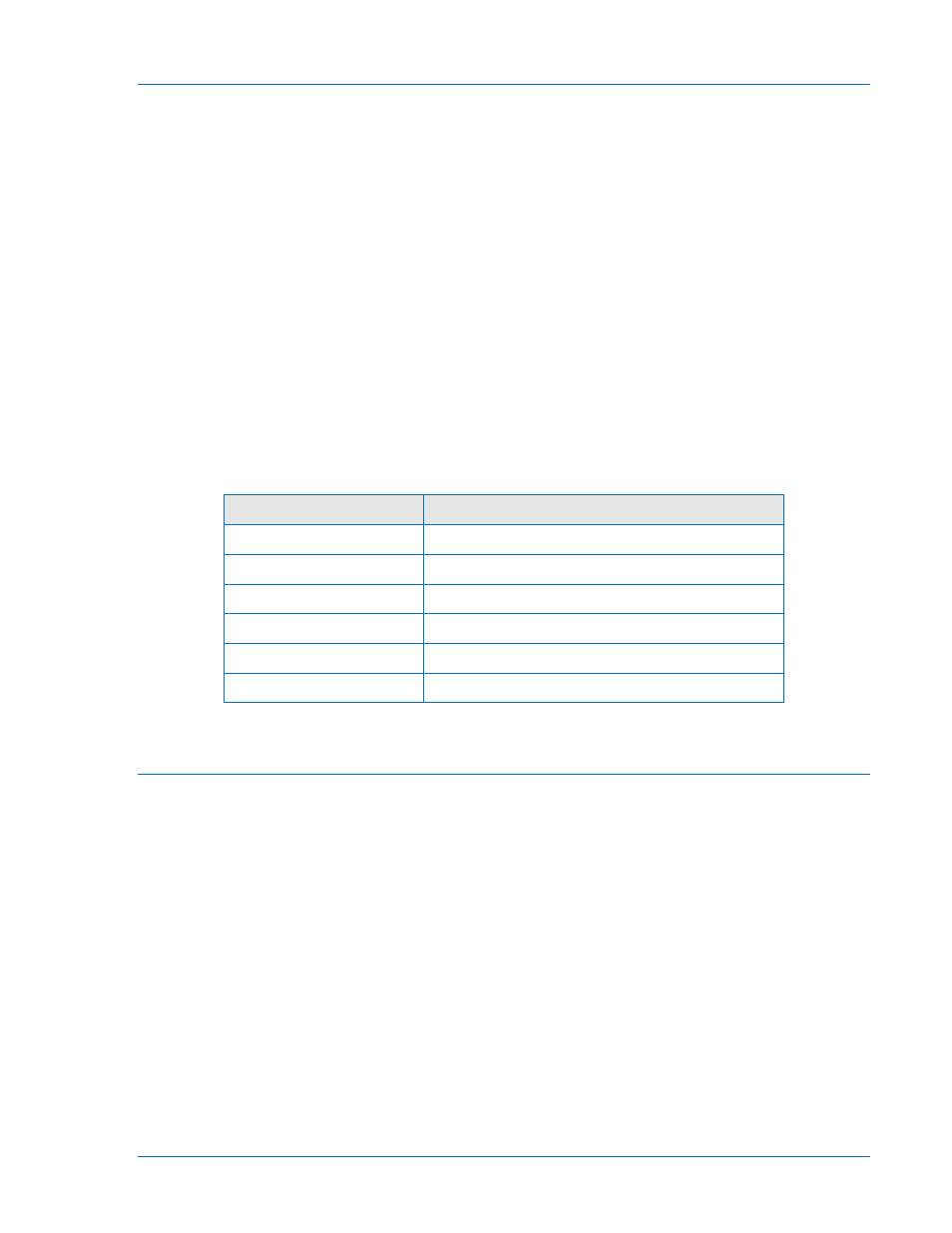
Table 8-29 lists the miscellaneous commands and the sections of this manual where detailed information
about each command may be found.
Table 8-29. Miscellaneous Logic Expressions
Command
Reference
SB-LOGIC
Section 6, Reporting and Alarms
SG-TRIGGER
Section 6, Reporting and Alarms
SP-79ZONE
Section 4, Protection and Control
SG-TARG
Section 6, Reporting and Alarms
SA-RESET
Section 6, Reporting and Alarms
SB-DUTY
Section 6, Reporting and Alarms
Application Tips
Trip Circuit Continuity and Voltage Monitor
OUT1 has a built in trip circuit voltage and continuity monitor that drives logic variable OUT1MON. This
variable can be used to improve breaker failure logic or to automatically enhance security during testing.
If the relay detects a loss of voltage or continuity in the breaker trip circuit, it is possible to speed up fault
clearing time by bypassing the breaker failure timer. Since relay failure and breaker failure are covered by
different backup actions, it is desirable to reduce common mode failure mechanisms. It is recommended
that separate control power fuses or breakers supply the feeder breaker and feeder protection circuits.
The equation for the Breaker Failure Trip logic (VO5) can be modified by ORing the Breaker Failure
Initiate with the expression VO10*OUT1MON. VO10 is designated in each of the preprogrammed logic
schemes as the Breaker Failure Initiate expression. Example 1 illustrates how the BFT logic expression is
modified. It is important that the breaker failure timer bypass logic also be disabled in test mode. Example
2 shows the expression for blocking the upstream instantaneous element. Figure 8-16 illustrates using the
trip circuit continuity monitor in breaker failure logic.
Example 1. Breaker failure trip expression: SL-VO5=BFT+VO10*OUT1MON*IN4*/343
Example 2. Block upstream instantaneous expression: SL-VO4=VO12*/VO5*/OUT1MON*IN4*/343
If the internal breaker failure function block is not being used, the trip circuit continuity and voltage monitor
alarm can be used to detect when the test paddle or test switches have been opened. This will
automatically place the relay in the test mode. Each of the preprogrammed logic schemes has logic to
9289900990 Rev R
BE1-851 Application
8-61