Slaveselect register, Document revision history, Document revision history -11 – Altera Embedded Peripherals IP User Manual
Page 117
Most bits (
IROE
,
ITOE
,
ITRDY
,
IRRDY
, and
IE
) in the
control
register control interrupts for status
conditions represented in the
status
register. For example, bit 1 of
status
is
ROE
(receiver-overrun
error), and bit 1 of control is
IROE
, which enables interrupts for the
ROE
condition. The SPI core asserts an
interrupt request when the corresponding bits in
status
and
control
are both 1.
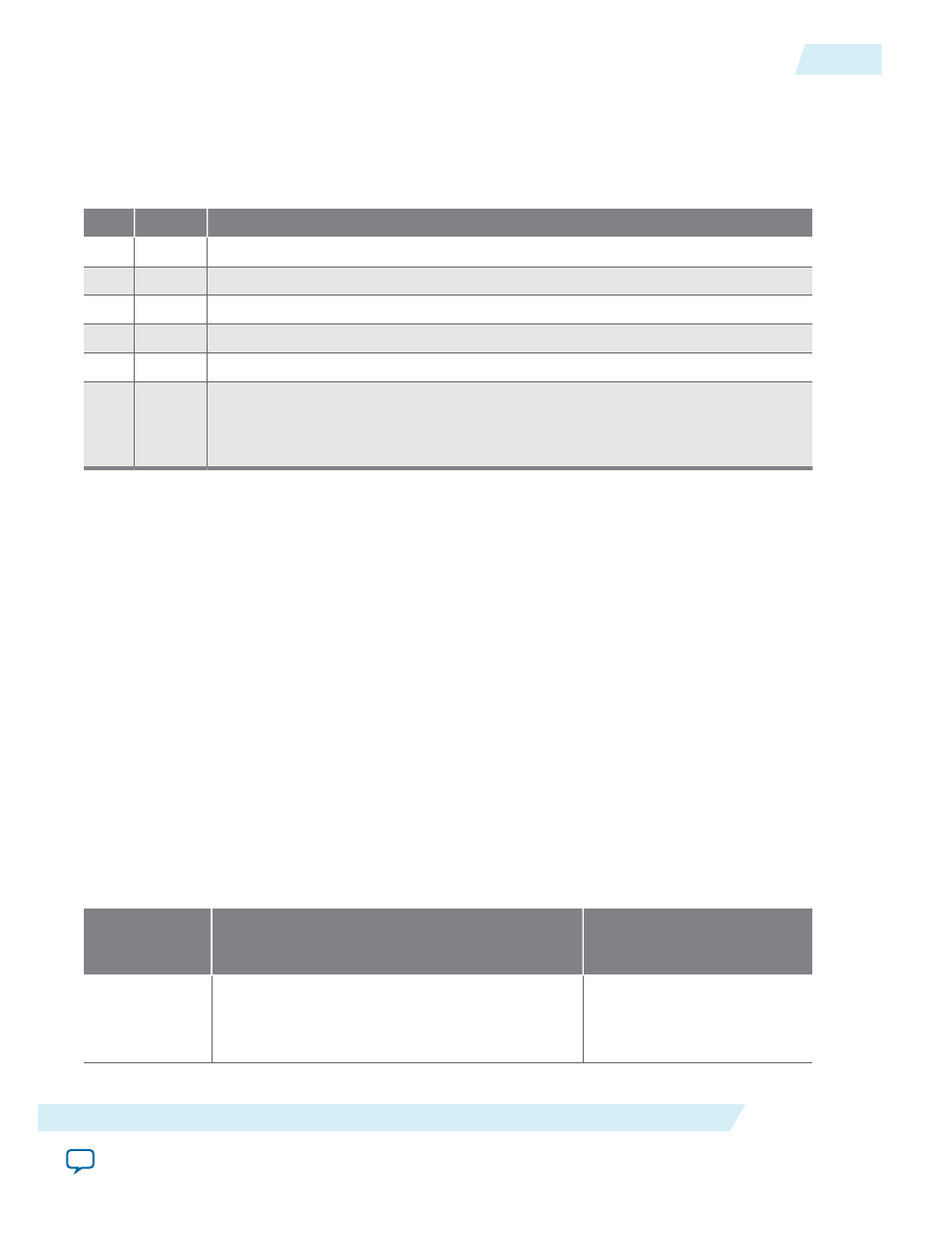
Table 10-7: control Register Bits
#
Name
Description
3
IROE
Setting
IROE
to 1 enables interrupts for receive-overrun errors.
4
ITOE
Setting
ITOE
to 1 enables interrupts for transmitter-overrun errors.
6
ITRDY
Setting
ITRDY
to 1 enables interrupts for the transmitter ready condition.
7
IRRDY
Setting
IRRDY
to 1 enables interrupts for the receiver ready condition.
8
IE
Setting
IE
to 1 enables interrupts for any error condition.
10
SSO
Setting
SSO
to 1 forces the SPI core to drive its
ss_n
outputs, regardless of whether
a serial shift operation is in progress or not. The slaveselect register controls which
ss_n outputs are asserted.
SSO
can be used to transmit or receive data of arbitrary
size, for example, greater than 32 bits.
After reset, all bits of the
control
register are set to 0. All interrupts are disabled and no
ss_n
signals are
asserted.
slaveselect Register
The
slaveselect
register is a bit mask for the
ss_n
signals driven by an SPI master. During a serial shift
operation, the SPI master selects only the slave device(s) specified in the
slaveselect
register.
The
slaveselect
register is only present when the SPI core is configured in master mode. There is one
bit in
slaveselect
for each
ss_n
output, as specified by the designer at system generation time.
A master peripheral can set multiple bits of
slaveselect
simultaneously, causing the SPI master to
simultaneously select multiple slave devices as it performs a transaction. For example, to enable
communication with slave devices 1, 5, and 6, set bits 1, 5, and 6 of
slaveselect
. However, consideration
is necessary to avoid signal contention between multiple slaves on their
miso
outputs.
Upon reset, bit 0 is set to 1, and all other bits are cleared to 0. Thus, after a device reset, slave device 0 is
automatically selected.
Document Revision History
Table 10-8: Document Revision History
Date and
Document
Version
Changes Made
Summary of Changes
December
2010
v10.1.0
Removed the “Device Support”, “Instantiating the
Core in SOPC Builder”, and “Referenced
Documents” sections.
—
UG-01085
2014.24.07
slaveselect Register
10-11
SPI Core
Altera Corporation