Interrupt behavior, Interrupt behavior -9 – Altera Embedded Peripherals IP User Manual
Page 240
Bit
Number
Bit Name
Read/
Write/
Clear
Description
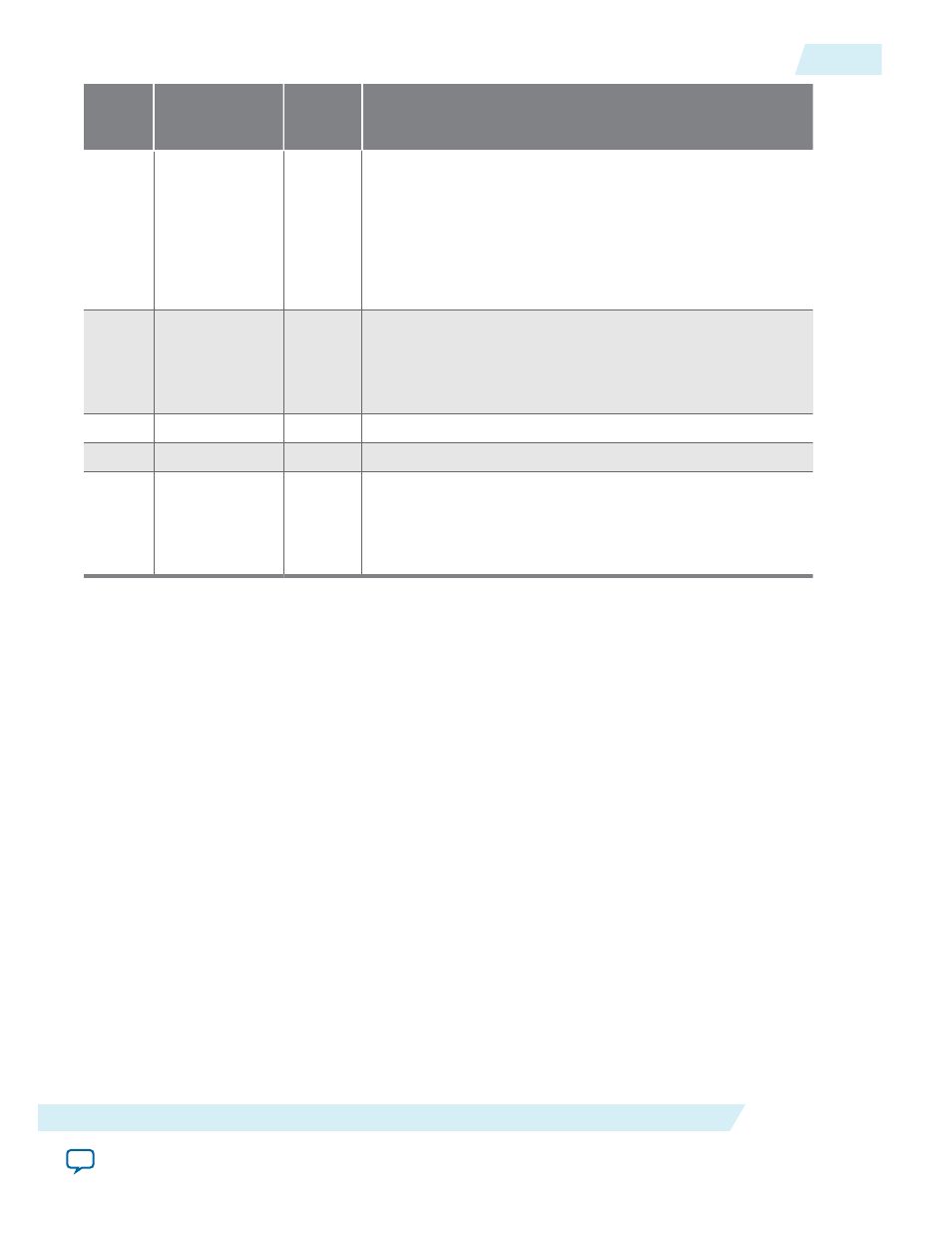
8
RCON
RW
Reads from a constant address. When
RCON
is 0, the read
address increments after every data transfer. This is the
mechanism for the DMA controller to read a range of
memory addresses. When
RCON
is 1, the read address does
not increment. This is the mechanism for the DMA
controller to read from a peripheral at a constant memory
address. For details, see the Addressing and Address
Incrementing section.
9
WCON
RW
Writes to a constant address. Similar to the
RCON
bit, when
WCON
is 0 the write address increments after every data
transfer; when
WCON
is 1 the write address does not
increment. For details, see Addressing and Address
Incrementing.
10
DOUBLEWORD
RW
Specifies doubleword transfers.
11
QUADWORD
RW
Specifies quadword transfers.
12
SOFTWARERESET
RW
Software can reset the DMA engine by writing this bit to 1
twice. Upon the second write of 1 to the
SOFTWARERESET
bit,
the DMA control is reset identically to a system reset. The
logic which sequences the software reset process then resets
itself automatically.
The data width of DMA transactions is specified by the
BYTE
,
HW
,
WORD
,
DOUBLEWORD
, and
QUADWORD
bits.
Only one of these bits can be set at a time. If more than one of the bits is set, the DMA controller behavior
is undefined. The width of the transfer is determined by the narrower of the two slaves read and written.
For example, a DMA transaction that reads from a 16-bit flash memory and writes to a 32-bit on-chip
memory requires a halfword transfer. In this case,
HW
must be set to 1, and
BYTE
,
WORD
,
DOUBLEWORD
, and
QUADWORD
must be set to 0.
To successfully perform transactions of a specific width, that width must be enabled in hardware using the
Allowed Transaction hardware option. For example, the DMA controller behavior is undefined if
quadword transfers are disabled in hardware, but the
QUADWORD
bit is set during a DMA transaction.
Executing a DMA software reset when a DMA transfer is active may result in permanent bus lockup (until
the next system reset). The
SOFTWARERESET
bit should therefore not be written except as a last resort.
Interrupt Behavior
The DMA controller has a single IRQ output that is asserted when the
status
register’s
DONE
bit equals 1
and the control register’s
I_EN
bit equals 1.
Writing the
status
register clears the
DONE
bit and acknowledges the IRQ. A master peripheral can read
the
status
register and determine how the DMA transaction finished by checking the
LEN
,
REOP
, and
WEOP
bits.
UG-01085
2014.24.07
Interrupt Behavior
23-9
DMA Controller Core
Altera Corporation