Subtree mask – H3C Technologies H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers User Manual
Page 123
18-3
be uniquely identified by a string of numbers {1.2.1.1.5}. This string of numbers is the OID of the
managed object A.
A subtree can be identified by the OID of the root node of the subtree. For example, the OID of the
subtree with the root node being B is the OID of node B –– {1.2.1.1}.
Figure 18-2 MIB tree
A
2
6
1
5
2
1
1
2
1
B
Subtree mask
A subtree OID used with a subtree mask defines a view subtree. A subtree mask is in hexadecimal
format. After it is converted to binary bits, each bit corresponds to a node of the OID.
1 means precise matching, that is, the OID of the MIB object to be accessed must be identical with
the subtree OID.
0 means wildcard matching, that is, the OID of the MIB object to be accessed can be different from
the subtree OID.
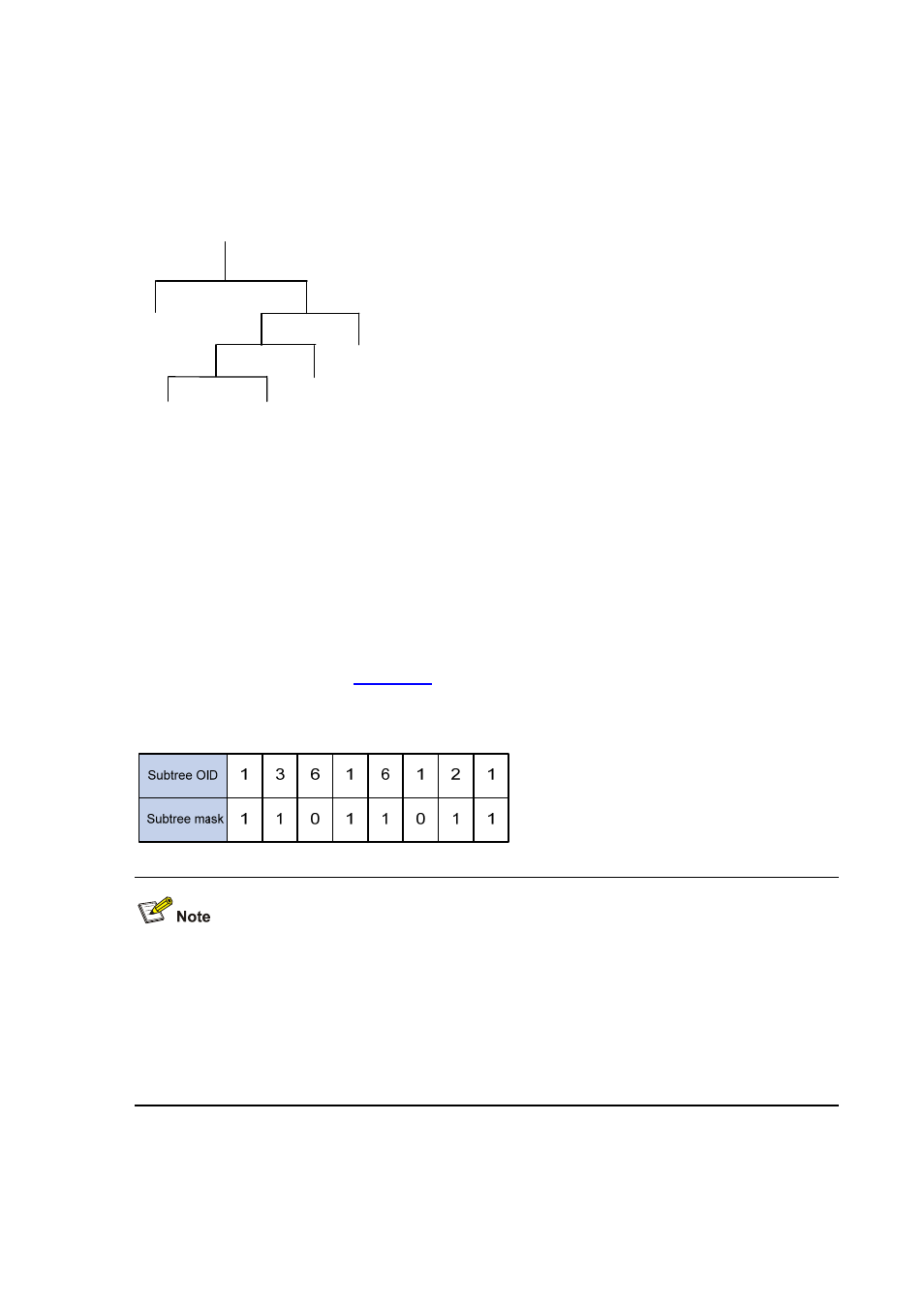
For example, provided the subtree mask 0xDB (11011011 in binary) and the subtree OID 1.3.6.1.6.1.2.1,
their relationship is as shown in
. The view determined by them includes all the nodes under
the subtree whose OID is 1.3.*.1.6.*.2.1, where * represents any number.
Figure 18-3 Subtree OID and subtree mask
If the number of bits in the subtree mask is greater than the number of nodes of the OID, the
excessive bits of the subtree mask will be ignored during subtree mask-OID matching.
If the number of bits in the subtree mask is smaller than the number of nodes of the OID, the short
bits of the subtree mask will be set to 1 during subtree mask-OID matching.
If no subtree mask is specified, the default subtree mask (all Fs) will be used for mask-OID
matching.