Zilog Z80230 User Manual
Page 115
SCC/ESCC
User Manual
UM010903-0515
Data Communication Modes
108
Some synchronous protocols require that certain characters be excluded from CRC calculation.
This is possible in the SCC because CRC calculations are enabled and disabled on the fly. To give
the processor sufficient time to decide whether or not a particular character should be included in
the CRC calculation, the SCC contains an 8-bit time delay between the receive shift register and
the CRC checker. The logic also guarantees that the calculation only starts or stops on a character
boundary by delaying the enable or disable until the next character is loaded into the receive data
FIFO. Because the nature of the protocol requires that CRC calculation disable/enable be selected
before the next character gets loaded into the Receive FIFO, users cannot take advantage of the
FIFO.
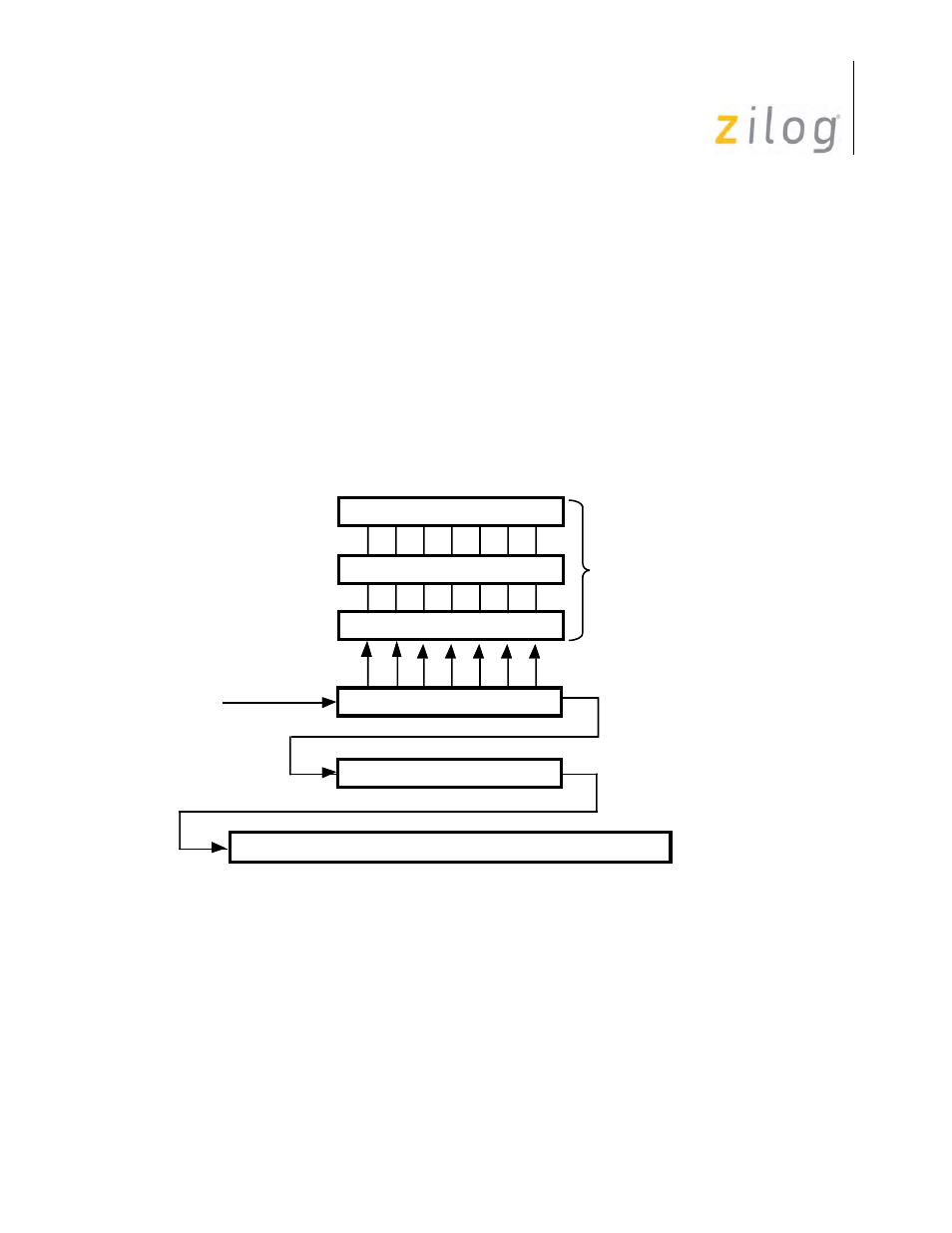
To understand how this works see
and the following explanation. Consider a case where
the SCC receives a sequence of eight bytes, called A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H, with A received first.
Now suppose that A is the sync character, the CRC is calculated on B, C, E, and F, and that F is the
last byte of this message. This process is used to control the SCC.
Receive CRC Data Path
Before A is received, the receiver is in Hunt mode and the CRC is disabled. When A is in the
receive shift register, it is compared with the contents of WR7. Since A is the sync character, the
bit patterns match and receive leaves Hunt mode, but character A is not transferred to the receive
data FIFO.
Receive Data FIFO
Receive Shift Register
CRC Checker
Eight Bit Time Delay
Receive Data
3 Bytes Deep for NMOS/CMOS
8 Bytes Deep for ESCC