And ×8 variations, Table 1–7 on – Altera IP Compiler for PCI Express User Manual
Page 10
1–8
Chapter 1: Datasheet
General Description
IP Compiler for PCI Express User Guide
August 2014
Altera Corporation
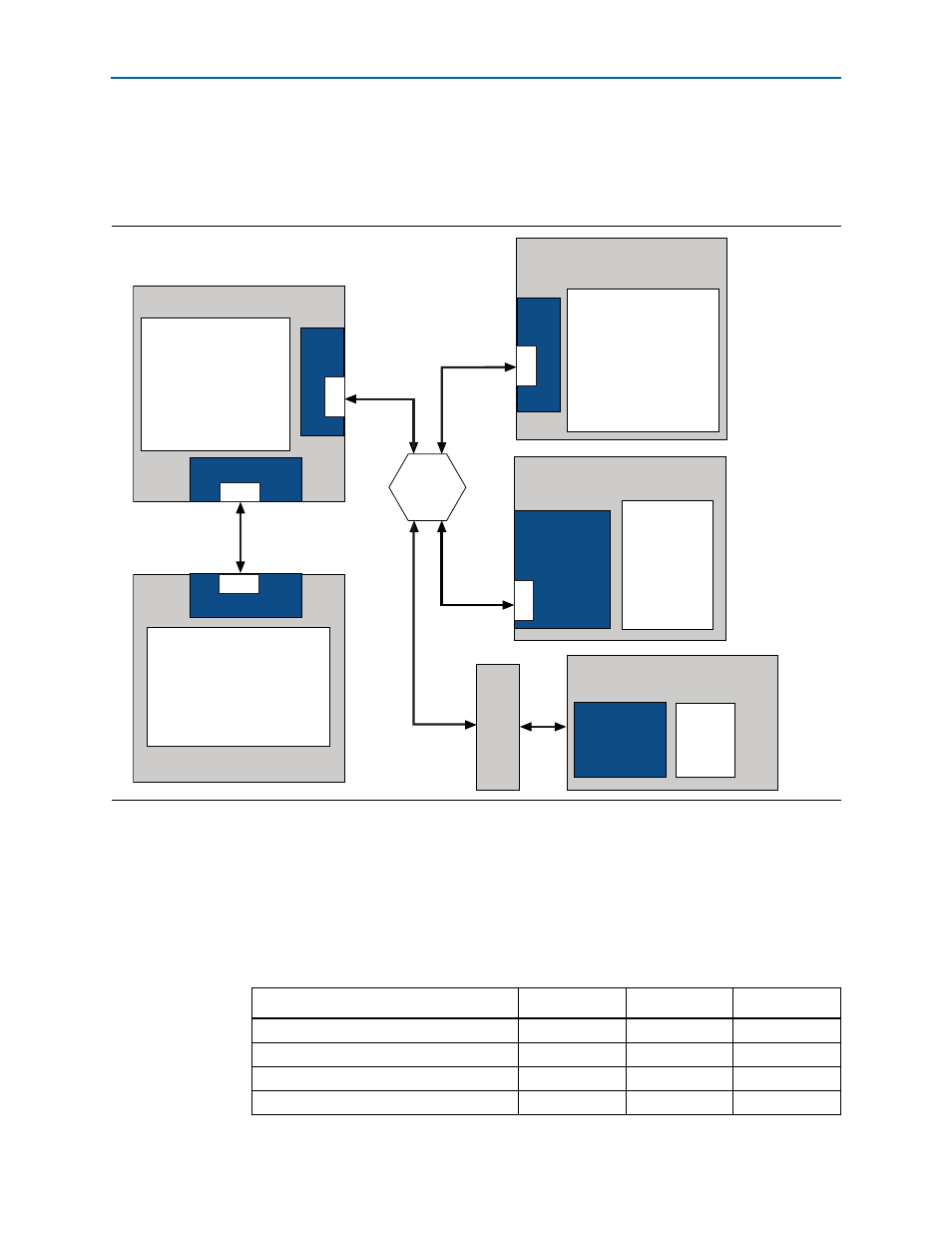
illustrates a heterogeneous topology, including an Altera device with two
PCIe hard IP root ports. One root port connects directly to a second FPGA that
includes an endpoint implemented using the hard IP IP core. The second root port
connects to a switch that multiplexes among three PCI Express endpoints.
If you target a device that includes an internal transceiver, you can parameterize the
IP Compiler for PCI Express to include a complete PHY layer, including the MAC,
PCS, and PMA layers. If you target other device architectures, the IP Compiler for PCI
Express generates the IP core with the Intel-designed PIPE interface, making the IP
core usable with other PIPE-compliant external PHY devices.
lists the protocol support for devices that include HSSI transceivers.
Figure 1–3. PCI Express Application with Two Root Ports
PCIe Link
PCIe Hard IP Block
RP
Switch
PCIe
Hard IP
Block
RP
User Application
Logic
PCIe Hard IP Block
EP
PCIe
Hard IP
Block
EP
User Application
Logic
IP Compiler
for
PCI Express
Soft IP
Implementation
EP
User Application
Logic
PHY
PIPE
Interface
User
Application
Logic
PCIe Link
PCIe Link
PCIe Link
PCIe Link
User Application
Logic
Altera FPGA with Embedded PCIe
Hard IP Blocks
Altera FPGA with Embedded PCIe
Hard IP Blocks
Altera FPGA with Embedded PCIe
Hard IP Blocks
Altera FPGA Supporting IP Compiler for
PCI Express Soft IP Implementation
IP Compiler
for
PCI Express
Soft IP
Implementation
Table 1–7. Operation in Devices with HSSI Transceivers (Part 1 of 2)
Device Family
×1
×4
×8
Stratix IV GX hard IP–Gen1
Yes
Yes
Yes
Stratix IV GX hard IP–Gen 2
Yes
Yes
Yes
Stratix IV soft IP–Gen1
Yes
Yes
No
Cyclone IV GX hard IP–Gen1
Yes
Yes
No