3 torque reference filter, 1) torque reference filter, Torque reference filter guide – Yaskawa Sigma-5 User Manual: Design and Maintenance - Rotary Motors User Manual
Page 201
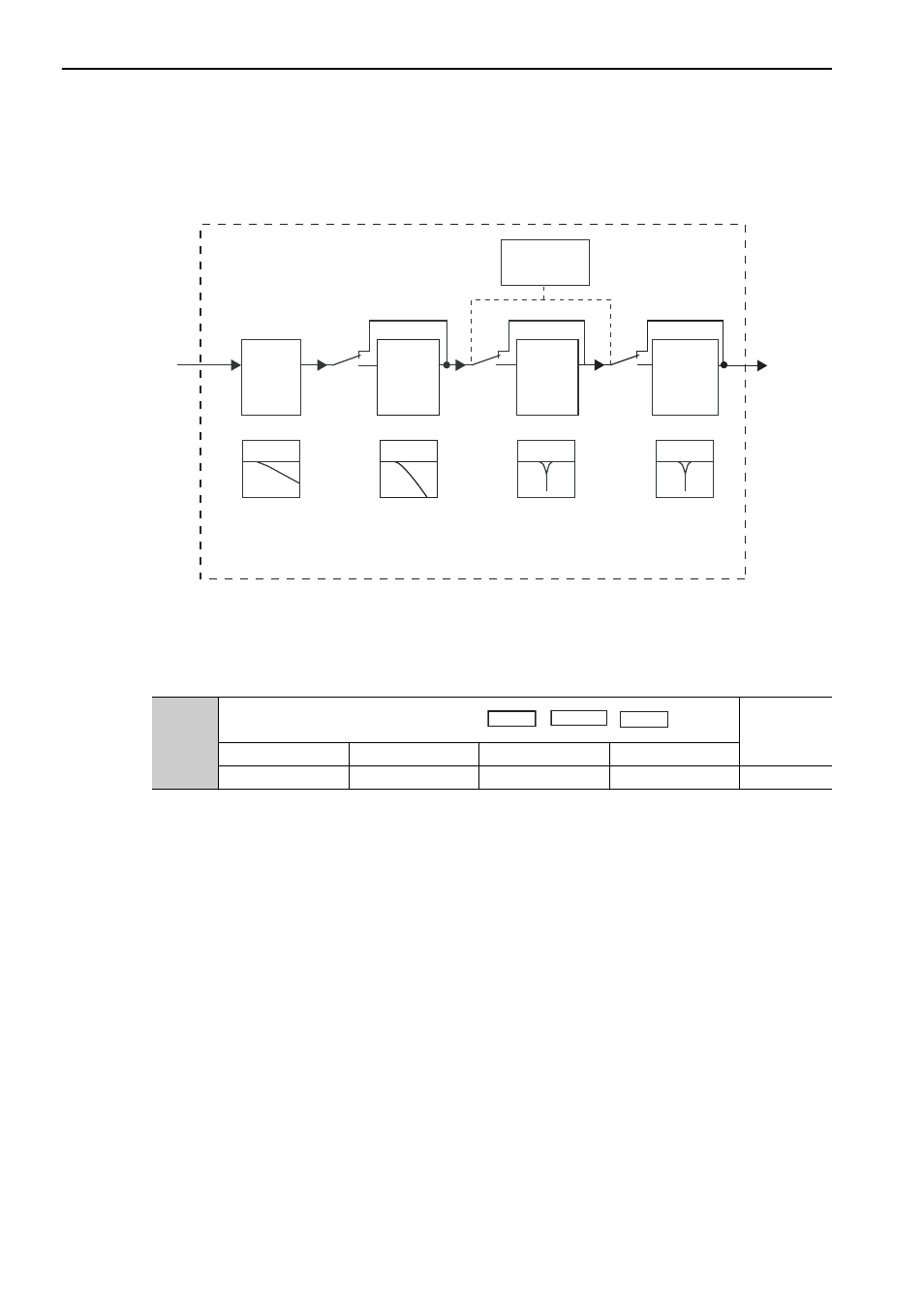
5 Adjustments
5.9.3 Torque Reference Filter
5-64
5.9.3 Torque Reference Filter
As shown in the following diagram, the torque reference filter contains first order lag filter and notch filters
arrayed in series, and each filter operates independently. The notch filters can be enabled and disabled with the
Pn408.
(1) Torque Reference Filter
If you suspect that machine vibration is being caused by the servo drive, try adjusting the filter time constants.
This may stop the vibration. The lower the value, the better the speed control response will be, but there is a
lower limit that depends on the machine conditions.
Torque Reference Filter Guide
• Use the speed loop gain (Pn100 [Hz]) and the torque filter time constant (Pn401 [ms]).
Adjusted value for stable control: Pn401 [ms]
≤ 1000/ (2π × Pn100 [Hz] × 4)
Critical gains: Pn401 [ms] < 1000/ (2
π × Pn100 [Hz] × 1)
Torque
reference
before
filtering
1st step
1st Torque
Reference
Filter
(Pn401)
Torque Related
Function Switch
Pn408
Notch filter
Notch filter
First order lag filter
Torque
reference
after
filtering
Second order lag filter
2nd step
2nd Torque
Reference
Filter
(Pn40F,
Pn410)
2nd
Notch
Filters
(Pn40C,
Pn40D and
Pn40E)
1st
Notch
Filters
(Pn409,
Pn40A
and Pn40B)
* The 2nd torque reference filter is available when Pn40F is set to a value less than 5000
and not available when Pn40F is set to 5000 (factory setting).
*
Pn401
1st Step 1st Torque Reference Filter
Time Constant
Classification
Setting Range
Setting Unit
Factory Setting
When Enabled
0 to 65535
0.01 ms
100
Immediately
Tuning
Speed
Position
Torque