Rotation – Yaskawa Sigma-5 User Manual: Design and Maintenance - Rotary Motors User Manual
Page 249
8.1 System Configuration and Connection Example for SERVOPACK with Fully-closed Loop Control
8-7
Fully-closed Loop Control
8.1.5 Encoder Output Pulse Signals from SERVOPACK with an External Encoder
by Renishaw plc
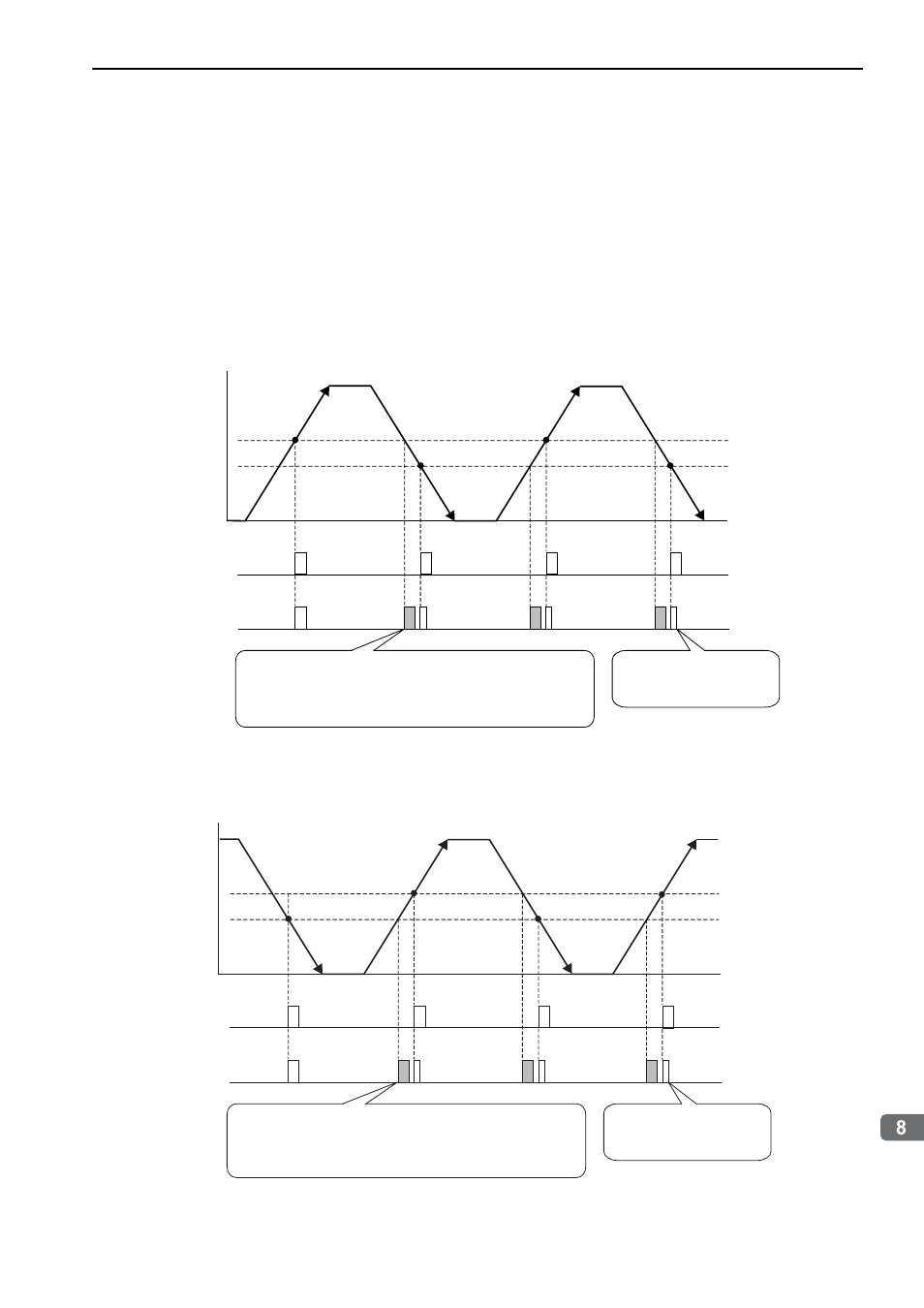
The output position of the zero point signal (Ref) will depend on the direction of movement for some models
of external encoders by Renishaw plc.
In such case, the phase-C pulses of the SERVOPACK are output at two positions.
For details on the specifications of the zero-point signals for a external encoder, refer to the manual for the
Renishaw external encoder.
(1) When Passing 1st Zero Point Signal (Ref) in Forward Direction and Returning after
Power ON
(2) When Passing 1st Zero Point Signal (Ref) in Reverse Direction and Returning after
Power ON
Machine position
Power ON
Zero point signal
㧔Ref㧕
Phase C
Time
Second pulse is half as wide
as the phase-A pulse.
No zero point signal (Ref) is sent from the external encoder.
However, a phase-C pulse will be sent from the SERVOPACK
when moving in the reverse direction, because it is the same
position from which a phase-C pulse was sent from the
SERVOPACK when moving in a forward direction.
Rotation
Machine position
Power ON
Zero point signal
㧔Ref㧕
Phase C
Time
Second pulse is half as wide
as the phase-A pulse.
No zero point signal (Ref) is sent from the external encoder.
However, a phase-C pulse will be sent from the SERVOPACK
when moving in the forward direction, because it is the same
position from which a phase-C pulse was sent from the
SERVOPACK when moving in a reverse direction.
Rotation