Programming 20, B5-02 proportional gain setting, B5-03 integral time setting – Yaskawa F7 Drive Programming Manual User Manual
Page 28: B5-04 integral limit setting, B5-05 derivative time setting
Programming 20
b5-02 Proportional Gain Setting
Setting Range:
0.00 to 25.00
Factory Default: 2.00
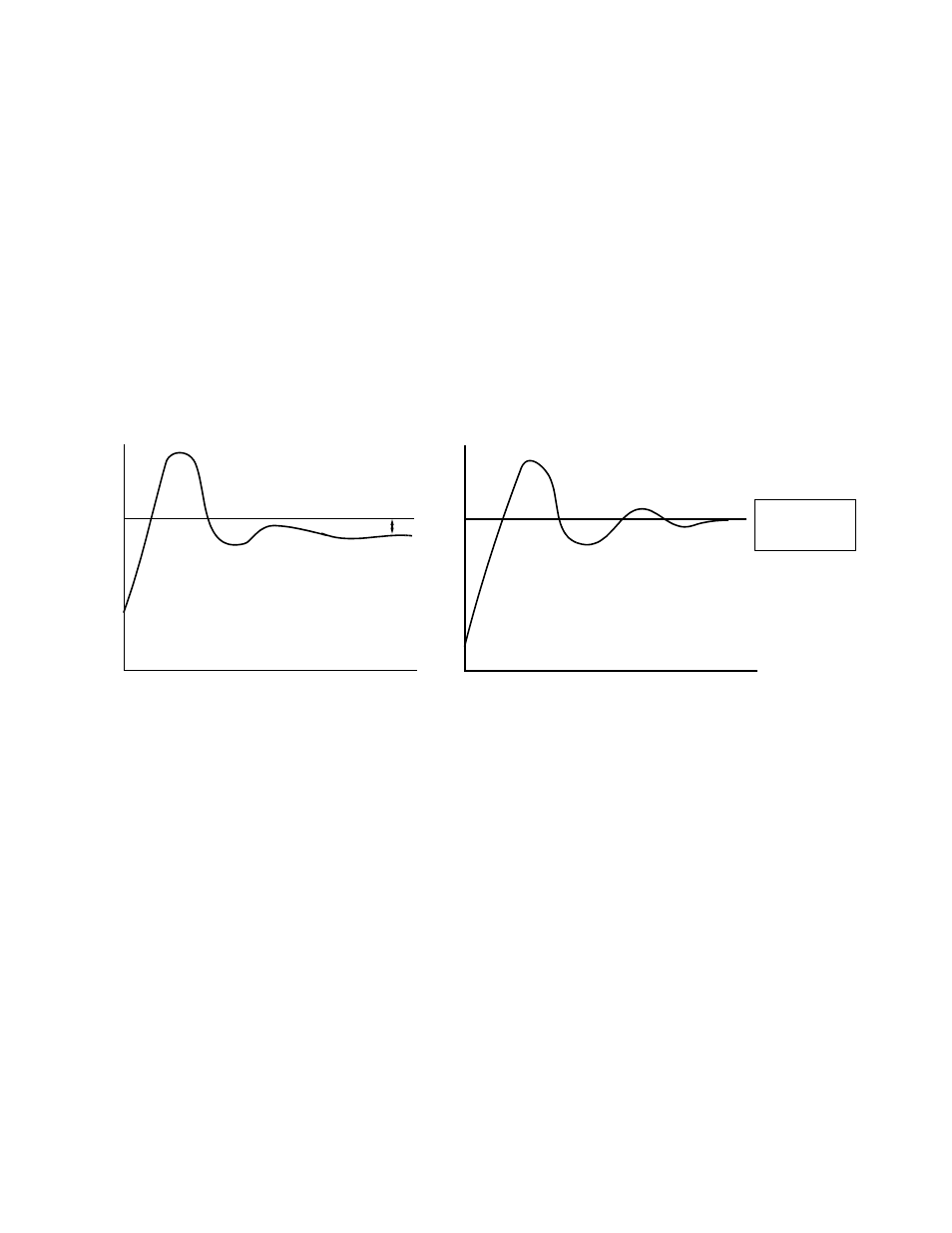
The proportional gain will apply a straight multiplier to the calculated difference (error) between the PID Setpoint and the measured
transmitter feedback at terminal A2. A large value will tend to reduce the error but may cause instability (oscillations) if too high. A
small value may allow to much offset between the setpoint and feedback (See Figure below).
b5-03 Integral Time Setting
Setting Range:
0.0 to 360.0 Seconds
Factory Default: 5.0 Seconds
The Integral factor of PID functionality is a time-based gain that can be used to eliminate the error (difference between the
setpoint and feedback at steady state). The smaller the Integral Time set into b5-03, the more aggressive the Integral factor will
be. To turn off the Integral Time, set b5-03= 0.00.
Fig. 17 PID Feedback Response Characteristics
b5-04 Integral Limit Setting
Setting Range:
0.0 to 100.0%
Factory Default: 100.0%
On some applications, especially those with rapidly varying loads, the output of the PID function may have large oscillations.
To suppress these oscillations, a limit can be applied to the intrigue factor by programming b5-04.
b5-05 Derivative Time Setting
Setting Range:
0.00 to 10.00 Seconds
Factory Default: 100.0%
The derivative calculation attempts to control the remaining overshoot left over after the proportion and integral calculations.
If the system is approaching the intended value very rapidly, the derivative control produces a strong braking action to prevent
overshoot. If the system is already stable with very little deviation change, derivative control has very little effect. The
derivative time is used to dampen oscillations and reduce overshoot, thus improving stability. Setting the derivative time to a
larger number produces more braking action in the control system. A setting of 0.00 disables derivative control.
Zero
offset with
Integral Action
No Intregral
With Intregral
Me
asured Feed
back
Me
asured
Fee
dback
Setpoint
Offset
Setpoint
Feedback
Feedback
TIME
TIME