3 simple network management protocol – PLANET SGSD-1022 User Manual
Page 97
User’s Manual of SGSD-1022 / SGSD-1022P
SGSW-2840 / SGSW-2840P
4.3 Simple Network Management Protocol
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a communication protocol designed specifically for managing devices on a
network. Equipment commonly managed with SNMP includes switches, routers and host computers. SNMP is typically used to
configure these devices for proper operation in a network environment, as well as to monitor them to evaluate performance or
detect potential problems.
Managed devices supporting SNMP contain software, which runs locally on the device and is referred to as an agent. A defined
set of variables, known as managed objects, is maintained by the SNMP agent and used to manage the device. These objects
are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB) that provides a standard presentation of the information controlled by
the agent. SNMP defines both the format of the MIB specifications and the protocol used to access this information over the
network.
The Managed Switch includes an onboard agent that supports SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3. This agent continuously monitors
the status of the Managed Switch hardware, as well as the traffic passing through its ports. A network management station can
access this information using software such as HP OpenView. Access to the onboard agent from clients using SNMP v1 and v2c
is controlled by community strings. To communicate with the switch, the management station must first submit a valid
community string for authentication.
Access to the switch using from clients using SNMPv3 provides additional security features that cover message integrity,
authentication, and encryption; as well as controlling user access to specific areas of the MIB tree.
The SNMPv3 security structure consists of security models, with each model having it’s own security levels. There are three
security models defined, SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3. Users are assigned to “groups” that are defined by a security
model and specified security levels. Each group also has a defined security access to set of MIB objects for reading and writing,
which are known as “views.” The switch has a default view (all MIB objects) and default groups defined for security models v1
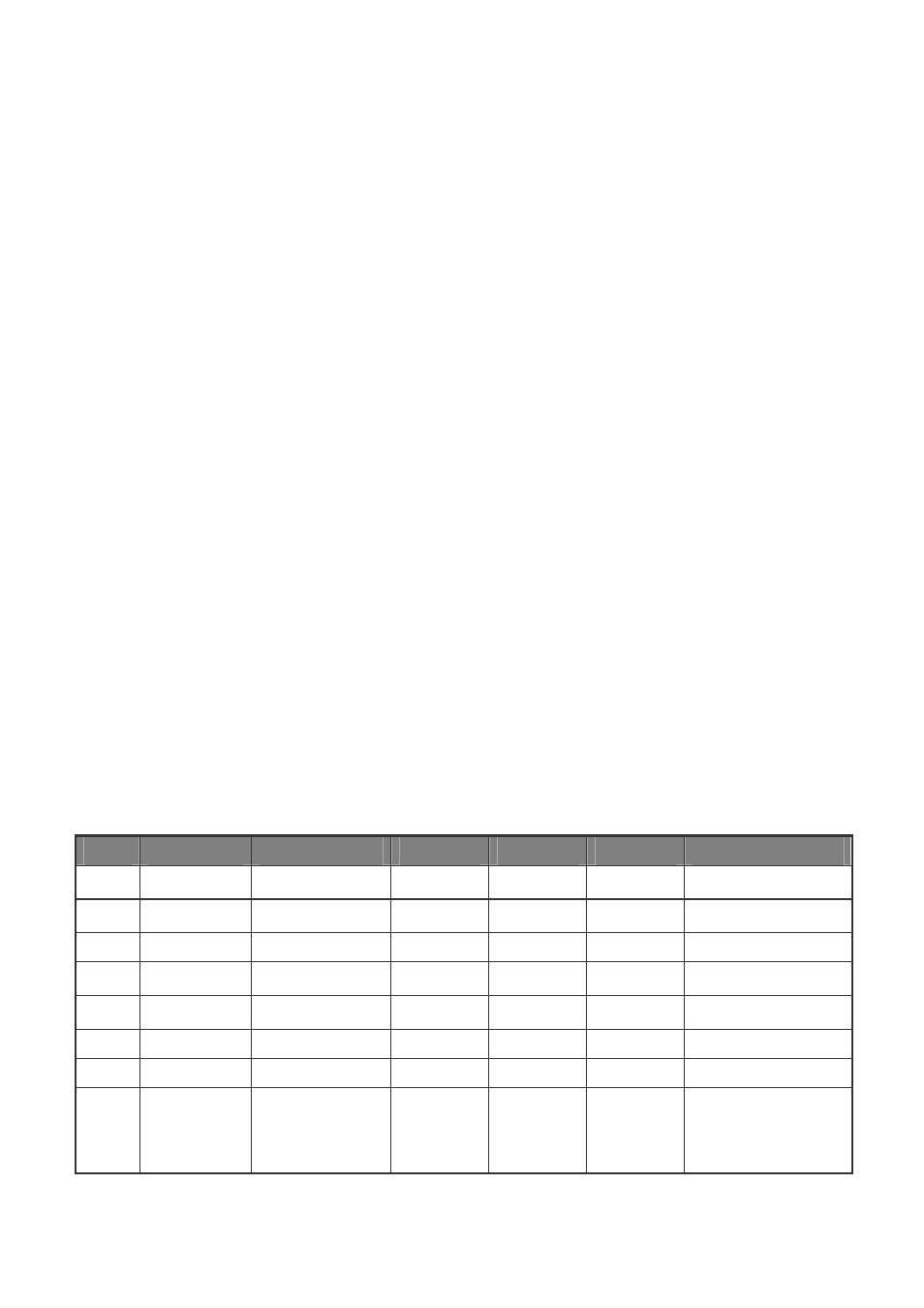
and v2c. The following table shows the security models and levels available and the system default settings.
Model
Level
Group
Read View
Write View
Notify View
Security
v1
noAuthNoPriv
public (read only) defaultview
none
none
Community string only
v1
noAuthNoPriv private(read/write) defaultview
defaultview
none
Community string only
v1
noAuthNoPriv user defined
user defined user defined
user defined Community string only
v2c
noAuthNoPriv public (read only)
defaultview
none
none
Community string only
v2c
noAuthNoPriv private (read/write)
defaultview defaultview none
Community
string
only
v2c
noAuthNoPriv user defined
user defined user defined
user defined Community string only
v3
noAuthNoPriv user defined
user defined user defined
user defined A user name match only
v3
AuthNoPriv
user defined
user defined
user defined
user defined Provides user
authentication via MD5
or SHA algorithms
97