2 data variables (m registers), 1) overview, 2) description – Yaskawa MP2000 Series: User's Manual for Motion Programming User Manual
Page 80: 3) programming examples
6 Variables (Registers)
6.2.2 Data Variables (M Registers)
6-8
6.2.2 Data Variables (M Registers)
(1) Overview
M registers are general-purpose variables that can be used in ladder logic programs, user functions, motion pro-
grams, and sequence programs. These are global variables that can be used as interfaces between motion pro-
grams, sequence programs, and ladder logic programs.
(2) Description
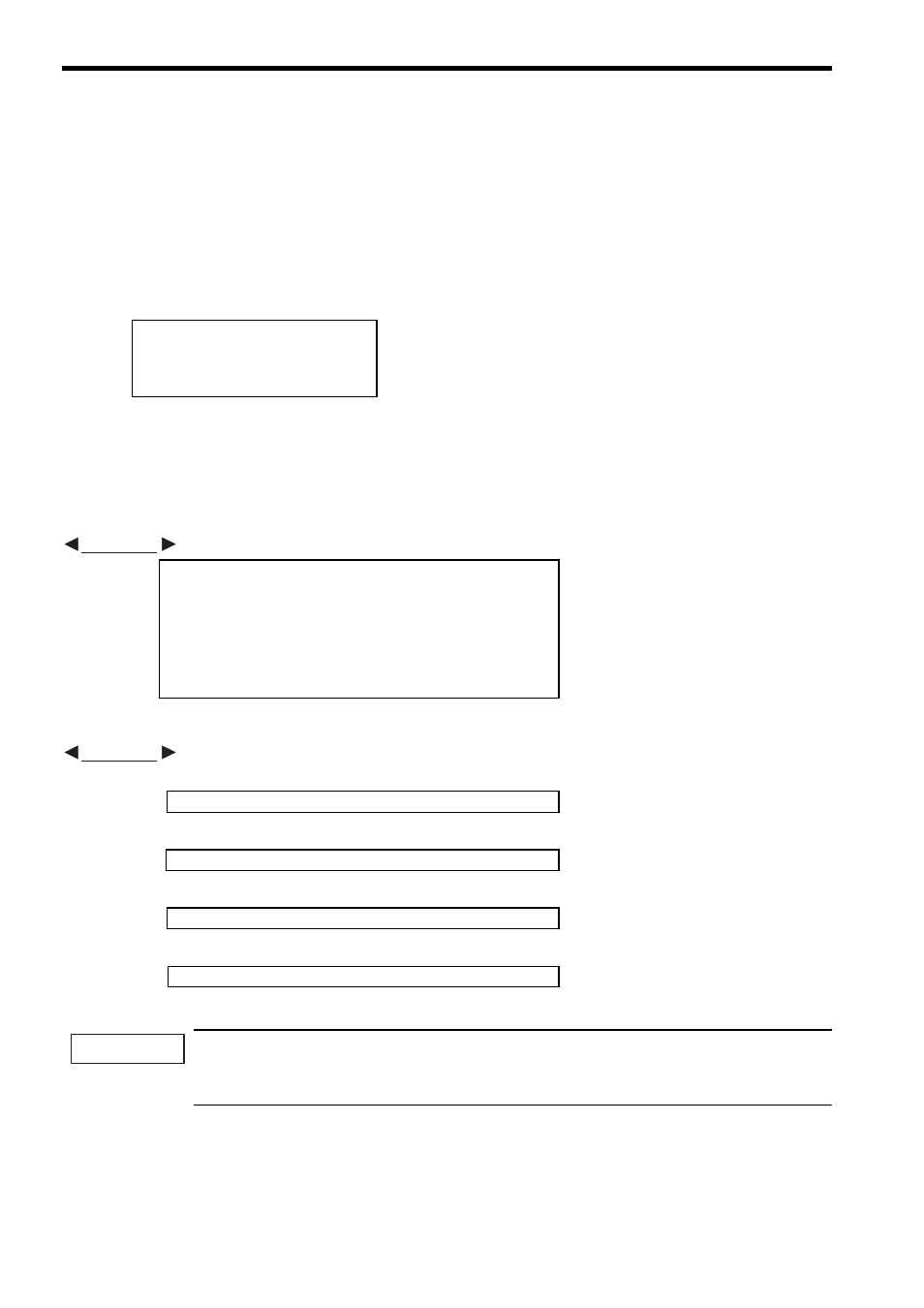
M registers are designated as follows:
The M register can be used as a variable for each type of operation and substituted for the operation result, or
specified as the variable for the positioning coordinate value or the speed. The variable number is expressed as a
decimal.
(3) Programming Examples
(a) Specifying the Position and Speed in Axis Move Commands as Variables
(b) Using Variables in Operations
• Bit Designation
• Integer Designation
• Double Integer Designation
• Real Number Designation
When the travel distance coordinate values or speed is designated as a variable in the following motion com-
mands, double integer data must be used.
MOV, MVS, MCW/MCC, ZRN, SKP, MVT, EXM, POS, ACC, SCC, IAC, IDC, IFP, FMX, INP, VEL
MB000000 to MB65534F
MW00000 to MW65534
ML00000 to ML65533
MF00000 to MF65533
• Parameter Reference unit = mm
When decimal point position = 3
ML00100=100000;
ML00102=200000;
ML00104=300000;
ML00106=500000;
MVS [X]ML00100 [Y]ML00102 [Z]ML00104 FML00106;
→ 100.000 mm
→ 200.000 mm
→ 300.000 mm
→ 500.000 mm/min
MB001001=IB00100 & IB00201;
MW00101=(MW00101 | MW00102) & FF0CH;
ML00200=((Ml00202*ML00204) / ML00206)*3;
MF00200=((MF00202*MF00204) / MF00206)*3.14;
EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE
IMPORTANT