3 using constants and variables, 1) constants, 2) variables – Yaskawa MP2000 Series: User's Manual for Motion Programming User Manual
Page 95
7.1 Motion Program Format
7-7
7
Programming
7.1.3 Using Constants and Variables
(1) Constants
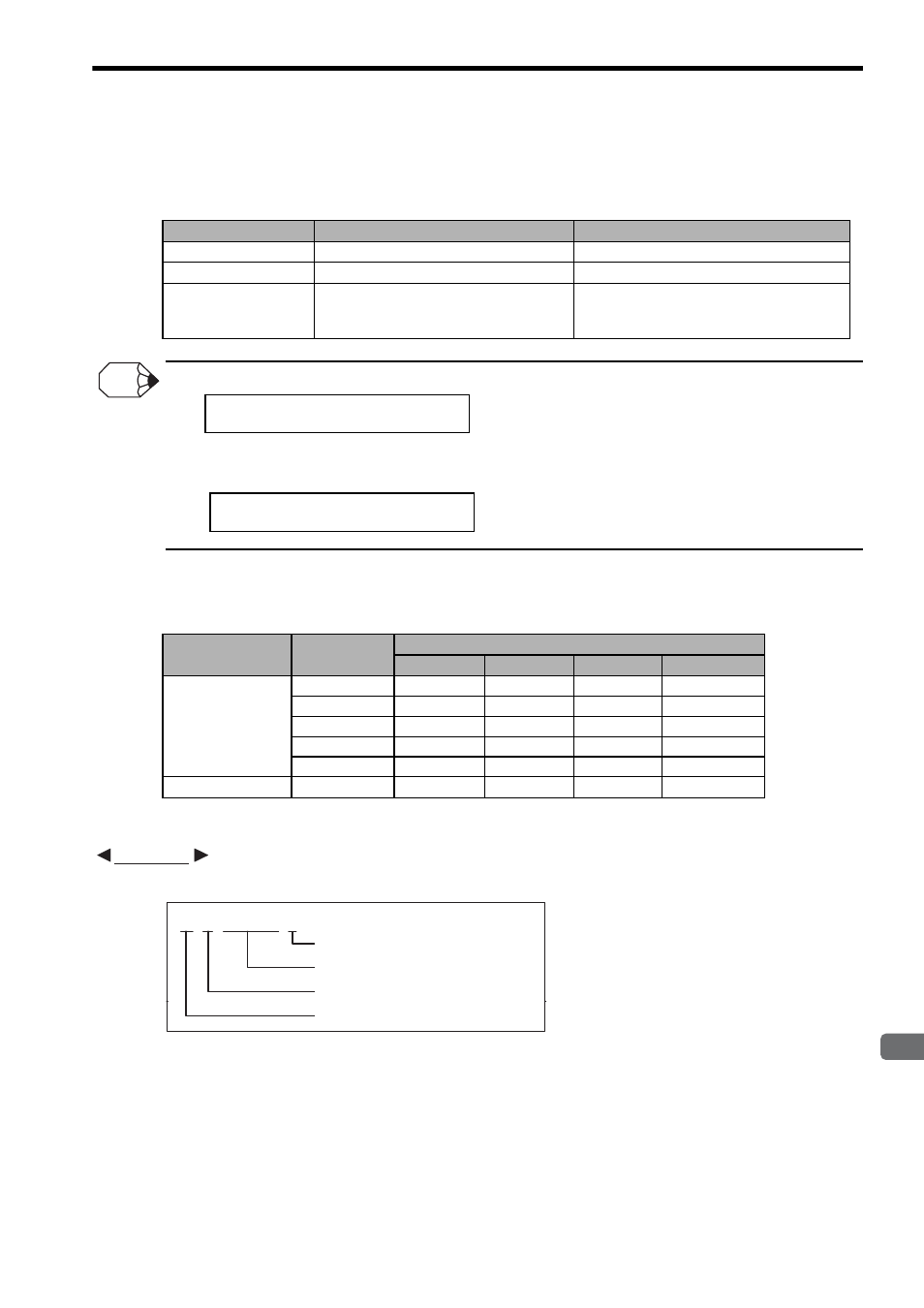
The constants that can be used in motion programs are listed below.
• The
− (minus) sign cannot be omitted, but the + (plus) sign can.
• A decimal integer value is multiplied by 1000 by adding K to the value. For a value such as position reference, adding a K
in place of three zeros makes it easy to read.
(2) Variables
The variables that can be used in motion programs are listed below.
Refer to Chapter 6 Variables (Registers) for details on variables.
A variable coding example is shown below.
Classification
Range
Coding Examples
Decimal Integers
-2147483648 to 2147483647
823, -2493, 123k, 123K
Hexadecimal Integers
00000000H to FFFFFFFFH
FFFABCDEH, 2345H, FH
Real Numbers
-214748.3648 to 214748.3647
Change according to the setting of the num-
ber of digits below the decimal point
763.0, 824.2, 234.56, -321.12345
[A1]+123 ⇒ [A1]123
[A1]-123 ⇒ [A1]-123
[A1]123k ⇒ [A1]123000
[A1]123K ⇒ [A1]123000
INFO
Classification
Variable Type
Data Type
Bit
Word
Long
Floating point
Global Variables
S register
SB
SW
SL
SF
M register
MB
MW
ML
MF
I register
IB
IW
IL
IF
O register
OB
OW
OL
OF
C register
CB
CW
CL
CF
Local Variables
D register
DB
DW
DL
DF
EXAMPLE
1 2 3 4 5 F
Data type: B, W, L, or F
Variable number
Bit position: Valid only with bit data
M B
Variable type: S, M, I, O, C, or D