Yaskawa AC Drive P1000 Bypass Technical Manual User Manual
Page 91
n
I Control
The output of I control is the integral of the deviation. It minimizes the offset between target and feedback value that typically
remains when pure P control is used. The integral time (I time) constant determines how fast the offset is eliminated.
n
D Control
D control predicts the deviation signal by multiplying its derivative (slope of the deviation) with a time constant, then adds
this value to the PID input. This way the D portion of a PID controller provides a braking action to the controller response and
can reduce the tendency to oscillate and overshoot.
D control tends to amplify noise on the deviation signal, which can result in control instability. Only use D control when
absolutely necessary.
n
PID Operation
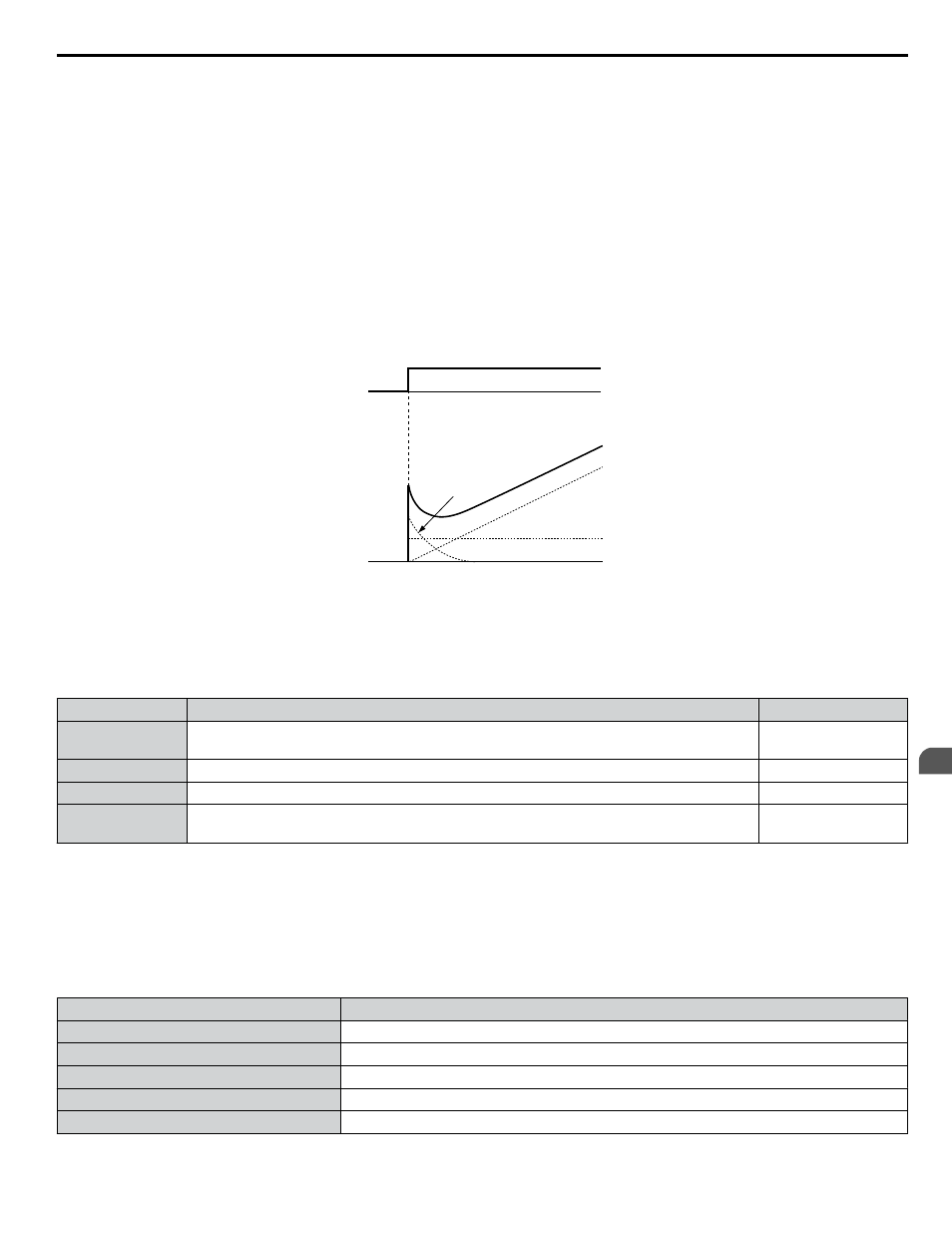
To better demonstrate PID functionality,
illustrates how the PID output changes when the PID input (deviation)
jumps from 0 to a constant level.
PID input
I control
PID Output
D control
Time
PID output
Time
P control
Figure 5.11 PID Operation
n
Using PID Control
Applications for PID control are listed in
.
Table 5.2 Using PID Control
Application
Description
Sensors Used
Speed Control
Machinery speed is fed back and adjusted to meet the target value. Synchronous control is
performed using speed data from other machinery as the target value
Tachometer
Pressure
Maintains constant pressure using pressure feedback.
Pressure sensor
Fluid Control
Keeps flow at a constant level by feeding back flow data.
Flow rate sensor
Temperature
Control
Maintains a constant temperature by controlling a fan with a thermostat.
Thermocoupler,
Thermistor
n
PID Setpoint Input Methods
The PID setpoint input depends on the PID function setting in parameter b5-01.
If parameter b5-01 is set to 1 or 2, the frequency reference source in b1-01 (or b1-15) or one of the inputs listed in
becomes the PID setpoint.
If b5-01 is set to 3 or 4, then the PID setpoint can be input from one of the sources listed in
.
Table 5.3 PID Setpoint Sources
PID Setpoint Source
Settings
Analog Input A1
Set H3-02 = C
Analog Input A2
Set H3-10 = C
Analog Input A3
Set H3-06 = C
MEMOBUS/Modbus Register 0006 H
Set bit 1 in register 000F H to 1 and input the setpoint to register 0006 H
Pulse Input RP
Set H6-01 = 2
5.2 b: Application
YASKAWA SIEP YAIP1B 01A YASKAWA AC Drive – P1000 Bypass Technical Manual
91
5
Programming