1 communication methods – Yaskawa MP2300S Basic Module User Manual
Page 191
6.1 Communication Methods
6-2
6.1 Communication Methods
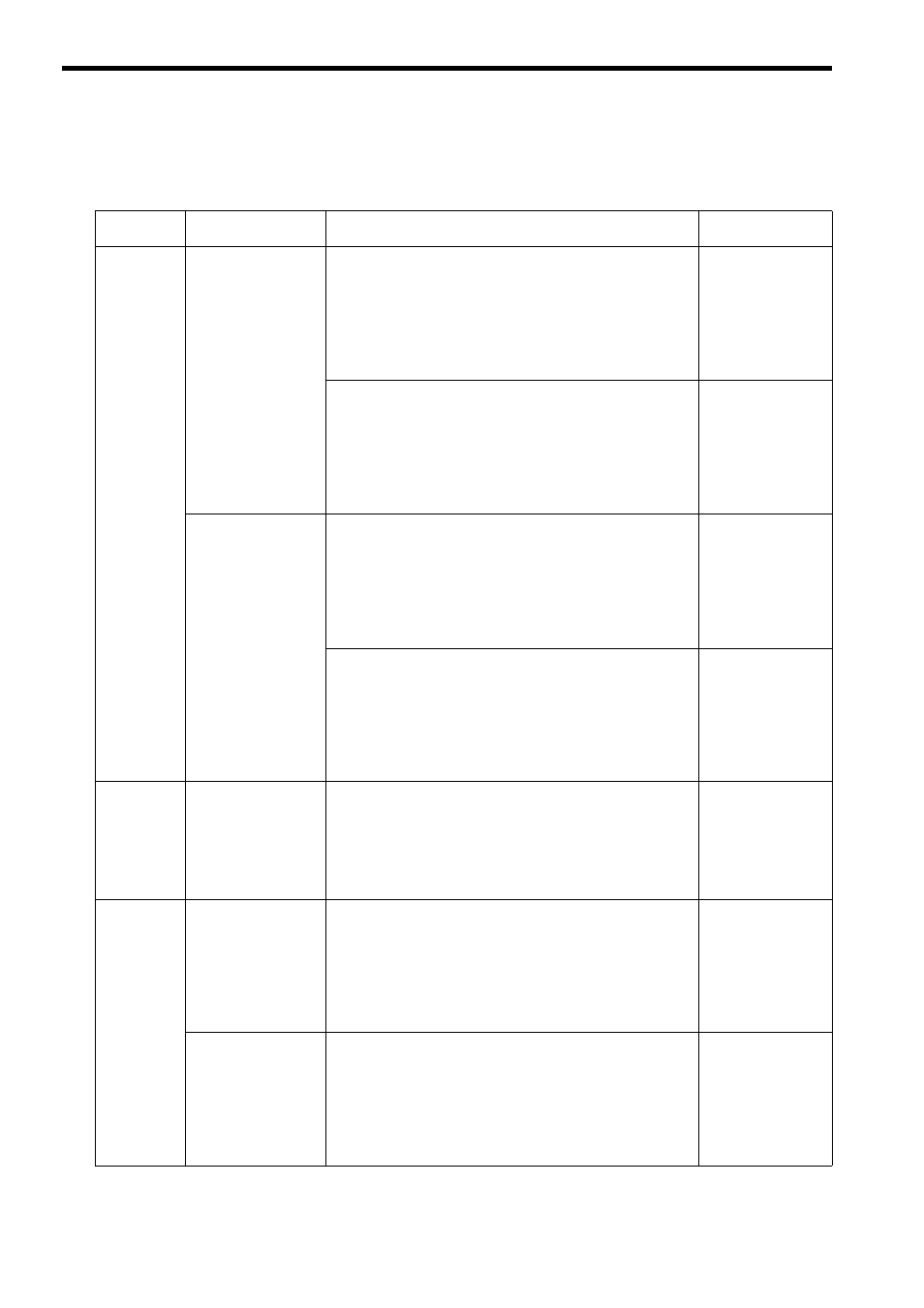
The following table provides the appropriate mode of communication for each remote device and purpose.
Note: For information on applications where the remote device is a PLC or Windows computer, refer to the
Machine Controller MP2300S/MP2310/MP2400 Basic Module Supplement for Ethernet Communications
(manual number: SIEP C880700 37).
Remote
Equipment
Purpose
Communication Method
Remarks
Other MP
Series
When other MP series
equipment reads/writes
the coil state or register
content of MP2300S
Uses the Extended MEMOBUS communication protocol.
The remote equipment (master) creates ladder programs using the
MSG-SND function.
The MP2300S (slave) uses the automatic receive function. (You do
not need to create ladder programs.)
⇒
Refer to 6.2.1 When the MP2300S Acts as Slave (automatic
receive function is used)
MP2300S can com-
municate with only
one master using the
automatic receive
function.
Uses the Extended MEMOBUS communication protocol.
The remote equipment (master) creates ladder programs using the
MSG-SND function.
The MP2300S (slave) creates ladder programs using the MSG-RCV
function.
⇒
Refer to 6.2.2 When the MP2300S Acts as Slave (ladder program
which uses a MSG-RCV function)
Communication with
multiple masters is
possible.
When MP2300S reads/
writes the coil state or
register content of other
MP series equipment
Uses the Extended MEMOBUS communication protocol.
The MP2300S (master) uses the I/O message communication func-
tion. (You do not need to create ladder programs.)
The remote equipment (slave) creates ladder programs using the
MSG-RCV function.
⇒
Refer to 6.2.3 When the MP2300S Acts as Master (I/O message
communication function is used)
Only the holding reg-
ister (M register) is
capable of reading/
writing using the I/O
message communica-
tion function.
It can communicate
with only one slave.
Uses the Extended MEMOBUS communication protocol.
The MS2300S creates ladder programs using the MSG-SND func-
tion.
The remote equipment (slave) creates ladder programs using the
MSG-RCV function.
⇒
Refer to 6.2.4 When the MP2300S Acts as Master (ladder pro-
gram which uses a MSG-SND function)
Registers other than
the holding register
are capable of reading/
writing.
Communication with
multiple slaves is
enabled.
Touch Panel
When a touch panel
reads/writes the coil
state or register content
of MP2300S
Uses the Extended MEMOBUS communication protocol.
Set the protocol for the touch panel side to the Extended MEMO-
BUS protocol.
The MP2300S (slave) uses the automatic receive function. (You do
not need to create ladder programs.)
⇒
Refer to 6.3 Communication with Touch Panel.
–
PLC Manu-
factured by
Mitsubishi
Electric
Corporation
When a PLC Manufac-
tured by Mitsubishi
Electric Corporation
reads/writes the
MP2300S register con-
tent.
Uses the MELSEC communication protocol.
The remote equipment (master) creates ladder programs using the
BUFSND function.
The MP2300S (slave) uses the automatic receive function. (You do
not need to create ladder programs.)
⇒
Refer to 6.4.1 When the MP2300S Acts as Slave (automatic
receive function is used)
The MP2300S can
communicate with
only one master when
using the automatic
receive function.
When an MP2300S
reads/writes the relay
state or register content
of PLC Manufactured
by Mitsubishi Electric
Corporation.
Uses the MELSEC communication protocol.
The MP2300S (master) uses the I/O message communication func-
tion. (You do not need to create ladder programs.)
The remote equipment (slave) needs to set the network parameters.
(You do not need to create ladder programs.)
⇒
Refer to 6.4.2 When the MP2300S Acts as Master (I/O message
communication function is used)
The MP2300S can
communicate with
only one slave when
using the I/O message
communication func-
tion.