3 zero point return (zret) – Yaskawa MP2000 Series: Built-in SVB or SVB-01 Motion Module User Manual
Page 177
6.2 Motion Command Details
6.2.3 Zero Point Return (ZRET)
6-16
6.2.3 Zero Point Return (ZRET)
When the Zero Point Return command (ZRET) is executed, the axis will return to the zero point of the machine coordi-
nate system.
The operation to detect the position of the zero point is different between an absolute encoder and an incremental
encoder.
With an absolute encoder, positioning is performed to the zero point of the machine coordinate system and command
execution is completed.
With an incremental encoder, there are 13 different methods (see below) that can be performed for the zero point return
operation.
For SVR, the machine coordinate system is initialized and the coordinates of the axis are set to show the axis being at
the zero point. As a result, a Zero Point Return operation will not be executed.
When using an SGDV SERVOPACK, the torque limit can be set and changed during SERVOPACK operation. For
details, refer to Setting and Changing Torque Limit during SGDV SERVOPACK Operations of 4.4.2 ( 12 ). When
using a DC Power Input
Σ-V Series SERVOPACK (Model: SGDV-
E1
), refer to 11.7.4 Motion Command
Operation for External Latches with DC Power Input
Σ
-V-series SERVOPACKs.
For more information on the maximum allowable value for acceleration and deceleration, refer to Changing the max-
imum value of acceleration and deceleration for SGDV SERVOPACKs of 4.4.2 ( 23 ).
( 1 ) Selecting the Zero Point Return Method (with an Incremental Encoder)
When an incremental encoder is selected for the Encoder Selection by fixed parameter No. 30 to 0, the coordinate sys-
tem data will be lost when the power supply is turned OFF. This command must be executed when the power supply is
turned ON again to establish a new coordinate system.
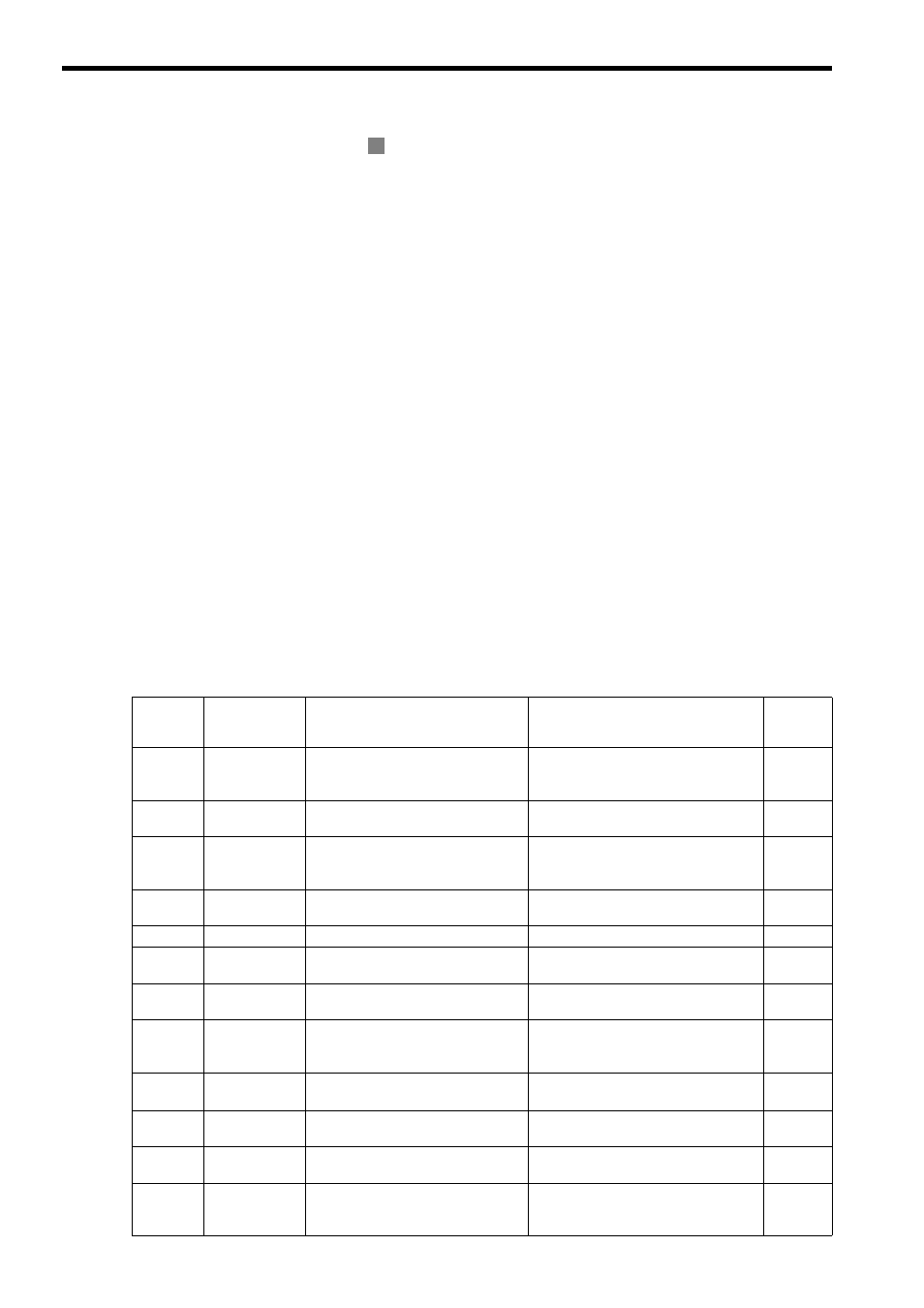
The following table lists the 13 zero point return methods that are supported by the MP2000 Series Machine Controller.
Select the best method for the machine according to the setting parameters. Refer to the section numbers indicated in
the Reference column for additional command information.
R
Setting
Parameter
OW
3C
Name
Method
Signal Meaning
Reference
0
DEC1 + C
Applies a 3-step deceleration method
using the deceleration limit switch and
phase-C pulse.
DEC1 signal: SERVOPACK DEC signal
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ a ]
1
ZERO
Uses the ZERO signal.
ZERO signal: SERVOPACK EXT1 signal
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ b ]
2
DEC1 + ZERO
Applies a 3-step deceleration method
using the deceleration limit switch and
ZERO signal.
DEC1 signal: SERVOPACK DEC signal
ZERO signal: SERVOPACK EXT1 signal
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ c ]
3
C
Uses the phase-C pulse.
−
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ d ]
4 to 10
Not used
−
−
−
11
C pulse Only
Uses only the phase-C pulse.
−
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ e ]
12
POT & C pulse
Uses the positive overtravel signal and
phase-C pulse.
P-OT: SERVOPACK P-OT signal
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ f ]
13
POT Only
Uses only the positive overtravel sig-
nal.
P-OT: SERVOPACK P-OT signal
This method must not be used if repeat
accuracy is required.
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ g ]
14
Home LS & C
pulse
Uses the home signal and phase-C
pulse.
HOME: SERVOPACK EXT1 signal
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ h ]
15
Home Only
Uses only the home signal.
HOME: SERVOPACK EXT1 signal
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ i ]
16
NOT & C pulse Uses the negative overtravel signal and
phase-C pulse.
N-OT: SERVOPACK N-OT signal
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ j ]
17
NOT Only
Uses only the negative overtravel sig-
nal.
N-OT: SERVOPACK N-OT signal
This method must not be used if repeat
accuracy is required.
6.2.3
( 7 ) [ k ]