2 ip routing policy, 1 introduction to routing policy, Outing – PLANET XGS3-24042 User Manual
Page 273: Olicy, 1 introduction to routing policy -2
34-2
Destination address: used to identify the destination address or destination network of an IP
packet.
Network mask: used together with destination address to identify the destination host or the
network the layer3 switch resides. Network mask consists of several consecutive binary 1's, and
usually in the format of dotted decimal (an address consists of 1 to 4 255’s.) When “AND” the
destination address with network mask, we can get the network address for the destination host or
the network the layer3 switch resides. For example, the network address of a host or the segment
the layer3 switch resides with a destination address of 200.1.1.1 and mask 255.255.255.0 is
200.1.1.0.
Output interface: specify the interface of layer3 switch to forward IP packets.
IP address of the next layer3 switch (next hop): specify the next layer3 switch the IP packet will
pass.
Route entry priority: There may be several different next hop routes leading to the same destination.
Those routes may be discovered by different dynamic routing protocols or static routes manually
configured. The entry with the highest priority (smallest value) becomes the current best route. The
user can configure several routes of different priority to the same destination; layer3 switch will
choose one route for IP packet forwarding according to the priority order.
To prevent too large route table, a default route can be set. Once route table look up fails, the default route will
be chosen for forwarding packets.
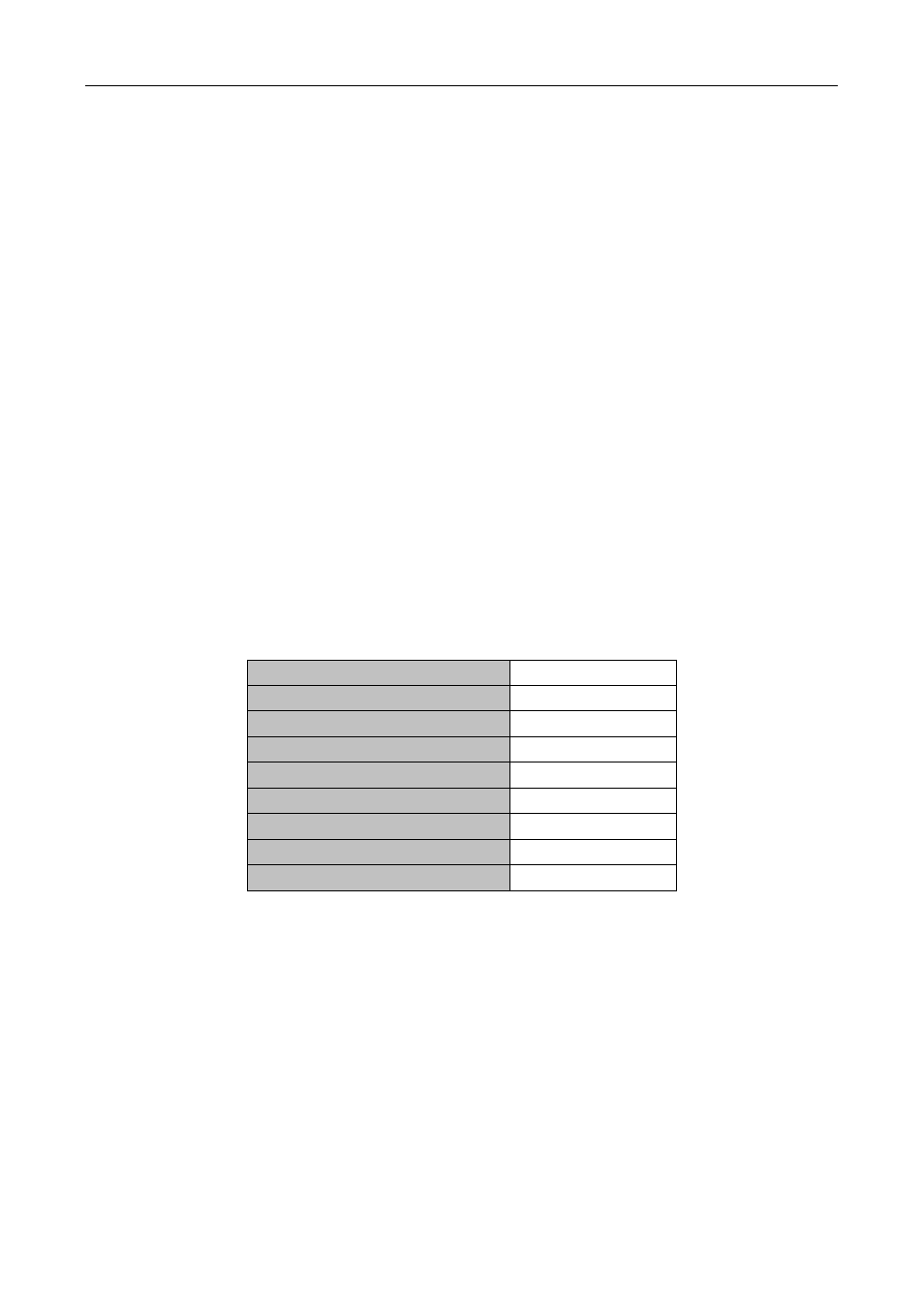
The table below describes the routing protocols supported by switch and the default route look up priority
value.
Routing Protocols or route type
Default priority value
Direct route
0
OSPF
110
Static route
1
RIP
120
OSPF ASE
150
IBGP
200
EBGP
20
Unknown route
255
34.2 IP Routing Policy
34.2.1 Introduction to Routing Policy
Some policies have to be applied when the router publishing and receiving routing messages so to filter
routing messages, such as only receiving or publishing routing messages meets the specified conditions. A
routing protocol maybe need redistribute other routing messages found by other protocols such as OSPF so
to increase its own routing knowledge; when the router redistributing routing messages from other routing
protocols there may be only part of the qualified routing messages is needed, and some properties may have
to be configured to suit this protocol.