4 ripng troubleshooting, Roubleshooting – PLANET XGS3-24042 User Manual
Page 303
37-9
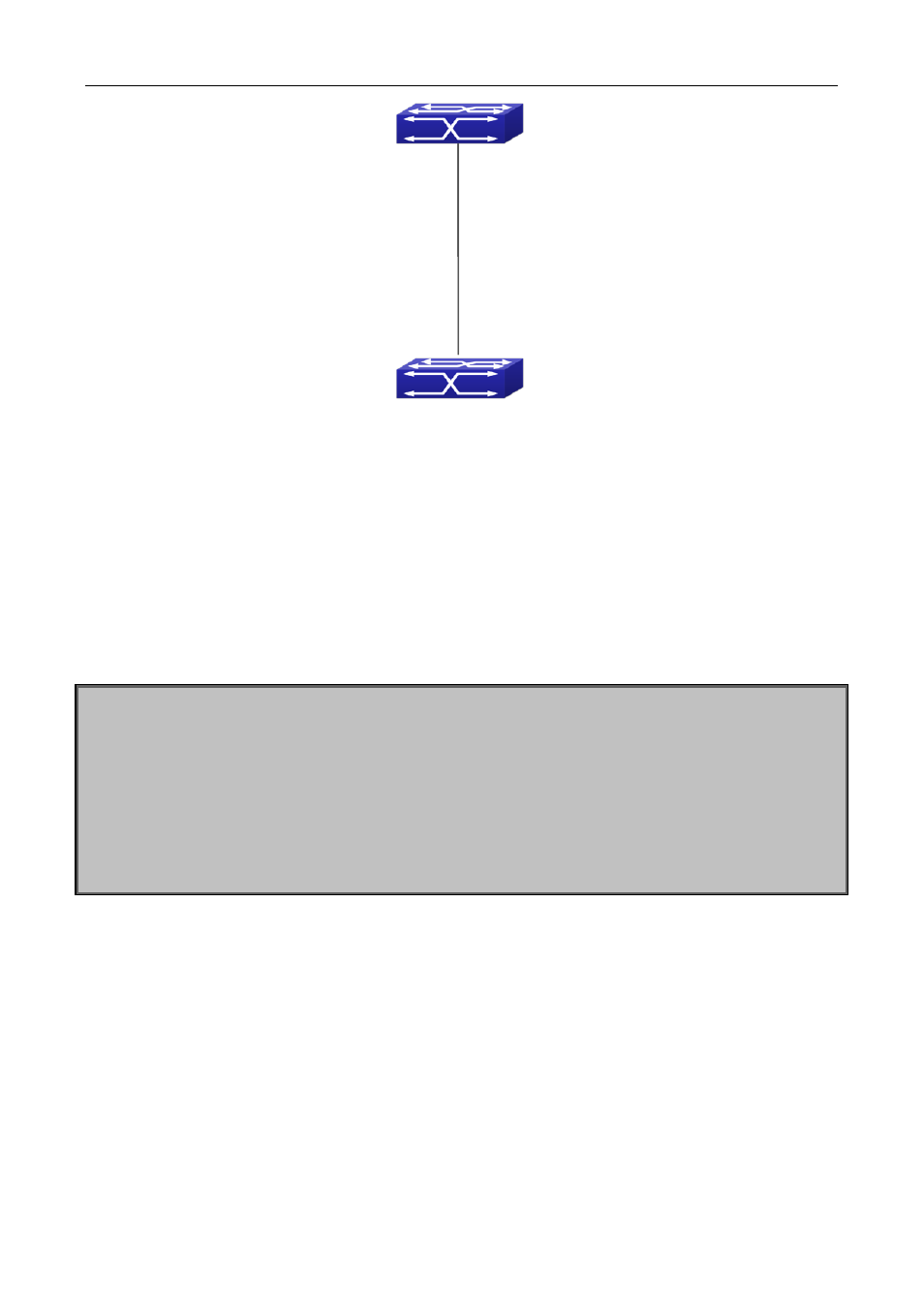
Figure 37-2 Typical application of RIPng aggregation
As the above network topology, S2 is connected to S1 through interface vlan1, there are other 4 subnet
routers of S2, which are 2001:1::20:0/112, 2001:1::21:0/112, 2001:1::22:0/112, 2001:1::23:0/112. S2 supports
route aggregation, and to configure aggregation route 2001:1::20:0/110 in interface vlan1 of S2, after that,
sending router messages to S2 through vlan1, and put the four subnet routers aggregated to one router as
2001:1::20:0/110, and send to S1, and not send subnet to neighbor. It can reduce the router table of S1, save
the memory.
S1 configuration list:
S1(config)#router ipv6 rip
S1(config-router) #network vlan 1
S2 configuration list:
S2(config)#router ipv6 rip
S2(config-router) #network vlan 1
S2(config-router) #exit
S2(config)#in vlan 1
S2(Config-if-Vlan1)# ipv6 rip agg 2001:1::20:0/110
37.4 RIPng Troubleshooting
The RIPng protocol may not be working properly due to errors such as physic connection, configuration error
when configuring and using the RIPng protocol. So users should pay attention to the following:
First ensure the physic connection is correct and the IP Forwarding command is open
Second, ensure the interface and link layer protocol are UP (use show interface command)
Then initiate the RIPng protocol (use router IPv6 rip command) and configure the port (use IPv6
router command), and set RIPng protocol parameter on corresponding interfaces.
After that, a RIPng protocol feature should be noticed ---the Layer 3 switch running RIPng transmits the
S1
S2
VLAN1
2001:1::1:1
VLAN1
2001:1::1:2
2001:1::20:0/110
2001:1::20:0/112
2001:1::21:0/112
2001:1::22:0/112
2001:1::23:0/112