6 configuration of parameters of sa-cache, 7 msdp configuration examples, 6 configuration of parameters of sa-cache -19 – PLANET XGS3-24042 User Manual
Page 420: 7 msdp configuration examples -19
48-19
no sa-request-filter [list
<access-list-number | access-list-name>]
command will remove the configured filter
rules for SA request packets.
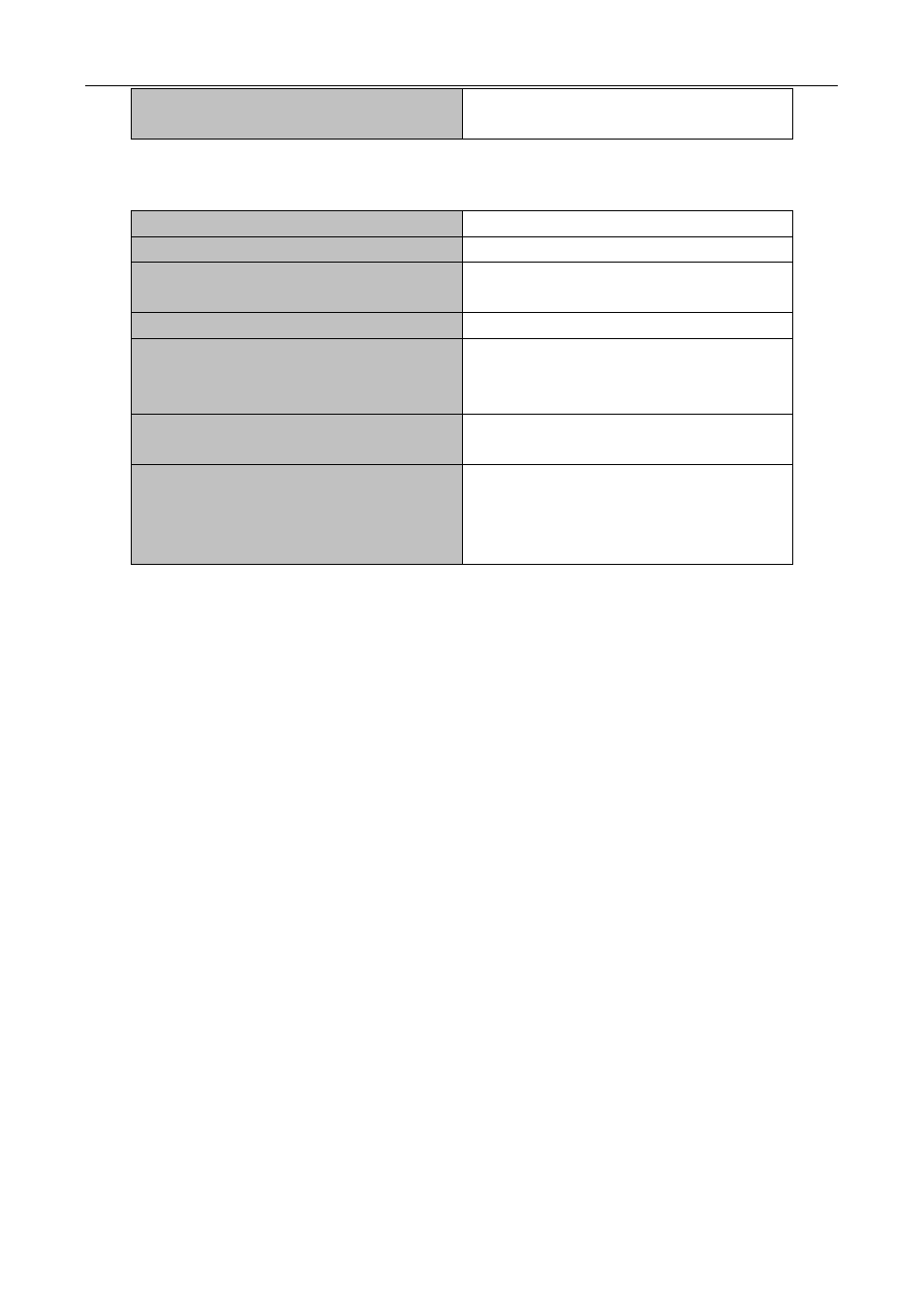
48.4.6 Configuration of Parameters of SA-cache
Commands
Explanation
MSDP Configuration Mode
cache-sa-state
no cache-sa-state
To enable the SA packet cache.
To disable the SA packets cache.
MSDP Configuration Mode
cache-sa-holdtime <150-3600>
no cache-sa-holdtime
The aging time for entries in the SA cache.
To restore the default aging time
configuration.
MSDP Configuration Mode or MSDP Peer
Configuration Mode
cache-sa-maximum <sa-limit>
no cache-sa-maximum
To configure the maximum size for the SA
cache.
To restore the size of the SA cache to the
default value.
48.4.7 MSDP Configuration Examples
Example 1: MSDP basic function.
Multicast Configuration:
1.
Suppose the multicast server is sending multicast datagram at 224.1.1.1;
2.
The designated router – DR, which is connected to the multicast server, encapsulate the multicast
datagram in the Register packets and send them to the RP(RP1) in the local domain;
3.
The RP unwraps the packets and sends them to all the domain members through the shared tree. The
members in the domain can be configured to be or not to be in the shared tree;
4.
At the same time, the source RP in the domain, generates a SA – Source Active message, and send it
to the MSDP entity – RP2.
5.
If there’s another member in the same domain with the MSDP entity which is named as RP3, RP3 will
distribute the multicast datagram encapsulated in the SA messages to the members of the shared tree,
and send join messages to the multicast source. That means RP creates an entry (S, G), and send join
messages for (S, G) hop by hop, so that (S, G) can reach the SPT which takes the multicast source as
the root across the PIM-SM domain.
If there no members in the same domain with MSDP entity – RP2, RP2 will not create the (S, G) entry
nor it will join the SPT which takes the multicast source as the root.
6.
When the reverse route has been set up, the multicast datagram from the source will be directly
delivered to RP3, and RP will forward the datagram to the shared tree. At this time, the router which is
closest to the domain members can determine itself whether or not to switch to SPT.