Wiring diagram for multiple connections, Network termination, Rs-485 interface – Yaskawa AC Drive Z1000 Bypass Technical Manual User Manual
Page 379: D.3 connecting to a network
u
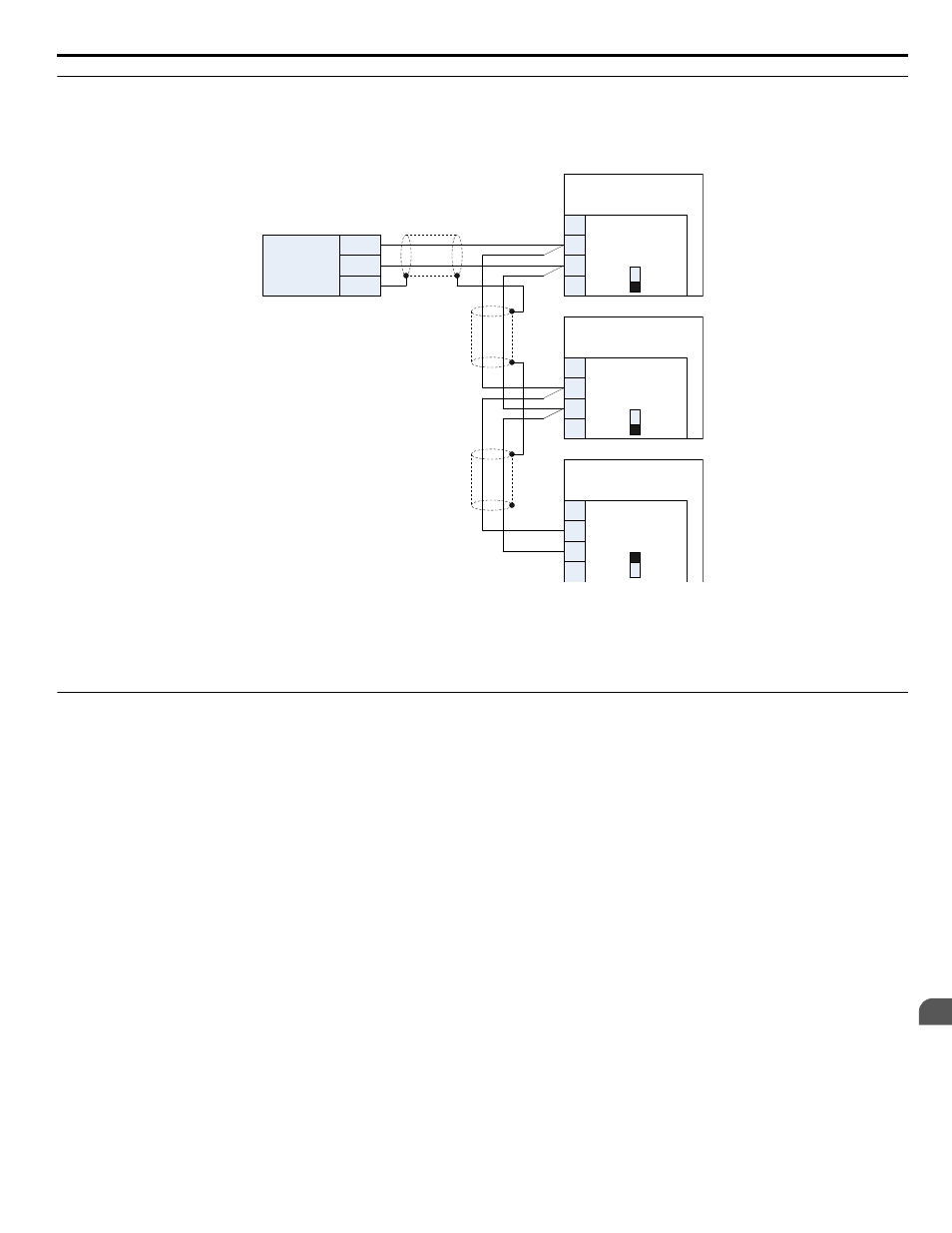
Wiring Diagram for Multiple Connections
explains the wiring diagrams for multiple connections using MEMOBUS/Modbus communication.
n
RS-485 Interface
CONTROLLER
1
2
3
4
+
-
SHLD
Bypass
S1
OFF
TB3
SHLD
TXRX-
TXRX+
IG5
1
2
3
4
Bypass
S1
OFF
TB3
SHLD
TXRX-
TXRX+
IG5
ON
1
2
3
4
Bypass
S1
SHLD
TXRX-
TXRX+
IG5
Bypass
Controller
Board A2
Bypass
Controller
Board A2
Bypass
Controller
Board A2
Figure D.3 Connection Diagram for Multiple Connections
Note:
Turn on DIP switch S1 on the bypass controller located at the end of the network. If S1 is missing, then an external 120 ohm resistor must
be placed across terminals TXRX+ and TXRX-. All other slave devices must have this DIP switch set to the OFF position (or if S1 is
missing, no external resistor is used).
u
Network Termination
The two ends of the MEMOBUS/Modbus network line have to be terminated with a 120 ohm resistor between the TXRX+
and TXRX- signals. The Z1000 Bypass has a built in termination resistor that can be enabled or disabled using DIP switch
S1. If a bypass is located at the end of a network line, enable the termination resistor by setting DIP switch S1 to the ON
position. Disable the termination resistor on all slaves that are not located at the network line end.
Note:
Some bypass controllers do not have DIP switch S1. If this is the case, then an external 120 ohm resistor must be placed across the
TXRX+ and TXRX- signals if the bypass controller is at the end of a network line.
D.3 Connecting to a Network
YASKAWA ELECTRIC SIEP YAIZ1B 01D YASKAWA AC Drive – Z1000 Bypass Technical Manual
379
D
MEMOBUS/Modbus Communications