Selecting a regenerative resistor – Yaskawa FSP Amplifier User Manual
Page 139
FSP Amplifier User’s Manual
Chapter 5: Parameter Settings and Functions
5-72
5.6. Selecting a Regenerative Resistor
When the servomotor operates in Generator mode, power is returned to the servo
amplifier side. This is called regenerative power. The regenerative power is
absorbed by charging the smoothing capacitor, but when the capacitor’s charging
limit is exceeded, the regenerative power is then reduced by the regenerative
resistor.
The servomotor is driven in regeneration (generator) mode in the following
conditions:
• While decelerating to a stop during acceleration/deceleration operation.
• With a load on the vertical axis.
• During continuous operation with the servomotor driven from the load side
(negative load).
The capacity of the servo amplifier’s built-in regenerative resistor is designed for
short-term operation only, such as the deceleration stop period. Operation under a
negative load is not possible.
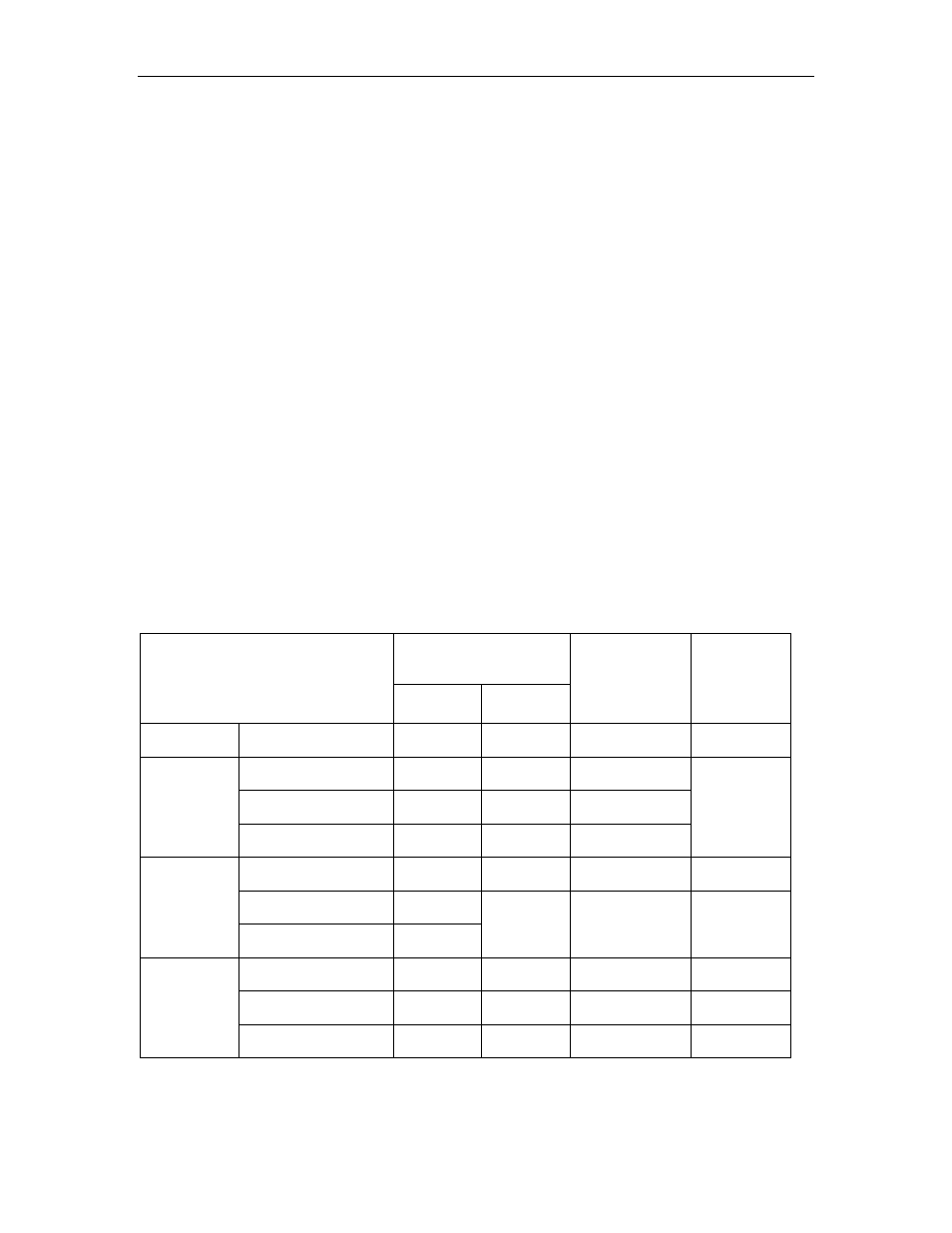
If the regenerative power exceeds the processing capacity of the servo amplifier,
install an external regenerative resistor. The following table shows the examples
of specifications for servo amplifier’s built-in resistor and the amount of
regenerative power (average values) that it can process.
Built-in Resistor
Specifications
Applicable Servo Amplifiers
Resistance
(Ω)
Capacity
(W)
Regenerative
Power
Processed by
Built-in
Resistor
*1
(W)
Minimum
Allowable
Resistance
(Ω)
Single-phase
100 V
FSP-A3B* to -02B*
—
—
—
40
FSP-A3A* to -04A*
—
—
—
FSP-08A* 50
60 12
Single-phase
200 V
FSP-15A* 25
140 28
40
FSP-10A* 50
60 12 40
FSP-20A* 25
Three-phase
400 V
FSP-30A* 12.5
140 28 12
FSP-05D* to -15D*
108
70
14
73
FSP-20D* & -30D*
45
140
28
44
Three-phase
400 V
FSP-50D* 32
180 36 28
*1.
The amount of regenerative power (average value) that can be processed is rated at 20% of the capacity of the
servo amplifier’s built-in regenerative resistor.