Synchronization state machines, Synchronization state, Machines – Altera Stratix GX Transceiver User Manual
Page 161
Altera Corporation
6–7
January 2005
Stratix GX Transceiver User Guide
GigE Mode
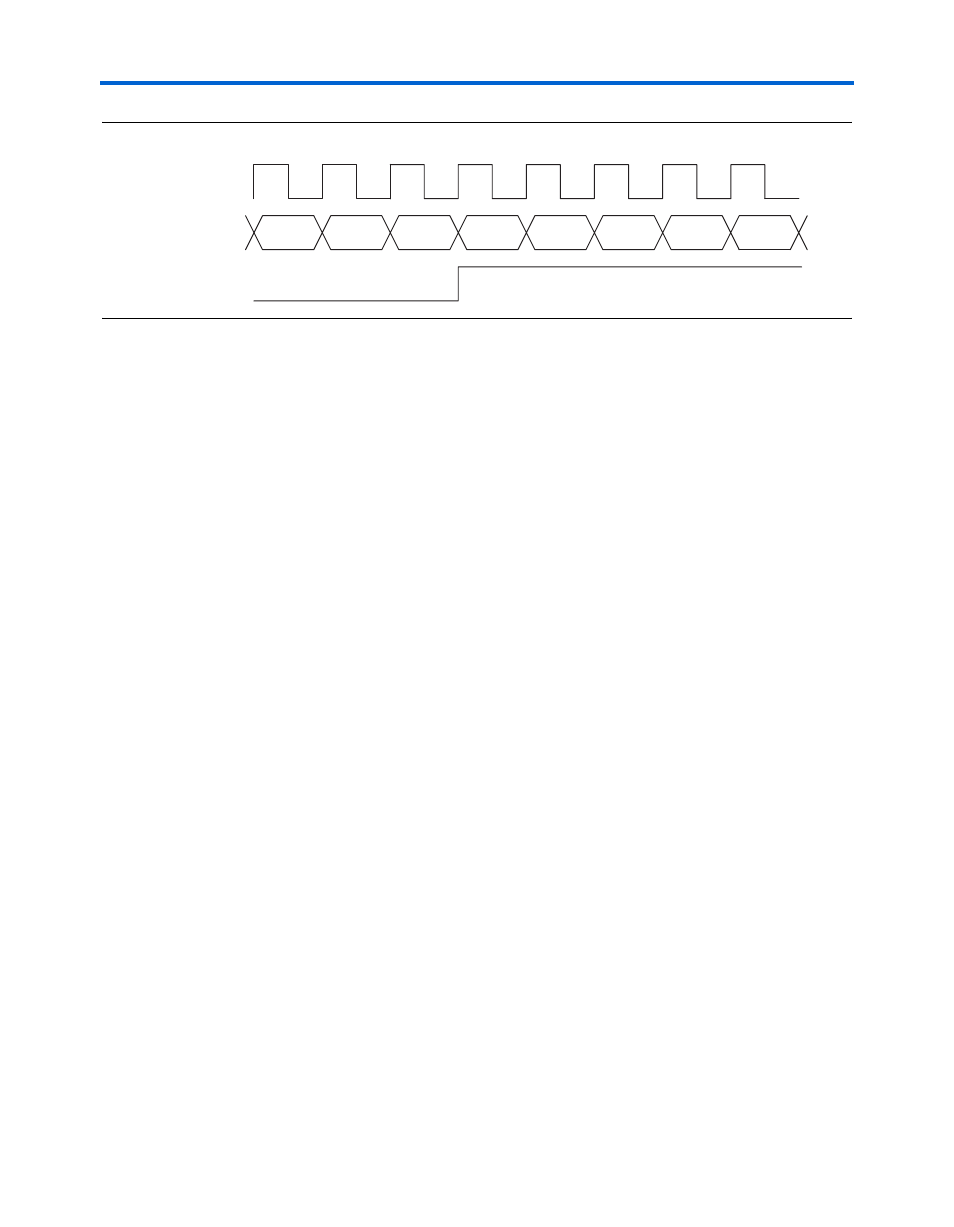
Figure 6–6. Example of Completed Synchronization
The receiver remains synchronized until it detects a series of bad code
groups or is reset. The IEEE 802.3 standard defines the bad code group as
four invalid code groups separated by fewer than three valid code
groups. If the receiver detects the bad code group or is reset, the
rx_syncstatus
signal goes low, and a /K28.4/ code appears on the
rx_out[]
port. GigE mode uses an embedded clocking scheme that
retimes all data that can potentially alter the code-group boundary. The
boundaries of the code-groups are re-aligned through a synchronization
process specified in the IEEE 802.3 standard.
Synchronization State Machines
Synchronization occurs when the receiver sees three consecutive ordered
sets. An ordered set defined for synchronization is a /K28.5/ comma
followed by any odd number of valid data code groups (/Dx.y/).
Although you can have a number of sync patterns based on the
synchronization rule, three sets of {/K28.5/ /Dx.y/} code groups are
the fastest way to achieve synchronization.
GigE mode requires a special synchronization sequence that follows the
IEEE 802.3 GMII PCS synchronization specification, as shown in
.
clock
rx_out[7:0]
rx_syncstatus
K28.4
K28.4
K28.4
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5