Section 8.1.5, Table 8.3 – Westermo RedFox Series User Manual
Page 169
Westermo OS Management Guide
Version 4.17.0-0
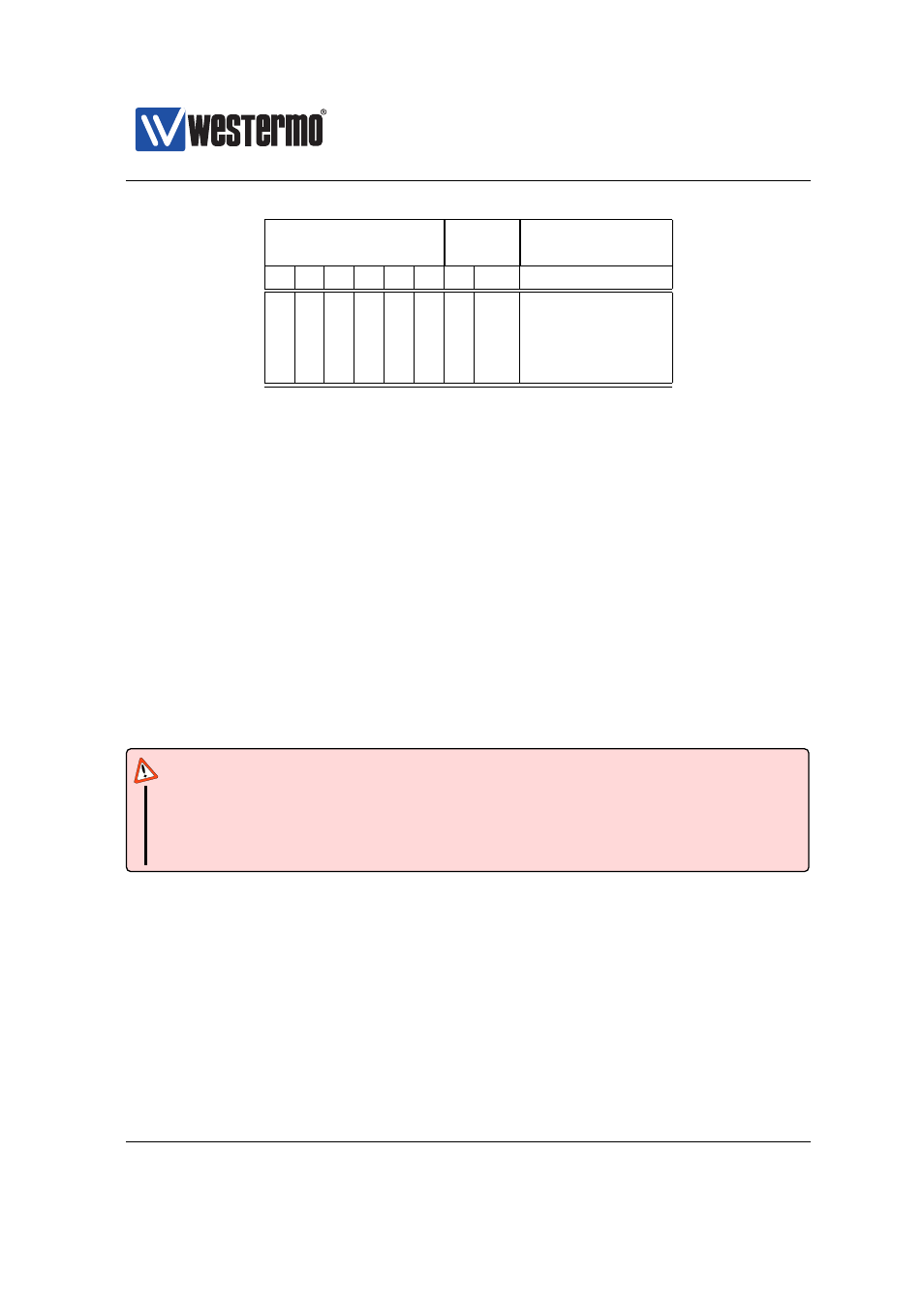
IP Priority
Queue
Queue number/
bits
bits
Traffic class
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
0
0
0
-
-
-
-
0
0
0 (lowest)
0
1
-
-
-
-
0
1
1
1
0
-
-
-
-
1
0
2
1
1
-
-
-
-
1
1
3 (highest)
Table 8.3: Mapping of IP priority bits to Queue/Traffic Class.
❼ For packets where priority was classified based on VLAN ID, VLAN tag, or
port priority, the outbound priority (3 bits) will be equal to the determined
inbound priority (3 bits).
❼ When priority is classified based on IP ToS/DiffServ, determining the out-
bound priority (3 bits) is more complex: the two most significant bits of the
outbound priority will be equal to the queue number (i.e., queue bits in
), while the least significant bit of the outbound priority is equal to
the least significant bit of the inbound port’s configured port priority.
E.g., if the packet is put in priority queue 2 (binary ’10’), and the port priority
of the inbound port has an odd value (least significant bit is ’1’), the packet
will carry priority value 5 (’101’) in its VLAN tag when sent on the outbound
port.
Warning
Configuration of layer-2 priority should be handled with care. In particular,
mapping user traffic to the highest priority queue is discouraged, since that
may affect time critical control traffic, such as FRNT traffic, already mapped
to the highest priority queue.
8.1.5
Link alarm
Each Ethernet port on the switch can be configured to indicate alarm when the
link comes up or goes down. The alarm is indicated in multiple ways:
❼ SNMP trap: An SNMP trap will be sent when a link changes state, i.e., both
when the link comes up, or when it goes down. This assumes that SNMP is
➞ 2015 Westermo Teleindustri AB
169