Section 31.1.5, 5 port forwarding – Westermo RedFox Series User Manual
Page 704
Westermo OS Management Guide
Version 4.17.0-0
31.1.5
Port Forwarding
Port Forwarding is commonly used together with NAPT, to enable access from the
Internet to a server inside the private network.
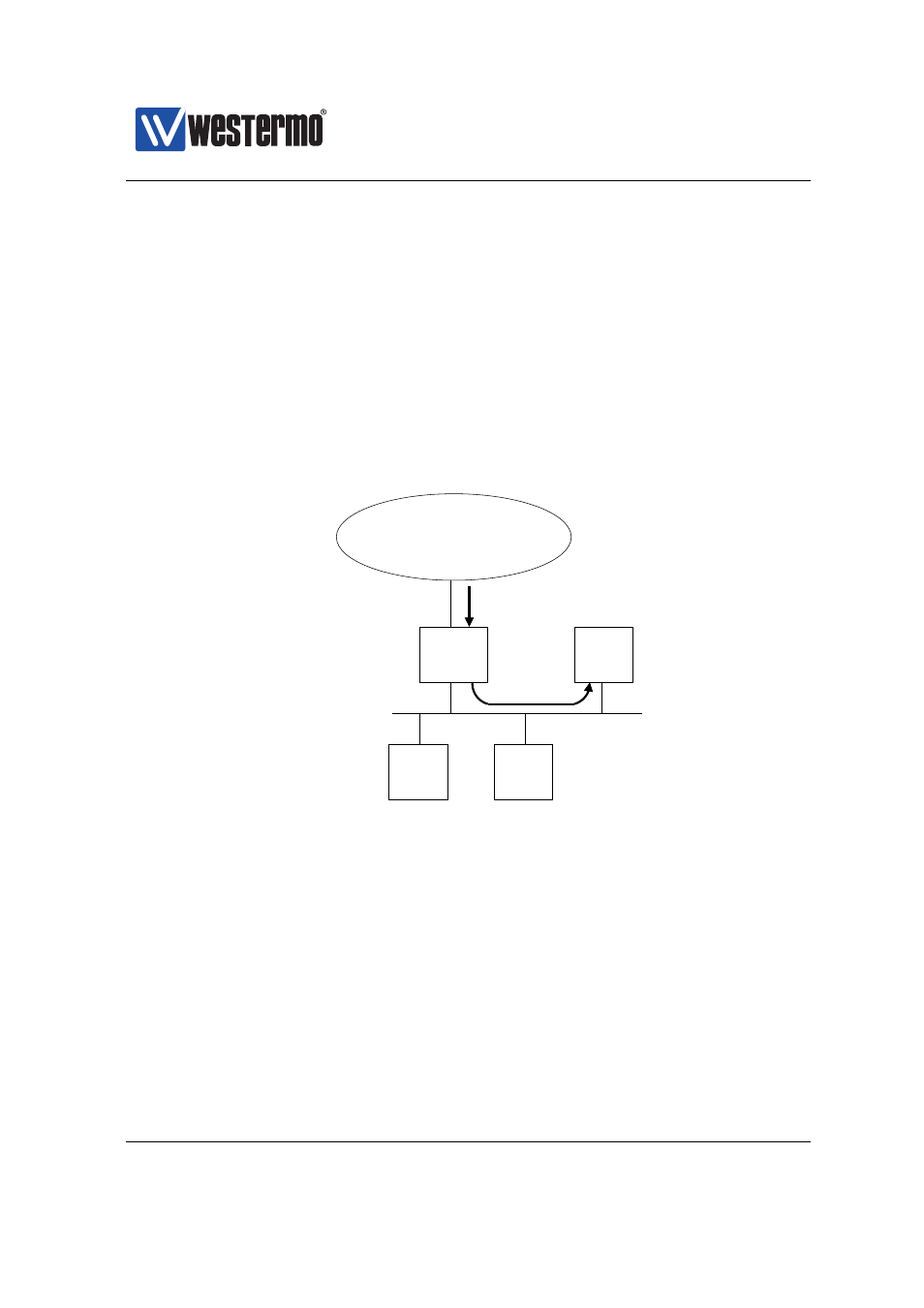
shows a typical setup
when port forwarding is useful:
❼ The switch acts as a NAT/NAPT gateway to the Internet: routing is enabled
(see
) and a NAPT rule defining the external (outbound) interface
has been configured (see
❼ A Web Server on the ”internal” network serves users on the Internet: A port
forwarding rule has been added to allow users on the Internet to initiate
connections to the Web server on host 192.168.0.2 (TCP port 80).
Gateway
Web
Server
Public Network (Internet)
Host
Host
.79
.33
.2
.1
Internal/Private Network
192.168.0.0/24
External Interface
TCP
Port 8080
Port 80
TCP
(public IP address,
e.g., 1.2.3.4)
NAT/NAPT
Figure 31.9: Use of port forwarding to enable Internet hosts to access a Web
server inside the private network via a NAT/NAPT gateway.
With port forwarding, users on the Internet will connect to the internal Web Server
as if it was running on the NAT/NAPT gateway, i.e., users on the Internet will
connect to the Web server using the public IP address (here 1.2.3.4) and TCP port
number (here 8080), without knowing that the traffic is forwarded to a server
inside the internal network.
704
➞ 2015 Westermo Teleindustri AB