5 zero return mode, Overview, Details – Yaskawa MP920 User's Manual Design User Manual
Page 136
4 Motion Control
4.2.5 Zero Return Mode
4-22
4.2.5
Zero Return Mode
Overview
The zero point return operation returns the machine to the machine-specific zero point.
When an incremental encoder is used, the system zero point position data is destroyed if the
power supply is disconnected. Therefore, after turning ON the power, the system zero point
must be repositioned. As a general rule, a pulse generator (PG) with a zero point pulse and a
limit switch showing the zero point area are used to determine the zero point.
There are two zero point return methods. One method uses motion commands, and the other
method uses the zero return control mode. Care is required because zero point return opera-
tions are different with these two methods.
Using the zero return mode is explained below.
Note: To use motion commands, see 4.4.9 Zero Point Setting (ZSET).
When an absolute encoder is used, position reference “0” will be the position control when
zero point return is selected.
Details
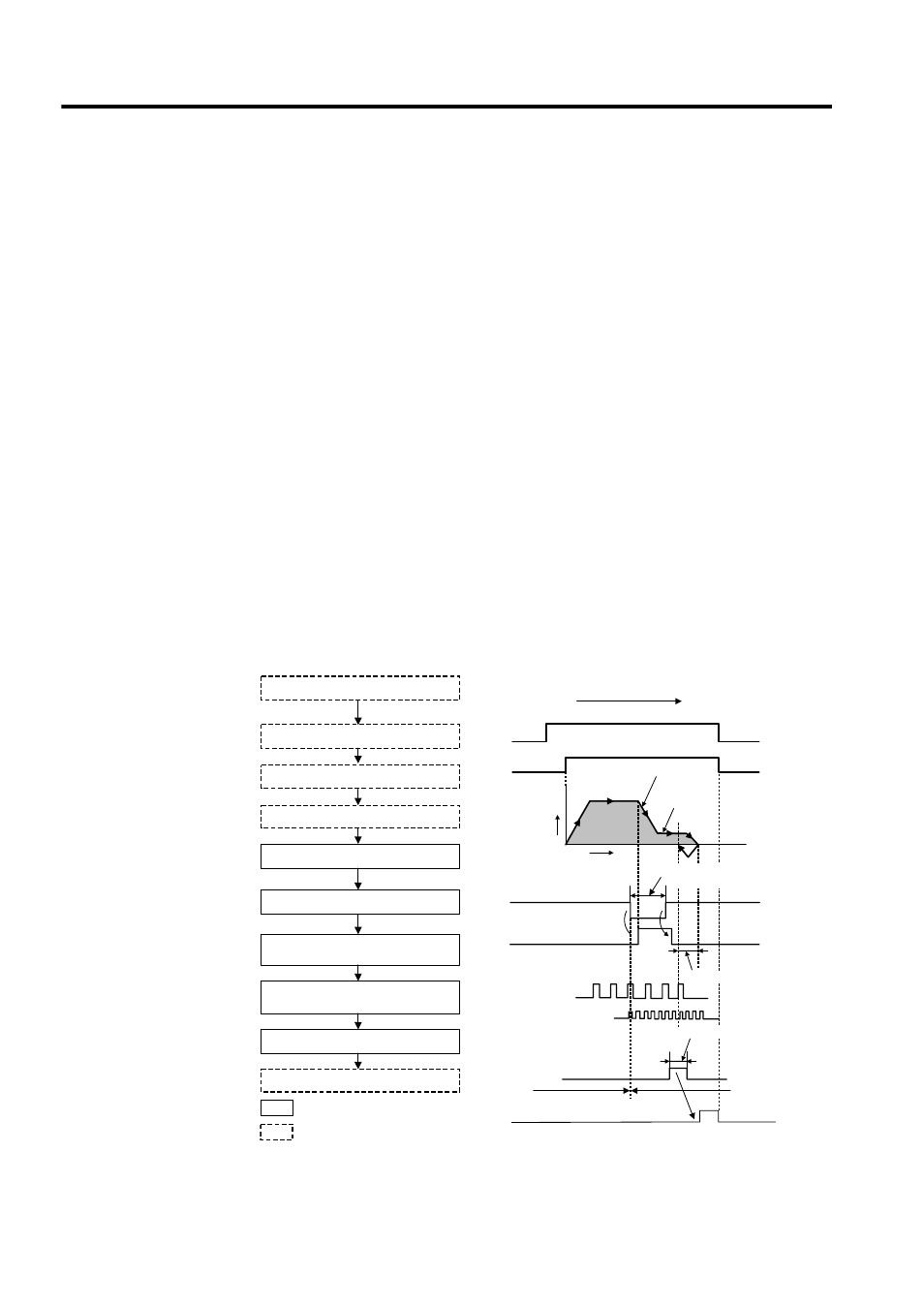
Use the following procedure to perform operation in the zero return mode.
* 1. If the machine is in Area B after the power is turned ON, a return can-
not be performed correctly. Be sure to move the machine back to Area
A before performing a return.
1. Set the motion fixed parameters.
2. Set the motion setting parameters.
3. Set the zero return mode (ZRN) to ON.
4. Set the RUN command (RUN) to ON.
ZRN
RUN
3.
4.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
5. Set the zero return mode to OFF.
/DECLS (limit switch)
LSDEC
ZRNC
The axis is moved at approach speed in the
zero point direction.
Zero point return direction (ZRNDIR)
Specified direction
Approach speed
Distance
Creep speed
External signal
(Deceleration point limit switch signal)
C-phase pulse
(Zero point pulse)
A
φ, Bφ
Pulse after multiplication
Area A
Area B *1
Speed
Time
: System execution
: User settings
Limit switch width
≥ 2 × Ts
(Ts: High-speed scan setting) *2
Zero point overtravel distance
Positioning completion range
a) When LSDEC turns ON, the axis is
decelerated to creep speed.
d) The zero point return completion signal
(ZRNC) turns ON.
b) LSDEC turns from ON to OFF, and
decelerates to a stop after detecting the
initial zero point pulse (C-phase pulse).
c) After decelerating to a stop, the axis is moved
only the zero point overtravel distance, and
stops at the zero point position.