5 functions, 1 standard system functions – Yaskawa MP920 User's Manual Design User Manual
Page 97
3.5 Functions
3-23
3
3.5
Functions
This section explains the methods of using and the advantages of the MP920 functions.
Functions are executed by being called from a parent, child, or grandchild drawing using the
FSTART instruction.
Unlike child and grandchild drawings, functions can be called from any drawing. The same
function can also be called simultaneously from drawings of different types and different hierar-
chies. Moreover, a function can also be called from another function that was previously created.
The following advantages can be obtained by using functions:
• Programs can be easily divided into parts.
• Programs can be easily prepared and maintained.
Functions are divided into standard system functions, which are provided by the system, and
user functions, which are defined by the user.
3.5.1
Standard System Functions
Seven functions, including the transfer function, are provided by the system as standard func-
tions. See Table 3.8. The user cannot change the standard system functions.
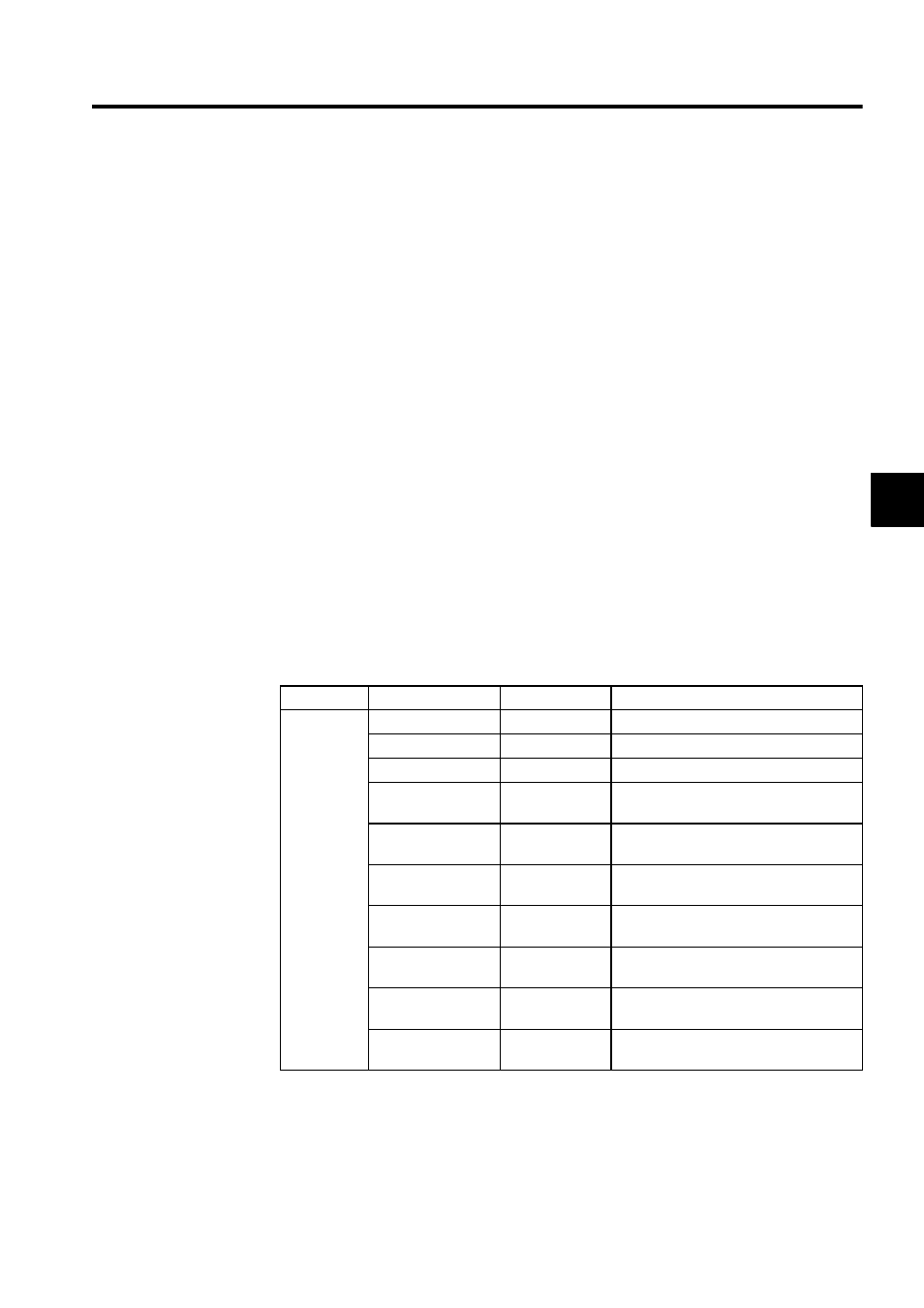
Table 3.8 List of Standard System Functions
Type
Name
Symbol
Description
System
Functions
Counter
COUNTER
Up/down counter
First-in first-out
FINFOUT
First-in or first-out stack
Trace function
TRACE
Data trace execution control
Data trace read
DTRC-RD
Data readout from data trace memory to
user memory
Inverter trace read
ITRC-RD
Reading inverter trace data to store it in
user registers
Failure trace
readout
FTRC-RD
Data readout from failure trace memory to
user memory
Send message
function
MSG-SND
Sending a message from a Communica-
tions Module
Receive message
function
MSG-RCV
Receiving a message from a Communica-
tions Module
Inverter constant
write
ICNS-WR
Writing 215IF-connected inverter con-
stants
Inverter constant
read
ICNS-RD
Reading 215IF-connected inverter con-
stants