3 zero point return (zret), 3 zer, 3 zero point return (zret) -15 – Yaskawa MP2200 Machine Controller User Manual
Page 245: 1 ) selecting the zero point return method
5.2 Motion Command Details
5-15
5.2.3 Zero Point Return (ZRET)
When the Zero Point Return command (ZRET) is executed, the axis will return to the zero point of
the machine coordinate system. The operation to detect the position of the zero point is different
between an absolute encoder and an incremental encoder. With an absolute encoder, positioning is
performed to the zero point of the machine coordinate system and command execution is completed.
With an incremental encoder, there are 17 different methods that can be performed for the Zero Point
Return operation.
( 1 ) Selecting the Zero Point Return Method
With an incremental encoder, the coordinate system data will be lost when the power supply is turned
OFF. This command must be executed when the power supply is turned ON again to establish a new
coordinate system.
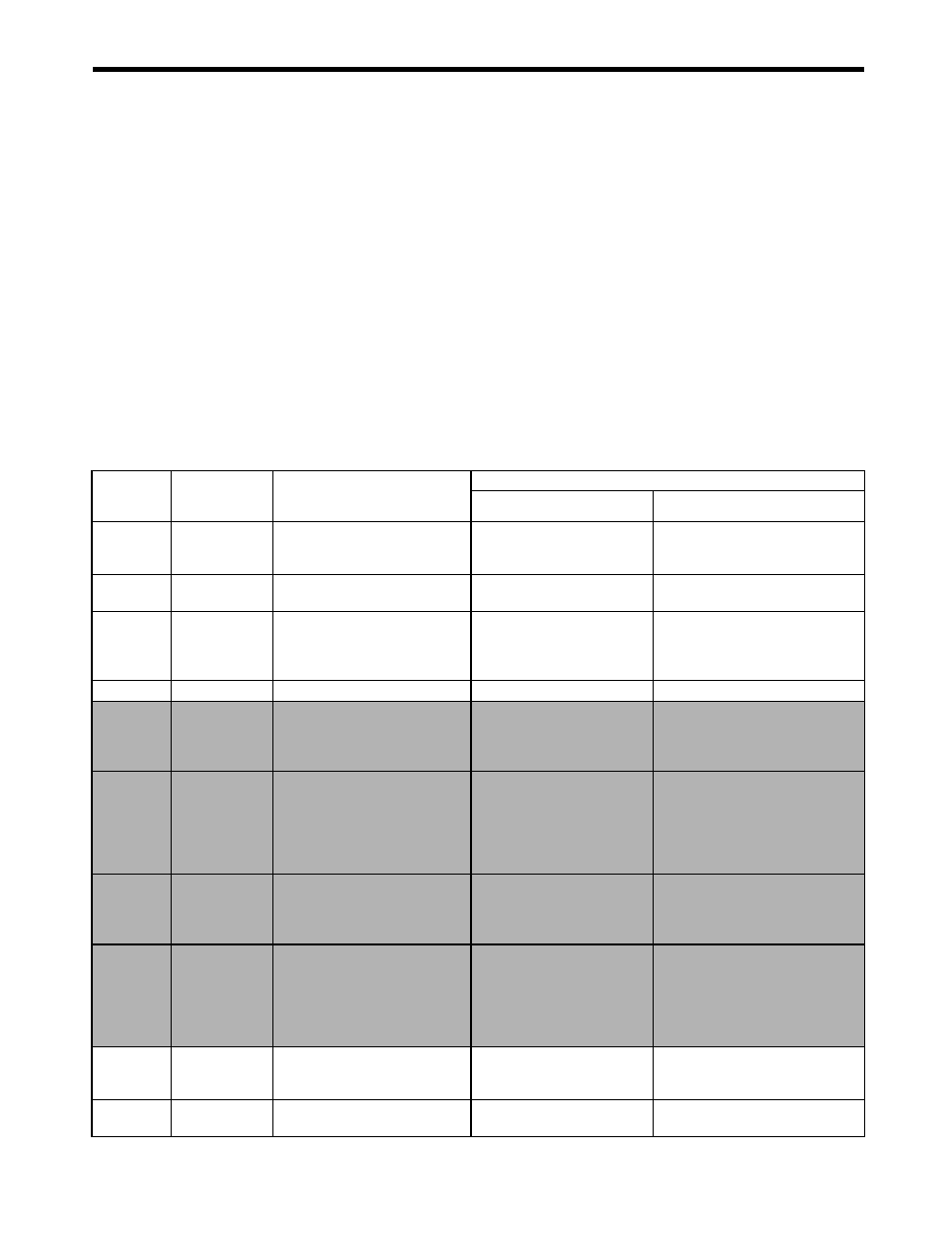
The 17 methods that are provided for the zero point return are listed in the following table. Select the
best method for the machine in the setting parameters.
Setting
Parameter
OW3C
Name
Method
Signal Meaning
SVB-01
SVA-01
0
DEC1 + C-
Phase
Applies a 3-step deceleration
method using the deceleration
limit switch and phase-C pulse.
DEC1 signal: SERVOPACK
DEC signal
DEC1: DI_5 or OW05, bit 8
∗
(Latched on phase-C signal.)
1
ZERO signal
Uses the ZERO signal.
ZERO signal: SERVOPACK
EXT1 signal
ZERO signal: DI_2
(Latched on ZERO signal.)
2
DEC 1 + ZERO
signal
Applies a 3-step deceleration
method using the deceleration
limit switch and ZERO signal.
DEC1 signal: SERVOPACK
DEC signal
ZERO signal: SERVOPACK
EXT1 signal
DEC1: DI_5 or OW05, bit 8
∗
ZERO signal: DI_2
(Latched on ZERO signal.)
3
C-Phase
Uses the phase-C pulse.
(Latched on phase-C signal.)
4
DEC2 + ZERO
Signal Method
This method uses the
deceleration limit switch as an
area signal and the ZERO
signal as the zero point signal.
−
DEC2: DI_5 or OW05, bit 8
*
ZERO signal: DI_2
(Latched on ZERO signal.)
5
DEC1 + LMT+
ZERO Signal
Method
This method uses the
deceleration limit switch and the
two home return limit signals
(LMT) as area signals and the
ZERO signal as the zero point
signal.
−
DEC1: DI_5 or OW05, bit 8
*
Reverse LMT: OW05, bit 9
Forward LMT: OW05, bit 10
ZERO signal: DI_2
(Latched on ZERO signal.)
6
DEC2 +
Phase-C
Signal Method
This method uses the
deceleration limit switch as an
area signal and the phase-C
signal as the zero point signal.
−
DEC2: DI_5 or OW05, bit 8*
(Latched on phase-C signal.)
7
DEC1 + LMT+
Phase-C
Signal Method
This method uses the
deceleration limit switch and the
two home return limit signals
(LMT) as area signals and the
phase-C signal as the zero
point signal.
−
DEC1: DI_5 or OW05, bit 8
*
Reverse LMT: OW05, bit 9
Forward LMT: OW05, bit 10
(Latched on phase-C signal.)
11
C pulse Only
Uses only the phase-C pulse.
−
P-OT: DI_3
N-OT: DI_4
(Latched on phase-C signal.)
12
POT & C pulse Uses the positive overtravel signal
and phase-C pulse.
POT: SERVOPACK P-OT
signal
P-OT: DI_3
(Latched on phase-C signal.)