4 servo gain adjustments, 1 servo gain parameters, 2 basic rules of gain adjustment – Yaskawa Sigma II Series Servo System User Manual
Page 265: 4 servo gain adjustments - 33, 4 servo gain adjustments -33, Servo gain parameters -33, Basic rules of gain adjustment -33
Sigma II User’s Manual
Chapter 6: Servo Adjustment
6 - 33
6.4 Servo Gain Adjustments
This section describes information on the basic rules of gain adjustments in the servo
amplifier, adjustment methods in a variety of cases, and reference set values.
6.4.1
Servo Gain Parameters
The following parameters must be set properly for servo gain adjustments.
•
Pn100: Speed loop gain
•
Pn101: Speed loop integral time constant
•
Pn102: Position loop gain
•
Pn401: Torque reference filter time constant
If the servo amplifier is used in the speed control mode with the analog voltage
reference, the position loop is controlled by the host device. Therefore, position
loop gain is adjusted through the host device.
If the host is not available for adjustments of position loop gain, set the speed
reference input gain in parameter Pn300. If the set value is improper, the servomotor
may not run at top speed.
6.4.2
Basic Rules of Gain Adjustment
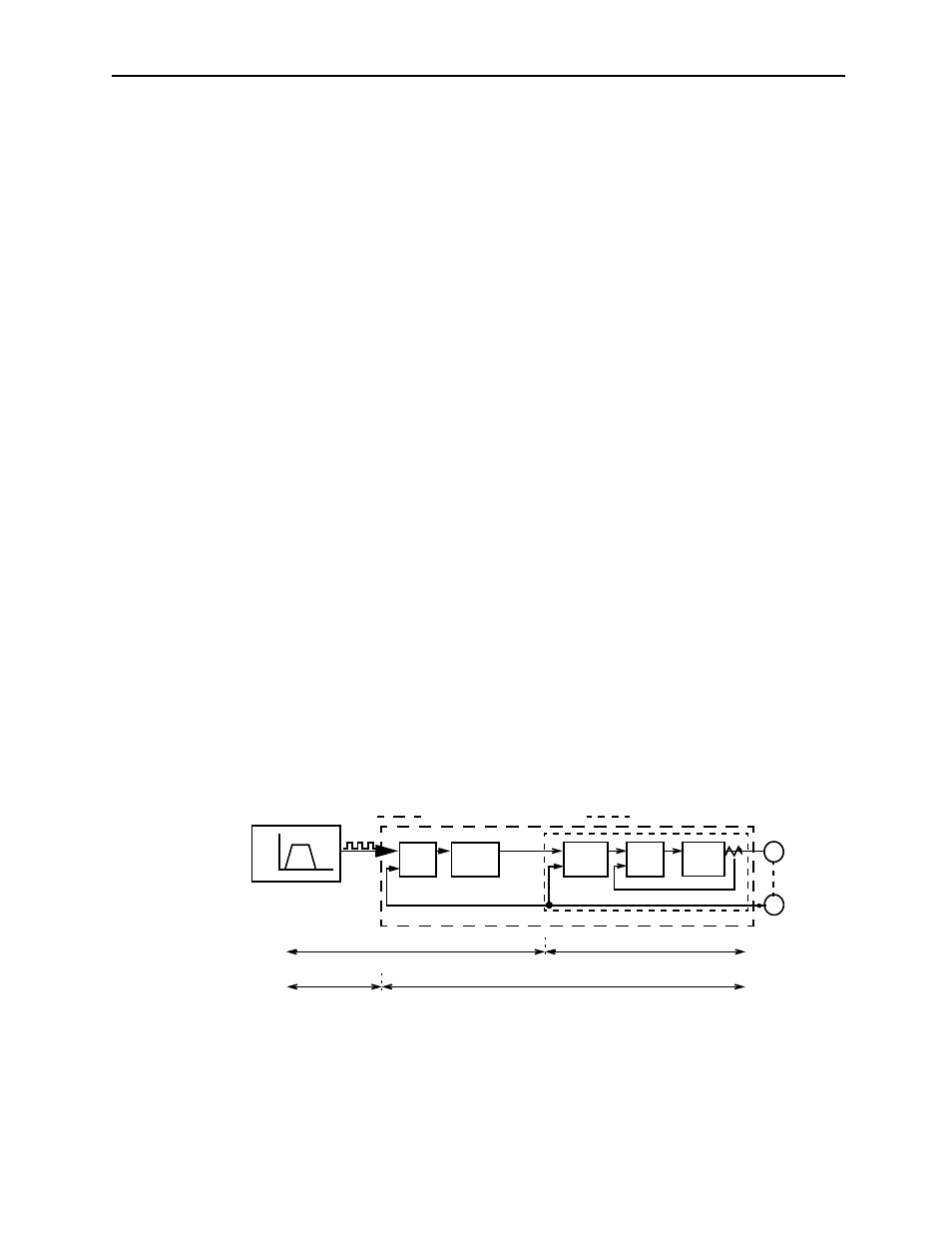
The servo system consists of three feedback loops (i.e., position loop, speed loop,
and current loop). The innermost loop must have the highest response speed and the
middle loop must have higher response speed than the outermost. If this principle is
not followed, it will result in vibration or poor responsiveness.
The servo amplifier is designed to ensure that the current loop has good response
performance. The user needs only to adjust the position loop and speed loop gain.
The servo system block diagram consists of the position, speed, and current loops, as
shown below.
•
Generally speaking, the responsiveness of the position loop cannot be higher than
that of the speed loop. Therefore, to increase the position loop gain, you must
Speed K
V
control
block T
i
K
P
= Position loop gain
K
V
= Speed loop gain
T
i
= Integral time constant
Speed
Speed pattern
Time
Error
Current
counter
Kp
(D to A
limit
block
Power
conversion
block
converter)
Analog
voltage
Pulse
train
In case of position control
In case of speed control
Position loop
Speed loop
Host controller (prepared by the user)
Servo amplifier
Host controller
Servo amplifier
(prepared by the user)
Position control moce
Speed control moce
Motor
SM
PG