Pid control operation, Pid control applications, Using pid control – Yaskawa G7 Drive User Manual
Page 315
6
-98
Using PID Control
PID control is a method of making the feedback value (detection value) match the set target value. By combin-
ing proportional control (P), integral control (I), and derivative control (D), you can even control targets
(machinery) with play time.
The characteristics of the PID control operations are given below.
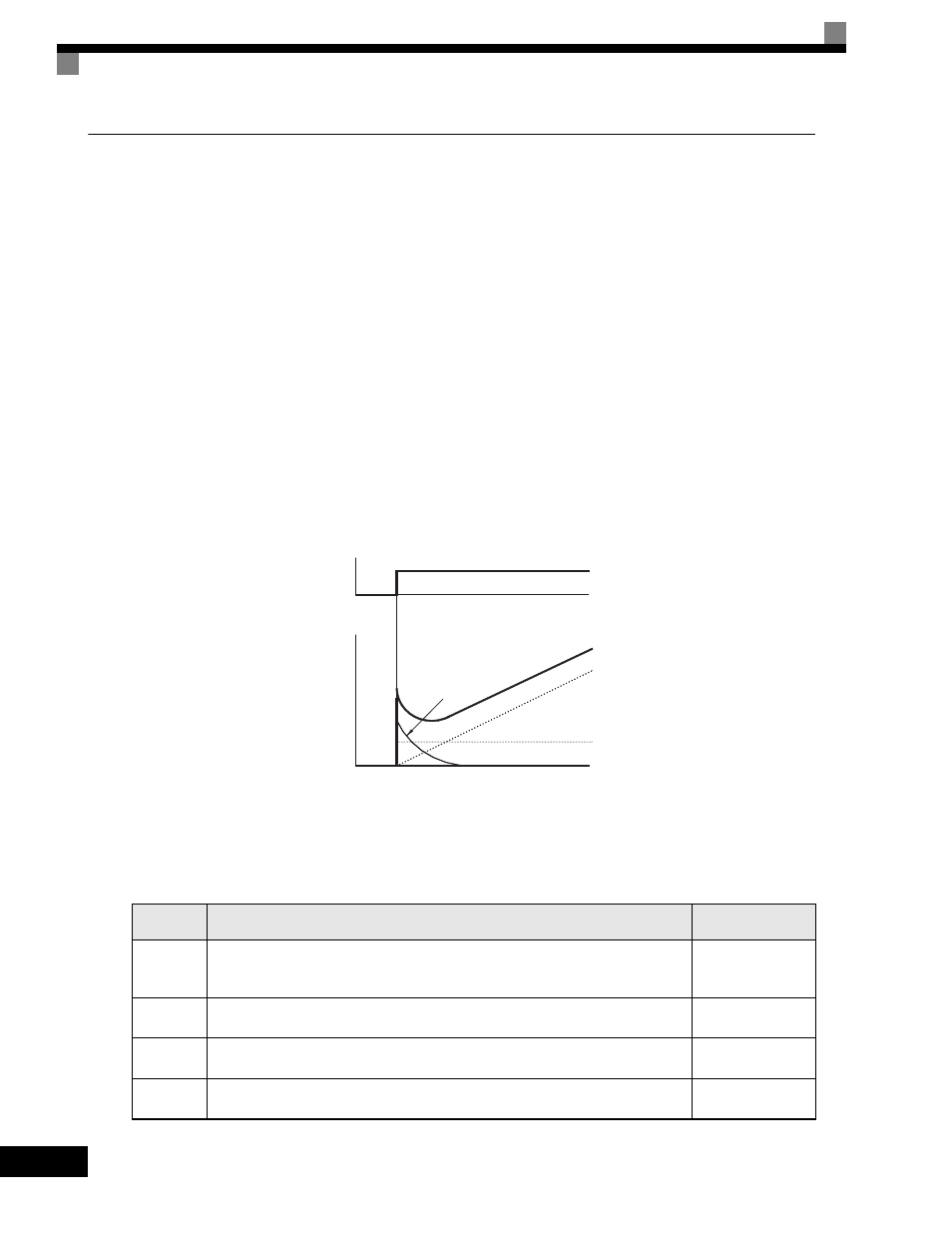
PID Control Operation
To understand the differences between each PID control operation (P, I, and D, the variation in the amount of
operation (output frequency) is as shown in the following diagram when the deviation (i.e., the difference
between the target value and feedback value) is fixed.
Fig 6.59 PID Control Operation
PID Control Applications
The following table shows examples of PID control applications using the Drive.
P control
Outputs the amount of operation proportional to the deviation. You cannot, however, set the
deviation to zero using P control alone.
I control
Outputs the amount of operation that integrates the deviation. Used for matching feedback
value to the target value. I control is not suited, however, to rapid variations.
D control
Outputs the amount of operation derived from the deviation. Can respond promptly to rapid
variations.
Application
Control Details
Example of
Sensor Used
Speed Con-
trol
• Feeds back machinery speed information, and matches speed to the target value.
• Inputs speed information from other machinery as the target value, and performs
synchronous control using the actual speed feedback.
Tachometer genera-
tor
Pressure
Control
Feeds back pressure information, and performs constant pressure control.
Pressure sensor
Flow Rate
Control
Feeds back flow rate information, and controls the flow rate highly accurately.
Flow rate sensor
Tempera-
ture Control
Feeds back temperature information, and performs temperature adjustment control by
rotating the fan.
• Thermocouple
• Thermistor
Deviation
I control
Amount of operation
D control
Time
PID control
Time
P control