Yaskawa SGDB User Manual
Page 15
1 . 1 Servo Mechanisms
3
Servo system could be defined in more detail as a mechanism that:
• Moves at a specified speed and
• Locates an object in a specified position
To develop such a servo system, an automatic control system involving feedback control
must be designed. This automatic control system can be illustrated in the following block dia-
gram:
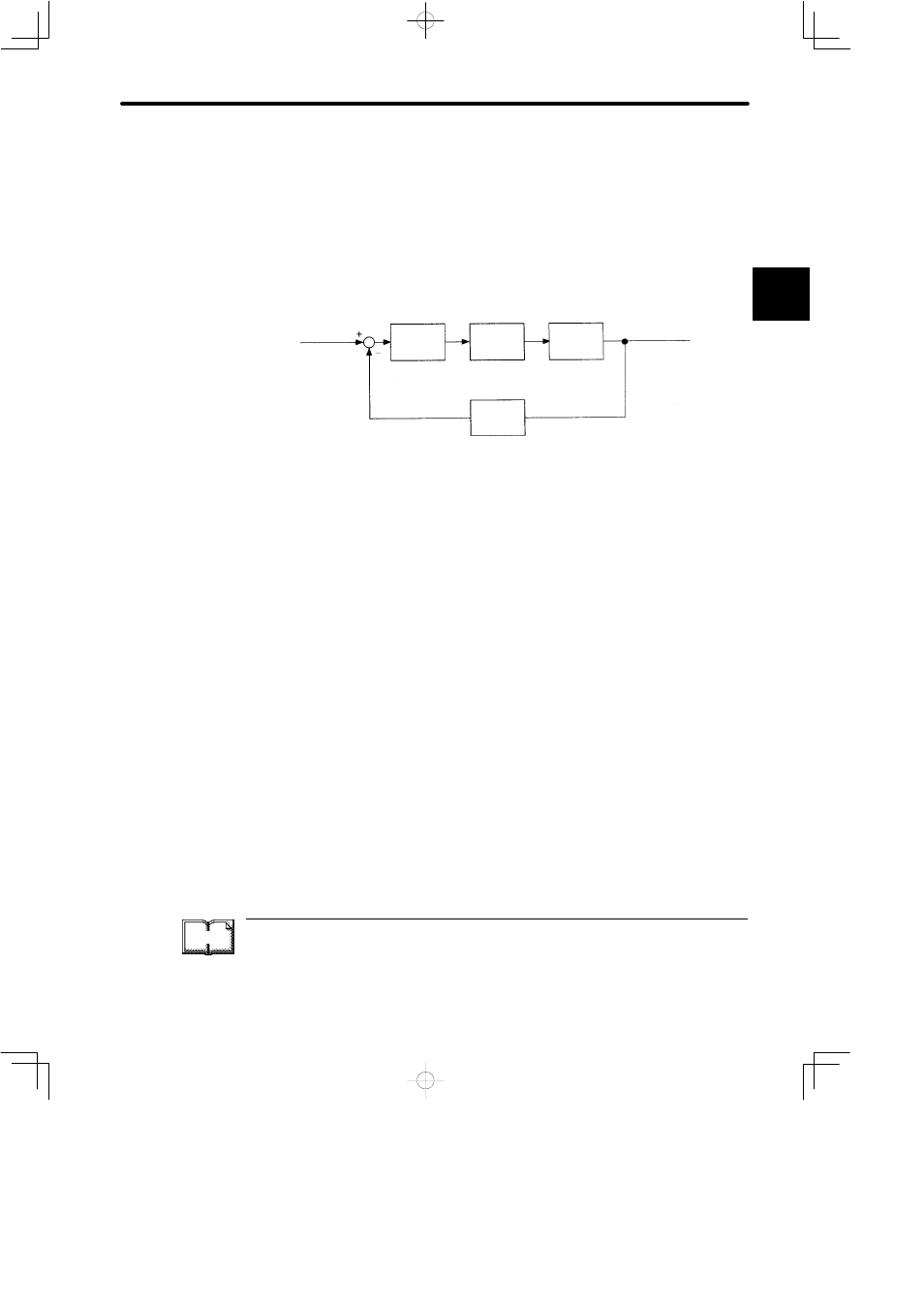
Configuration of Servo System
Specified position
input
Servo
amplifier
Servo
motor
Controlled
machine
(load)
Machine position
output
Feedback part
Detector
This servo system is an automatic control system that detects the machine position (output
data), feeds back the data to the input side, compares it with the specified position (input
data), and moves the machine by the difference between the compared data.
In other words, the servo system is a system to control the output data to match the
specified input data.
If, for example, the specified position changes, the servo system will reflect the changes.
In the above example, input data is defined as a position, but input data can be any physical
quantities such as orientation (angle), water pressure, or voltage.
Position, speed, force (torque), electric current, and so on are typical controlled values for a
servo system.
The main technical terms used in this manual are as follows:
1) Servo mechanism
2) Servo
Normally, servo is synonymous with servo mechanism. However, because “mechanism” is
omitted, the meaning becomes somewhat ambiguous. Servo may refer to the entire servo
mechanism but may also refer to an integral part of a servo mechanism such as a servomotor
or a servo amplifier. This manual also follows this convention in the use of the term “servo”.
TERMS
Feedback control
A control that returns process variables to the input side and forms a closed loop. It is also
called closed-loop control.
1