5 using electronic gear – Yaskawa SGDB User Manual
Page 91
3.2 Setting Parameters According to Host Controller
79
3.2.5 Using Electronic Gear
The electronic gear function enables the motor travel distance per input reference pulse
to be set to any value. It allows the host controller to perform control without having to
consider the machine gear ratio and the number of encoder pulses.
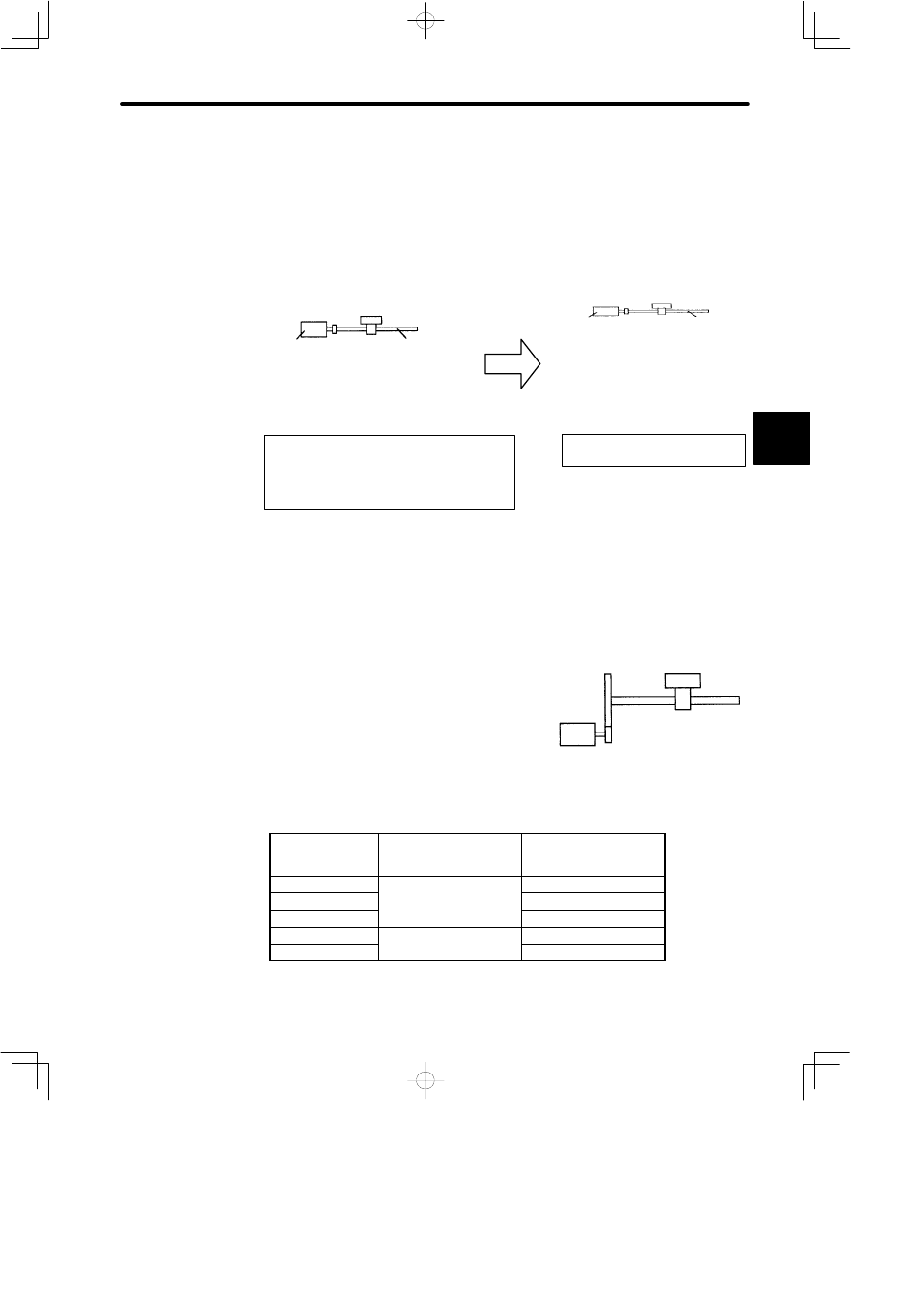
When Electronic Gear Function
is Not Used
When Electronic Gear Function
is Used
Workpiece
Number of
encoder
pulses: 2,048
Ball screw
pitch: 6 mm
Reference
unit: 1 μm
To move a workpiece 10 mm :
One revolution is equivalent to 6 mm, so
10 6 = 1.6666 (revolutions)
2048 x 4 (pulses) is equivalent to one revolution, so
1.6666 x 2,048 x 4 = 13,653 (pulses)
A total of 13653 pulses must be input as a reference.
The host controller needs to make this calculation.
Machine conditions and reference unit
must be defined for the electronic gear
function beforehand.
To move a workpiece 10 mm:
Reference unit is 1 μm, so
10 mm 1 μm = 10,000 pulses
Number of
encoder
pulses: 2,048
Ball screw
pitch: 6 mm
Workpiece
J
Setting the Electronic Gear
Calculate the electronic gear ratio (B/A) according to the procedure below and set the
value in Cn-24 and Cn-25.
1. Check the machine specifications.
Items related to electronic gear:
− Gear ratio
− Ball screw pitch
− Pulley diameter
2. Check the number of encoder pulses for the SGMj servomotor.
Motor Type
encoder
specifications
Encoder Type
Number of Encoder
Pulses Per Revolution
(P/R)
2
Incremental encoder
8192
3
2048
6
4096
W
Absolute encoder
1024
S
8192
Same as parameter Cn-11 settings.
3
Gear ratio
Ball screw pitch