2 servo configuration – Yaskawa SGDB User Manual
Page 17
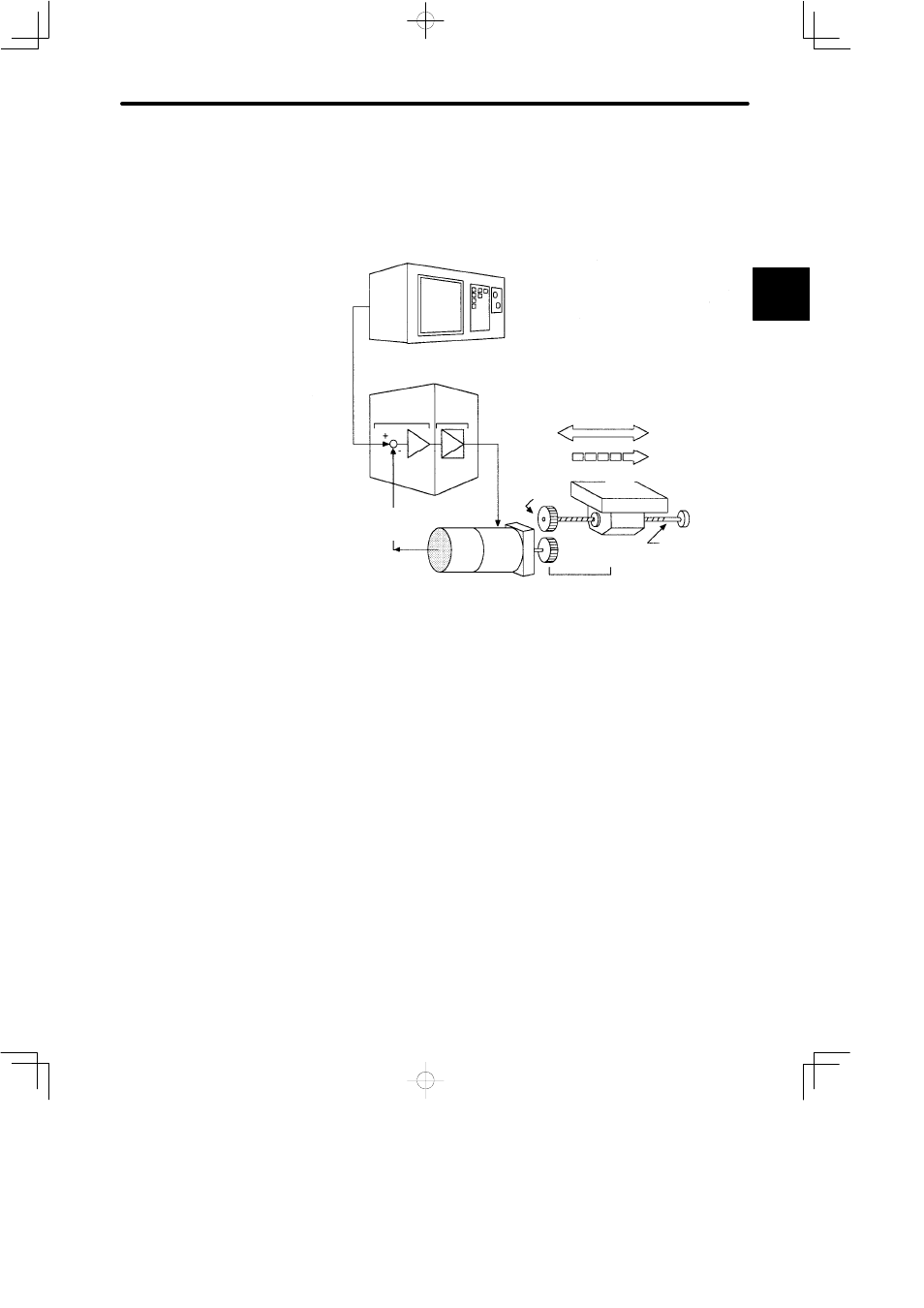
1.2 Servo Configuration
5
1.2
Servo Configuration
The following diagram illustrates a servo system in detail:
Position or
speed
reference
Host controller
Servo amplifier
Comparator Power
amplifier
(Input)
Motor
drive
circuit
(Output)
Position
Speed
Gear
Movable
table
Position or
speed
feedback
Controlled
system
Ball screw
Detector servomotor
Drive system
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(1) Controlled system: Mechanical system for which the position or speed is to be con-
trolled.
This includes a drive system that transmits torque from a servo-
motor.
(2) Servomotor:
A main actuator that moves a controlled system. Two types are
available: AC servomotor and DC servomotor.
(3) Detector:
A position or speed detector. Normally, an encoder mounted on
a motor is used as a position detector.
(4) Servo amplifier:
An amplifier that processes an error signal to correct the differ-
ence between a reference and feedback data and operates the
servomotor accordingly. A servo amplifier consists of a
comparator, which processes error signals, and a power ampli-
fier, which operates the servomotor.
(5) Host controller:
A device that controls a servo amplifier by specifying a position
or speed as a set point.
1