Voltage protection (be1-700v), 24 - overexcitation protection, Delta/wye transformer application -19 – Basler Electric BE1-700 User Manual
Page 75: Generator application -19, Voltage protection (be1-700v) -19, 24 - overexcitation protection -19, Table 4-12. fault type multipliers -19
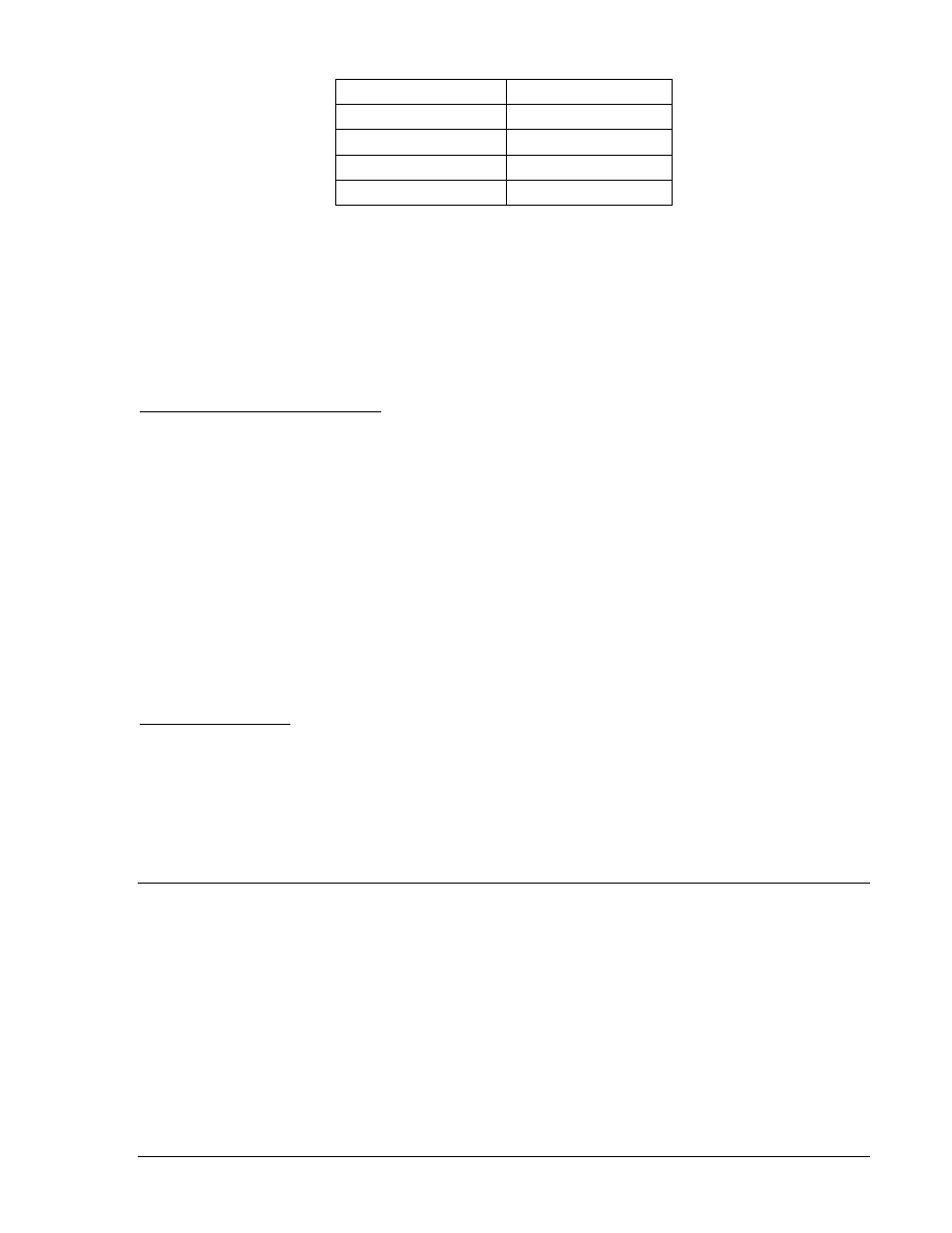
Table 4-12. Fault Type Multipliers
Fault Type
Multiplier
Ph-Ph
m = 1.732
Ph-Ph-G
m > 1.732
Ph-G
m = 3
3-phase
m = infinity
For example, a downstream phase 51 element has a pickup of 150 amperes. The upstream 51Q element
has a pickup of 200 amperes. To check the coordination between these two elements for a phase-to-
phase fault, the phase overcurrent element would be plotted normally with pickup at 150 amperes. The
51Q element would be shifted to the right by the appropriate factor m. Thus, the characteristic would be
plotted on the coordination graph with pickup at: (200 amperes)
∗ 1.732 = 346 amperes.
Generally, for coordination with downstream phase overcurrent devices, phase-to-phase faults are the
most critical to consider. All other fault types result in an equal or greater shift of the time current
characteristic curve to the right on the plot.
Delta/Wye Transformer Application
Often, the phase relays on the delta side of a delta/wye transformer must provide backup protection for
faults on the wye side. For faults not involving ground, this is not a problem since the phase relays will
see 1.0 per unit fault current for three-phase faults and 2/
√3 (1.15) per unit fault current for phase-to-
phase faults. However, for faults involving ground, the sensitivity is reduced because the zero-sequence
components are trapped in the delta not seen by the delta-side phase relays. The phase relays will see
only 1/
√3 (0.577) per unit current for phase-to-ground faults.
Negative-sequence overcurrent protection is immune to the effect caused by the zero-sequence trap and
30 degrees phase shift provided by the delta/wye transformer. For a phase-to-ground fault, the magnitude
of the negative-sequence components is 1/3 the magnitude of the total fault current. On a per unit basis,
this is true for the fault current on the delta side of the transformer as well. (The previous statement
specifies per unit since the actual magnitudes will be adjusted by the inverse of the voltage ratio of the
delta/wye transformer.) Thus, backup protection for phase-to-ground faults on the wye side of the
transformer can be obtained by using negative-sequence overcurrent protection on the delta side with the
pickup sensitivity set at 1/3 per unit of the magnitude of the phase-to-ground fault for which you wish to
have backup protection.
Generator Application
Generators have a maximum continuous rating for negative-sequence current. This is typically given in
terms of percent of stator rating. When using the 46 time current characteristic curve, the user should
convert the I
2
rating data to actual secondary current at the relay. This value, plus some margin (if
appropriate), should then be entered into the pickup setting. For example, generator ratings of 5 A of full-
load current (at the relay terminals) and 10 percent continuous I
2
, converts to 0.50 A. Therefore, the
minimum pickup setting for the 46 curve should be set at a value below 0.50 A. Continuous I
2
ratings for
generators are typically in the range of 3 to 15 percent of their full-load current rating.
VOLTAGE PROTECTION (BE1-700V)
BE1-700V voltage protection includes elements for overexcitation, phase & auxiliary undervoltage, phase
& auxiliary overvoltage, and negative-sequence overvoltage.
24 - Overexcitation Protection
Overexcitation occurs when a generator or transformer magnetic core becomes saturated. When this
happens, stray flux is induced in non-laminated components, causing overheating. The BE1-700 detects
overexcitation conditions with a volts/hertz element that consists of one alarm setting, one integrating time
characteristic with selectable exponents (3 sets of time curves), and two definite-time characteristics. This
allows the user to individually select an inverse-time characteristic, a composite characteristic with
inverse-time, and one or two definite-time elements, or a dual-level, definite-time element. The volts/hertz
element has two outputs: pickup and trip as shown in Figure 4-15.
9376700990 Rev M
BE1-700 Protection and Control
4-19