Bfd for bgp configuration example at the cli, Network requirements, Configuration procedure – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 520
495
[SecPathC-route-policy] quit
# Apply the routing policy localpref to the route from the peer 193.1.1.1 on SecPath C.
[SecPathC] bgp 200
[SecPathC-bgp] peer 193.1.1.1 route-policy localpref import
[SecPathC-bgp] quit
# Display the BGP routing table on SecPath D.
[SecPathD] display bgp routing-table
Total Number of Routes: 2
BGP Local router ID is 194.1.1.1
Status codes: * - valid, ^ - VPNv4 best, > - best, d - damped,
h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale
Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*>i 1.0.0.0 193.1.1.1 0 200 0 100i
* i 192.1.1.1 0 100 0 100i
The route 1.0.0.0/8 learned from SecPath C is the optimal.
BFD for BGP configuration example at the CLI
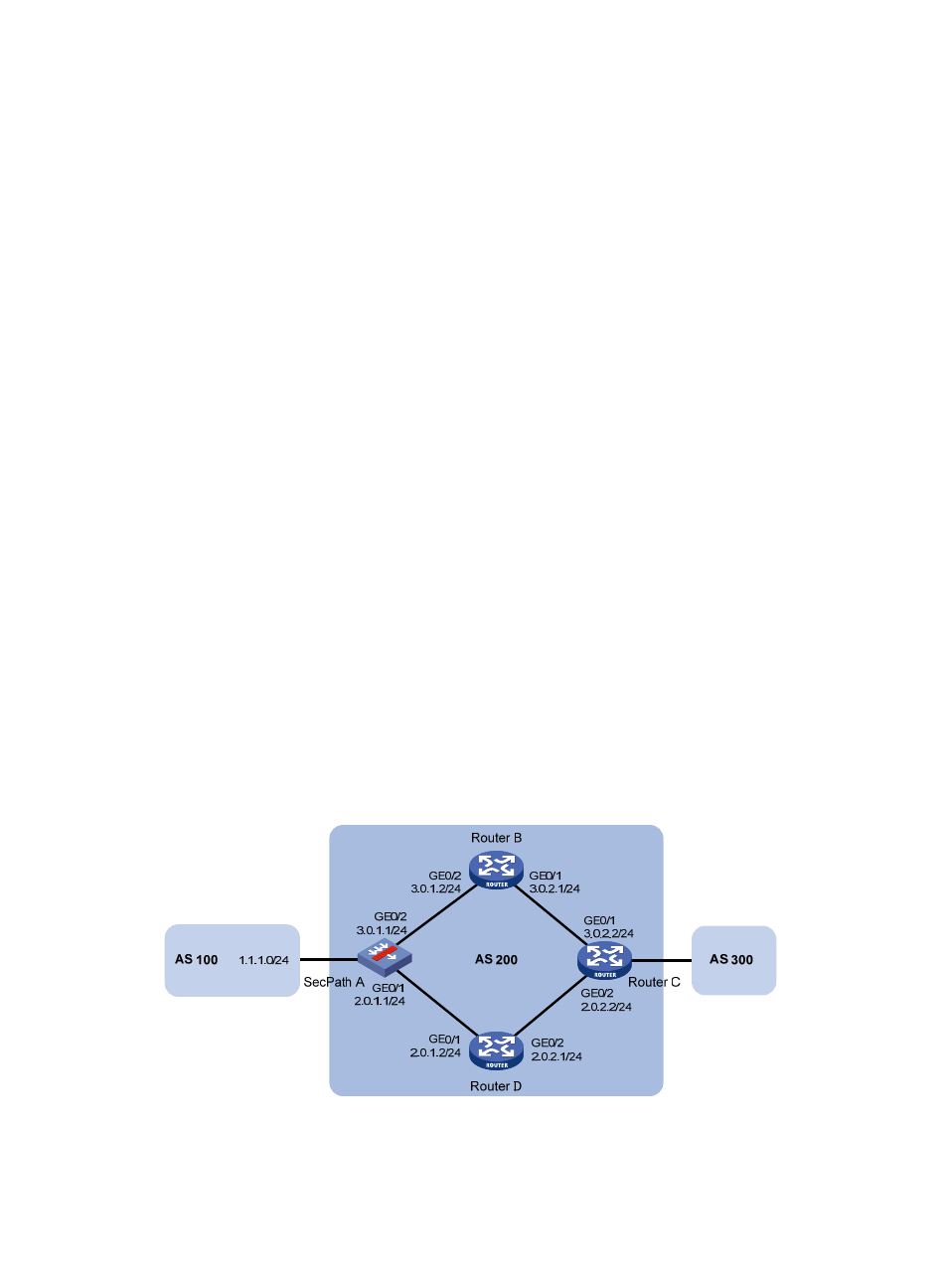
Network requirements
As shown in
:
•
Configure OSPF as the IGP in AS 200.
•
Establish two IBGP connections between SecPath A and Router C. When both links are working,
Router C adopts the link SecPath A<—>Router B<—>Router C to exchange packets with network
1.1.1.0/24. Configure BFD over the link. Then if the link fails, BFD can quickly detect the failure and
notify it to BGP. Then the link SecPath A<—>Router D<—>Router C takes effect immediately.
Figure 295 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)