Protocols and standards – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 710
685
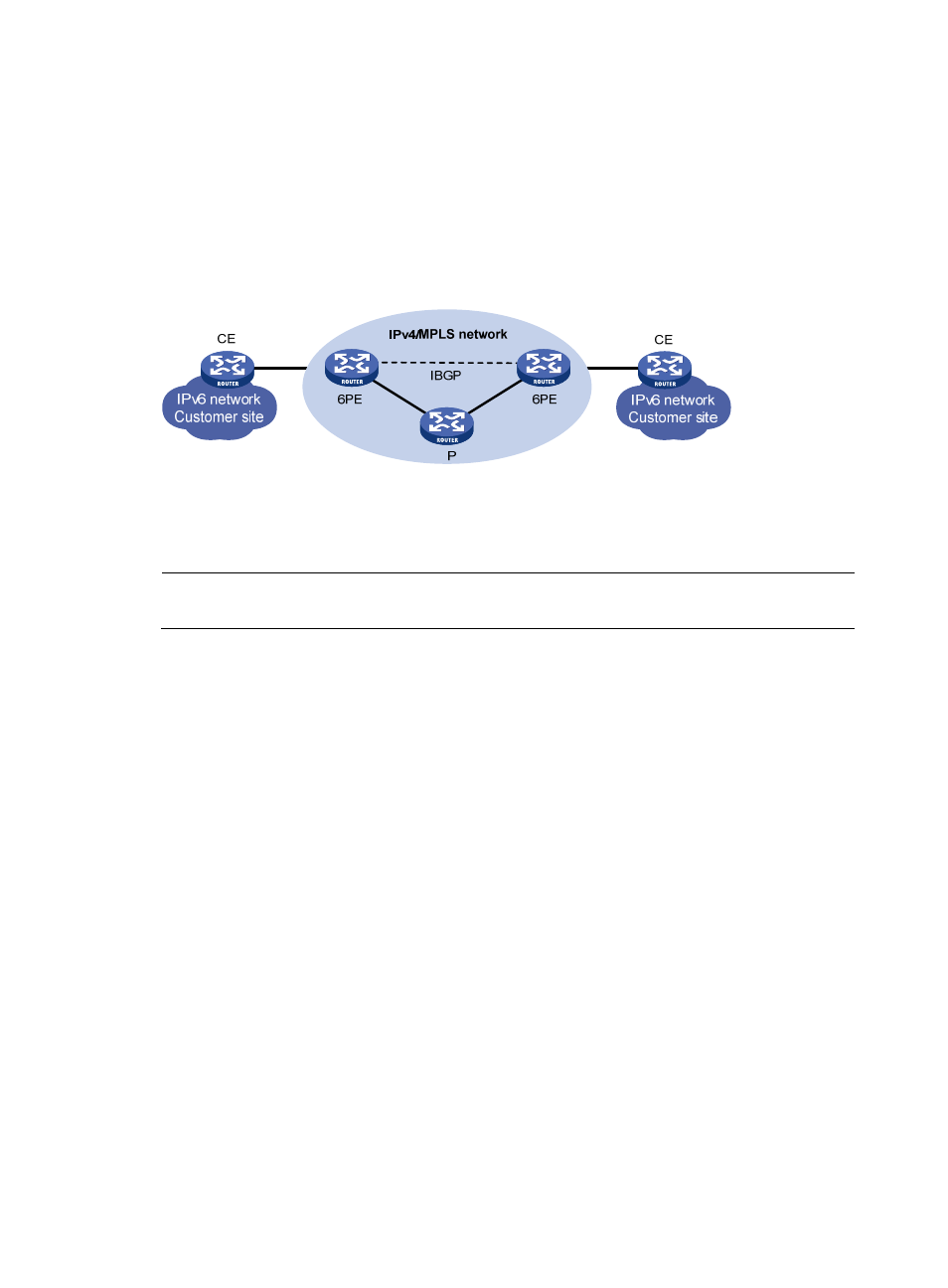
6PE
6PE is a transition technology by which Internet service providers (ISPs) can use existing IPv4 backbone
networks to allow communications between isolated IPv6 networks.
6PE adds labels to the IPv6 routing information of customer networks and advertises the information into
the IPv4 backbone network over Internal Border Gateway Protocol (iBGP) sessions. IPv6 packets are
labeled and forwarded over tunnels on the backbone network. The tunnels can be GRE tunnels or MPLS
LSPs.
Figure 358 Network diagram
When an ISP wants to utilize the existing IPv4/MPLS network to provide IPv6 traffic switching capability
through MPLS, only the PE routers need to be upgraded, so 6PE is a highly efficient solution. In addition,
the operation risk of 6PE is very low.
NOTE:
For more information or configuration related to 6PE, see "Configuring IPv6 BGP."
Protocols and standards
Protocols and standards related to IPv6 include:
•
RFC 1881, IPv6 Address Allocation Management
•
RFC 1887, An Architecture for IPv6 Unicast Address Allocation
•
RFC 1981, Path MTU Discovery for IP version 6
•
RFC 2375, IPv6 Multicast Address Assignments
•
RFC 2460, Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification
•
RFC 2461, Neighbor Discovery for IP Version 6 (IPv6)
•
RFC 2462, IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
•
RFC 2463, Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMPv6) for the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6)
Specification
•
RFC 2464, Transmission of IPv6 Packets over Ethernet Networks
•
RFC 2526, Reserved IPv6 Subnet Anycast Addresses
•
RFC 3307, Allocation Guidelines for IPv6 Multicast Addresses
•
RFC 3513, Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Addressing Architecture