Stateless dhcpv6 configuration example, Network requirements, Configuring secpath b – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 749: Configuring secpath a
724
Task Command
Remarks
Display DHCPv6 client statistics.
display ipv6 dhcp client statistics [ interface
interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin |
exclude | include } regular-expression ]
Available in any view
Display the DUID of the local
device.
display ipv6 dhcp duid [ | { begin | exclude |
include } regular-expression ]
Available in any view
Stateless DHCPv6 configuration example
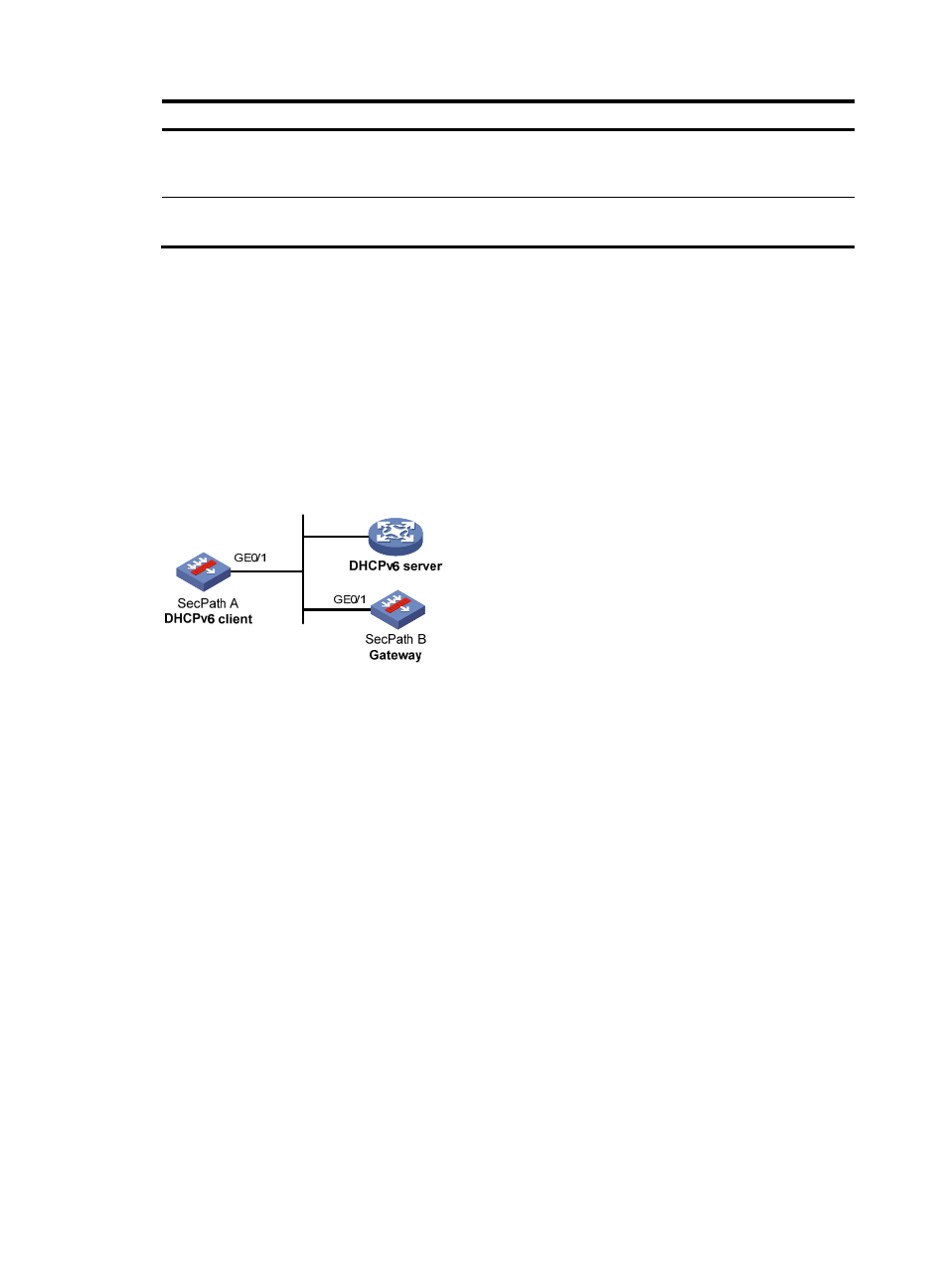
Network requirements
Through stateless DHCPv6, SecPath A obtains the DNS server address, domain name, and other
information from the DHCPv6 server.
SecPath B acts as the gateway to send RA messages periodically.
Figure 372 Network diagram
Configuring SecPath B
# Enable the IPv6 packet forwarding function.
<SecPathB> system-view
[SecPathB] ipv6
# Configure the IPv6 address of GigabitEthernet 0/1.
[SecPathB] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
[SecPathB-GigabitEthernet0/1] ipv6 address 1::1 64
# Set the O flag in the RA messages to 1.
[SecPathB-GigabitEthernet0/1] ipv6 nd autoconfig other-flag
# Enable SecPath B to send RA messages.
[SecPathB-GigabitEthernet0/1] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
Configuring SecPath A
# Enable the IPv6 packet forwarding function.
<SecPath> system-view
[SecPath] ipv6
# Enable stateless IPv6 address autoconfiguration on GigabitEthernet 0/1.