Types of mac address table entries, Mac address table-based frame forwarding – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 73
48
You can manually add MAC address entries to the MAC address table of the firewall to bind specific user
devices to the port. Because manually configured entries have higher priority than dynamically learned
ones, this prevents hackers from stealing data using forged MAC addresses.
Types of MAC address table entries
A MAC address table may contain the following types of entries:
•
Static entries—Manually configured and never age out.
•
Dynamic entries—Manually configured or dynamically learned and may age out.
•
Blackhole entries—Manually configured and never age out. Blackhole entries are configured for
filtering out frames with specific destination MAC addresses. For example, to block all packets
destined for a specific user for security concerns, you can configure the MAC address of this user
as a blackhole destination MAC address entry.
To adapt to network changes and prevent inactive entries from occupying table space, an aging
mechanism is adopted for dynamic MAC address entries. Each time a dynamic MAC address entry is
learned or created, an aging time starts. If the entry has not updated when the aging timer expires, the
firewall deletes the entry. If the entry has updated before the aging timer expires, the aging timer restarts.
NOTE:
A static or blackhole MAC address entry can overwrite a dynamic MAC address entry, but not vice versa.
MAC address table-based frame forwarding
When forwarding a frame, the firewall adopts the following forwarding modes based on the MAC
address table:
•
Unicast mode—If an entry is available for the destination MAC address, the firewall forwards the
frame out the outgoing interface indicated by the MAC address table entry.
•
Broadcast mode—If the firewall receives a frame with an all-ones destination address, or no entry
is available for the destination MAC address, the firewall broadcasts the frame to all the interfaces
except the receiving interface.
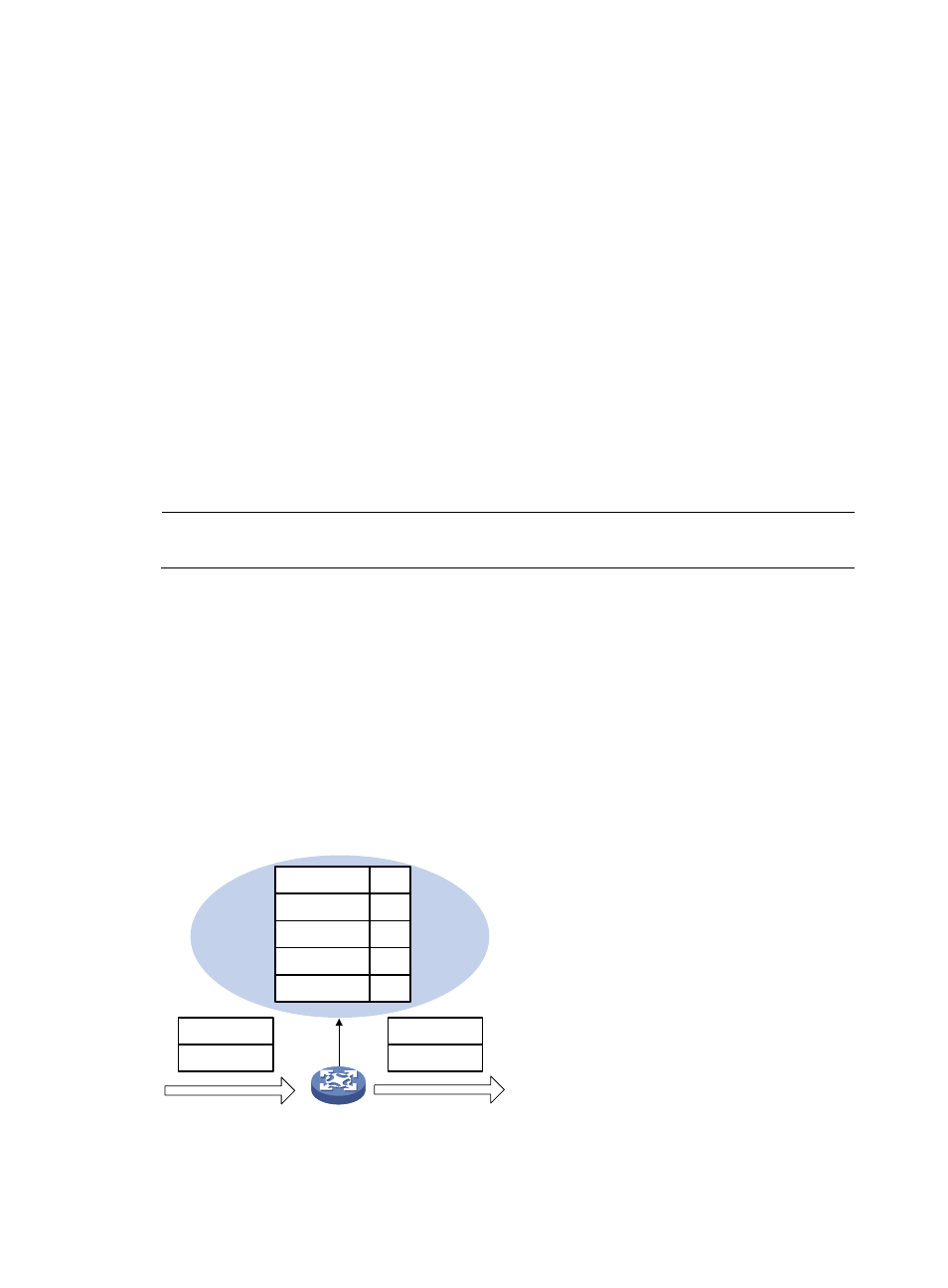
Figure 31 MAC address table of the firewall
Port 1
Port 2
MAC address
Port
MAC A
1
MAC B
1
MAC C
2
MAC D
2
MAC A
MAC B
MAC C
MAC D