Ipv6 bgp route reflector configuration example, Network requirements, Configuration procedure – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 833
808
IPv6 BGP route reflector configuration example
Network requirements
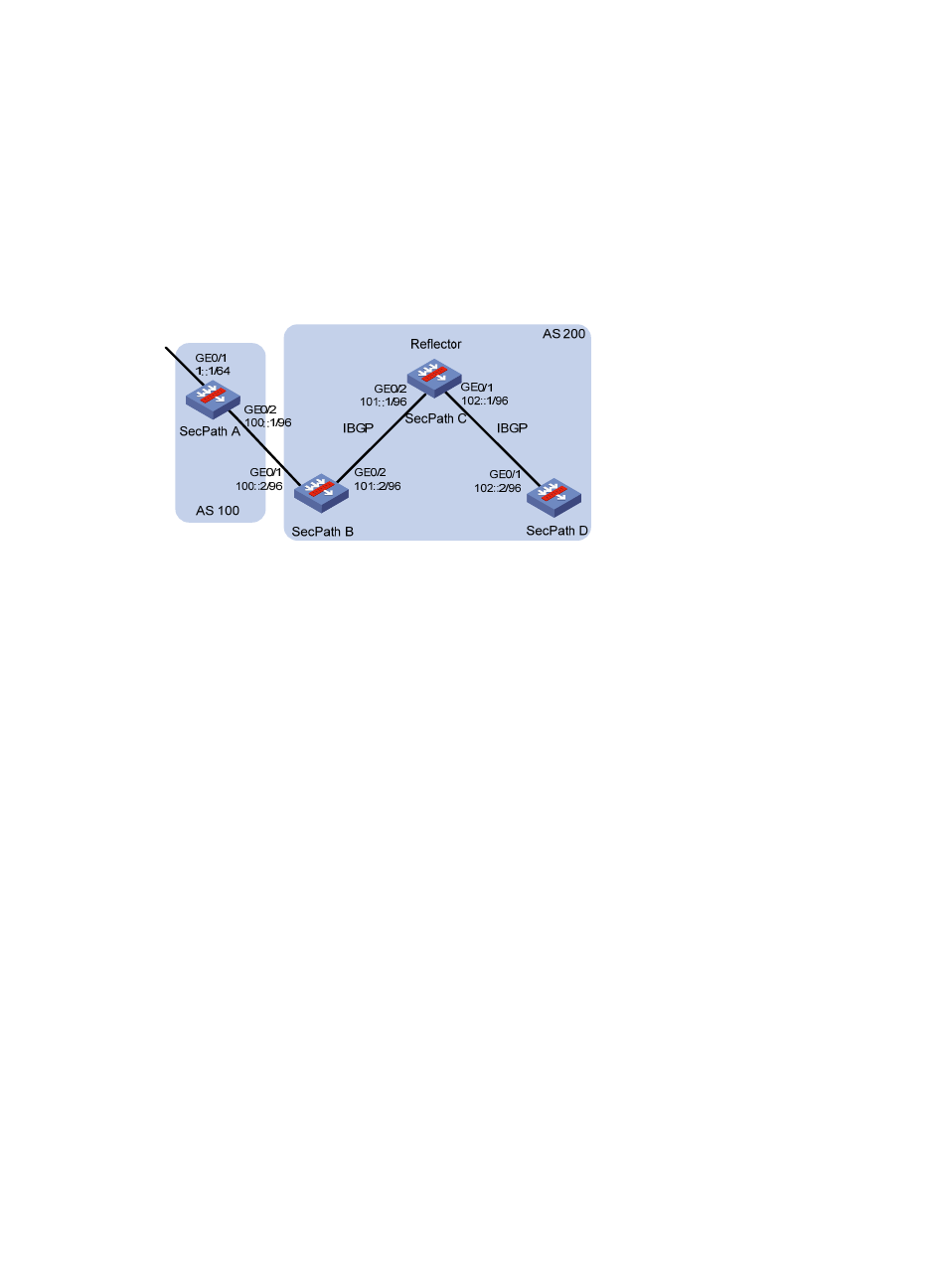
As shown in
, SecPath B receives an EBGP update and sends it to SecPath C, which is
configured as a route reflector with two clients: SecPath B and SecPath D.
SecPath B and SecPath D need not establish an IBGP connection because SecPath C reflects updates
between them.
Figure 389 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure IPv6 addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2.
Configure IPv6 BGP basic functions:
# Configure SecPath A.
<SecPathA> system-view
[SecPathA] ipv6
[SecPathA] bgp 100
[SecPathA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1
[SecPathA-bgp] ipv6-family
[SecPathA-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 100::2 as-number 200
[SecPathA-bgp-af-ipv6] network 1:: 64
# Configure SecPath B
<SecPathB> system-view
[SecPathB] ipv6
[SecPathB] bgp 200
[SecPathB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2
[SecPathB-bgp] ipv6-family
[SecPathB-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 100::1 as-number 100
[SecPathB-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 101::1 as-number 200
[SecPathB-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 101::1 next-hop-local
# Configure SecPath C.
<SecPathC> system-view
[SecPathC] ipv6
[SecPathC] bgp 200
[SecPathC-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3
[SecPathC-bgp] ipv6-family