Control mode selection, 2 general description, Table 1.1 control modes and their features – Yaskawa L1000E AC Drive Technical Manual for CIMR-LE Models for Elevator Applications User Manual
Page 28
1.2 General Description
28
YASKAWA ELECTRIC SIEP YAIL1E 01A YASKAWA AC Drive L1000E Technical Manual
◆ Control Mode Selection
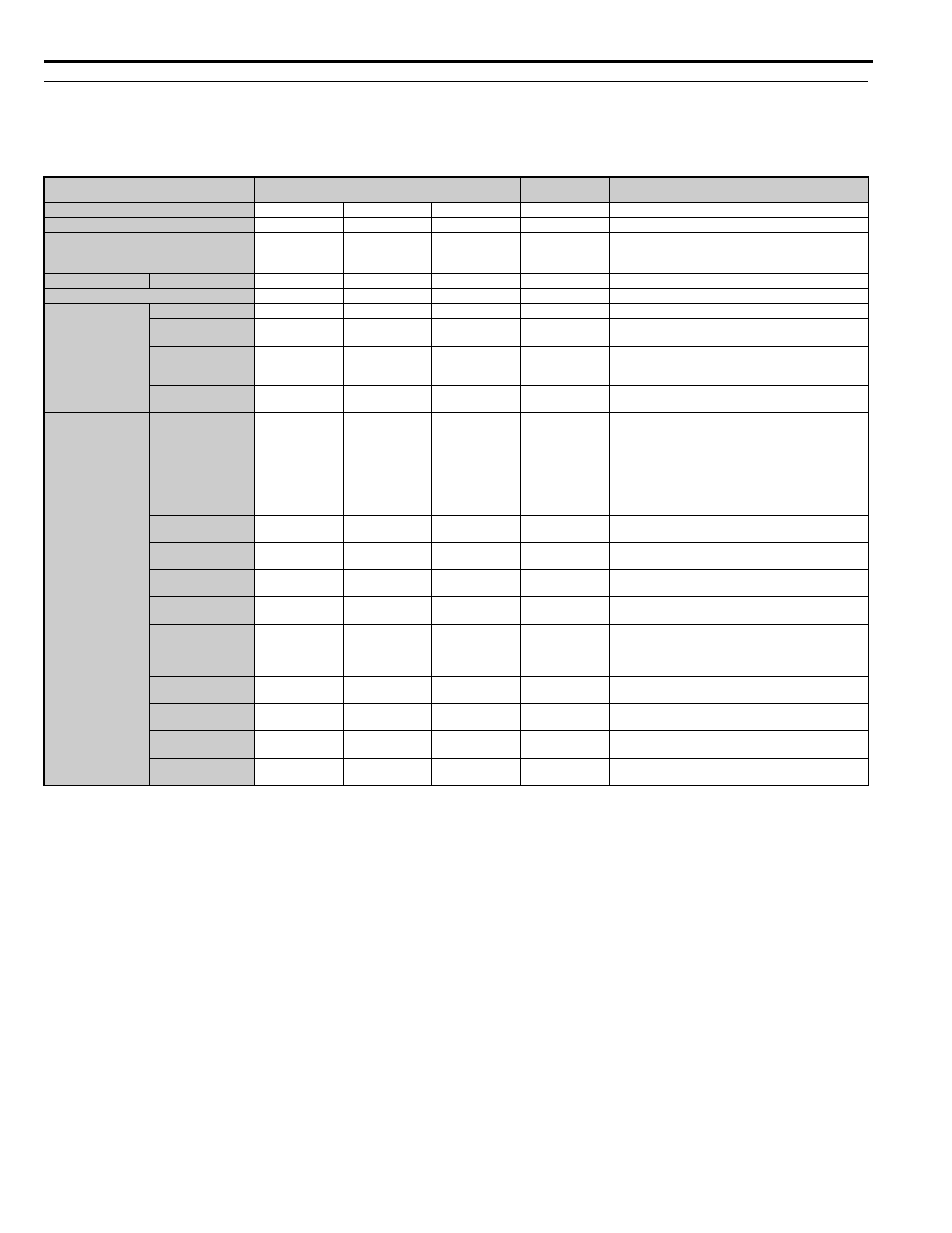
gives an overview of the L1000E motor control method (control modes) and their various features.
Table 1.1 Control Modes and their Features
Motor Type
Induction Motors
Permanent
Magnet Motors
Comments
Control Mode
V/f
OLV
CLV
CLV/PM
–
Parameter Setting
A1-02 = 0
A1-02 = 2
A1-02 = 3
A1-02 = 7
Default Setting is Open Loop Vector Control.
Basic Description
V/f control
Open Loop Vector
control
Closed Loop
Vector control
Closed Loop
Vector control for
PM motors
–
Type of Applications
Motor Type
IM
IM
IM
PM
–
PG Option Card
N/A
N/A
YES
YES
–
Control
Characteristics
Speed Control Range
1:40
1:200
1:1500
1:1500
May fluctuate with characteristics and motor temperature.
Speed Accuracy
±2 to 3%
±0.2%
±0.02%
±0.02%
Speed deviation when operating at constant speed. May
fluctuate with characteristics and motor temperature.
Speed Response
3 Hz
(approx.)
10 Hz
100 Hz
100 Hz
Max. frequency of a speed reference signal that the drive
can follow. May fluctuate with characteristics and motor
temperature.
Starting Torque
150% at 3 Hz
200% at 0.3 Hz
200% at
0 r/min
200% at
0 r/min
May fluctuate with characteristics and motor temperature.
Performance may differ by capacity.
Application-Specific
Auto-Tuning
Line to line
resistance
• Rotational
• Stationary
• Line to line
resistance
• Rotational
• Stationary
• Line to line
resistance
• Stationary
• Stationary
Stator
Resistance
• Encoder Offset
• Rotational
Back EMF
Constant
Automatically adjusts parameter settings that concern
electrical characteristics of the motor.
Torque Limit
N/A
YES
YES
YES
Sets the maximum torque for the motor to protect the load
and connected machinery.
Droop Function
N/A
N/A
YES
YES
Controls the load sharing between two motors that drive
the same mechanical system.
Energy-Saving
Control
N/A
N/A
N/A
YES
Saves energy by always operating the motor at its
maximum efficiency.
Inertia Compensation
N/A
N/A
YES
YES
Improves speed accuracy when the load changes by
compensating effects of the system inertia.
DC Injection at Start
and Stop/Position
Lock
YES
(DC injection
braking at start and
stop)
YES
(DC injection
braking at start and
stop)
YES
(Position Lock)
YES
(Position Lock)
Builds up motor torque during stop in order to prevent
movement of the elevator when the brake is released at
start and applied at stop.
Torque
Compensation
N/A
N/A
YES
YES
Avoids rollback at start using the analog signal from an
external load cell connected to the drive.
Anti Roll Back
N/A
N/A
N/A
YES
Prevents roll back at start without any external load
signal.
Slip Compensation
YES
YES
N/A
N/A
Adjusts the leveling speed reference in order to improve
the stopping accuracy.
Short Floor
YES
YES
YES
YES
Optimizes the stopping time at rides where the nominal
speed is not reached.