Using pid control – Yaskawa Matrix Converter User Manual
Page 259
6
-94
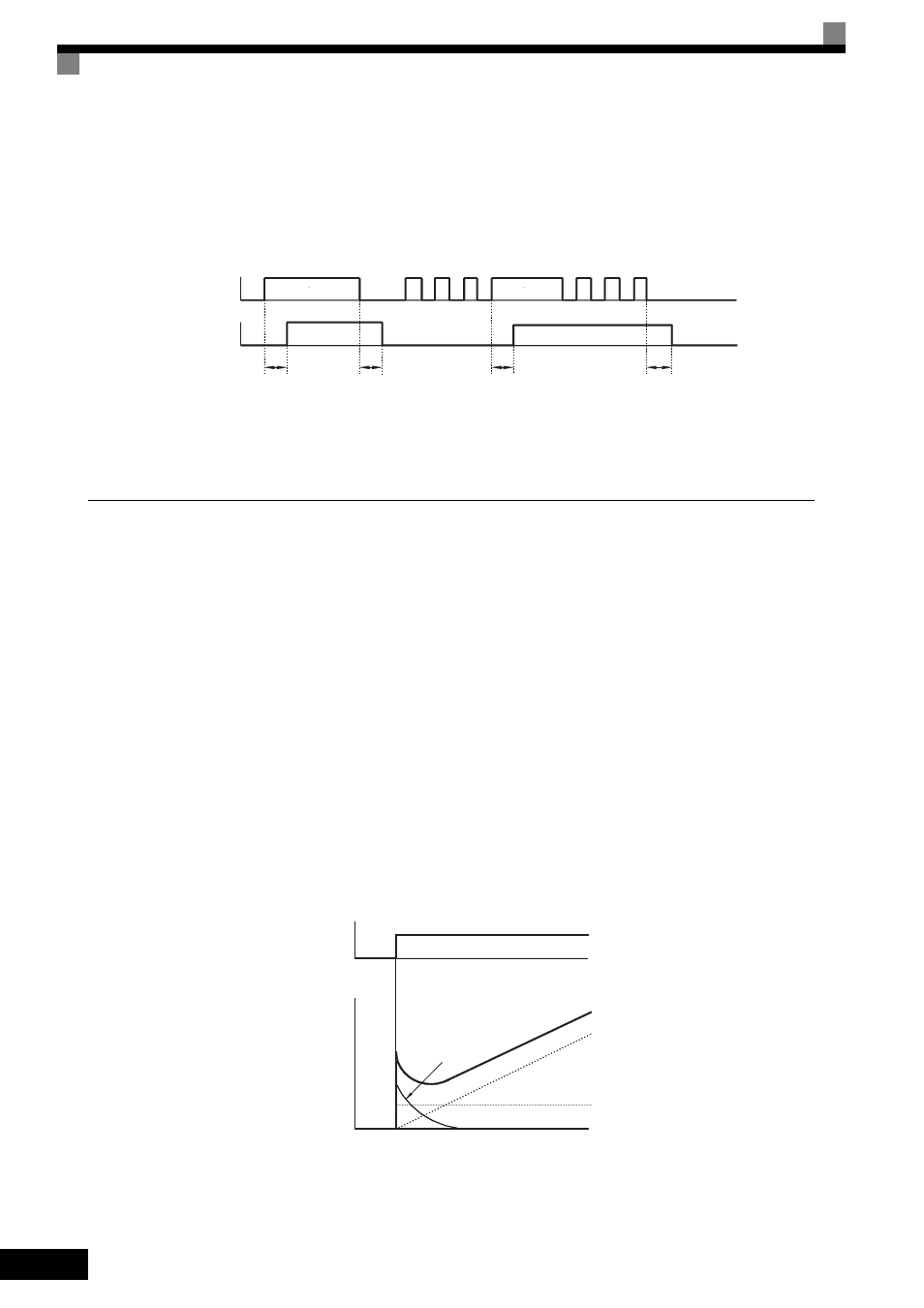
Setting Example
When the timer function input on time is longer than the value set in b4-01, the timer output function is turned
on. When the timer function input off time is longer than the value set in b4-02, the timer output function is
turned off. An example of timer function operation is given in the following diagram.
Fig 6.61 Timer Function Operation Example
Using PID Control
PID control is a method of making the feedback value (detection value) match the set target value. By combin-
ing proportional control (P), integral control (I), and derivative control (D), targets (machinery) with play time
can be controlled.
The characteristics of the PID control operations are given below.
•
P control: Outputs the amount of operation proportional to the deviation. The deviation can not be set to
zero using P control alone.
•
I control: Outputs the amount of operation that integrates the deviation. Used for matching feedback value
to the target value. I control is not suited, however, to rapid variations.
•
D control: Outputs the amount of operation derived from the deviation. Can respond promptly to rapid
variations.
PID Control Operation
To understand the differences between each PID control operation (P, I, and D, the variation in the amount of
operation (output frequency) is as shown in the following diagram when the deviation (i.e., the difference
between the target value and feedback value) is fixed.
Fig 6.62 PID Control Operation
on
on
b4-01
b4-02
b4-01
b4-02
on
on
Timer function input
Timer function output
Deviation
I control
Amount of operation
D control
Time
PID control
Time
P control