Circular path g2/ g3, 13 simple linear and cir c ular mo v e ments – HEIDENHAIN CNC Pilot 4290 V7.1 User Manual
Page 190
190
4.13 Simple Linear and Cir
c
ular Mo
v
e
ments
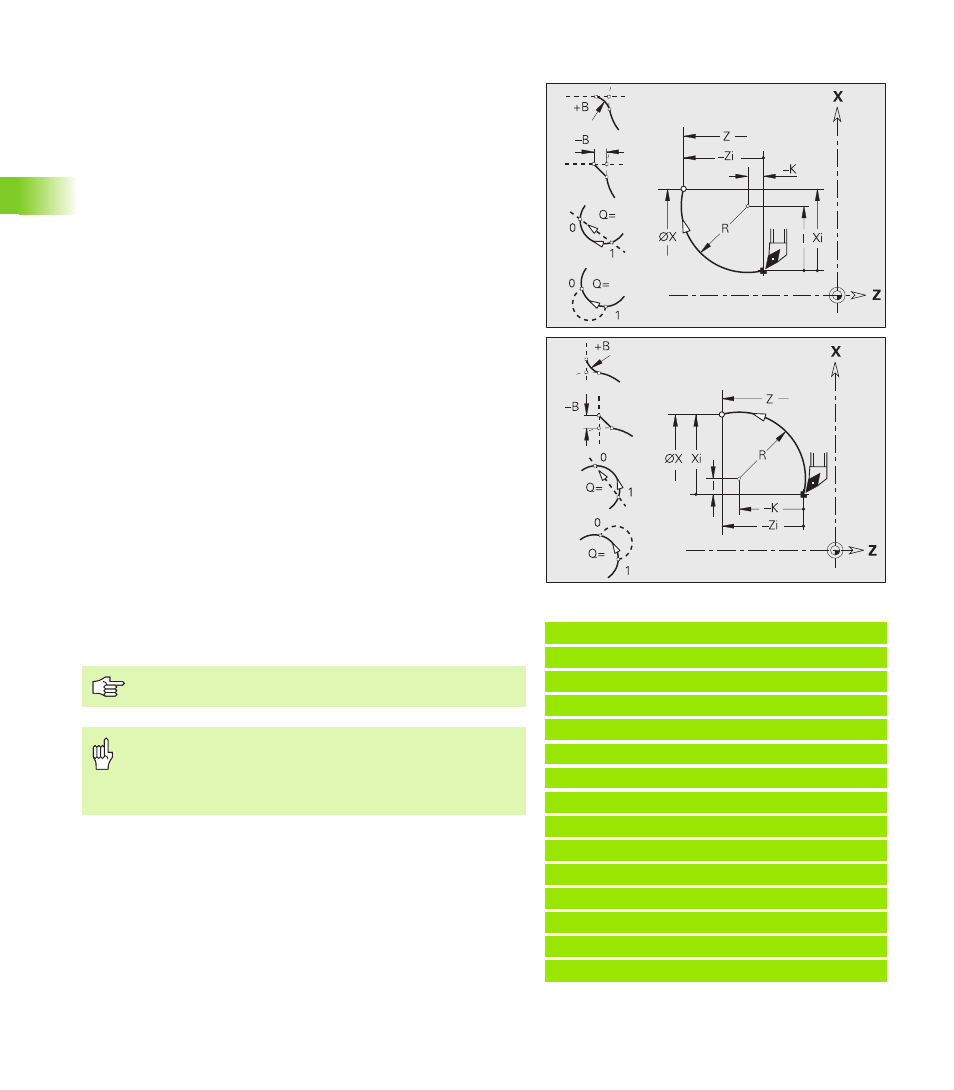
Circular path G2/ G3
G2/G3 moves the tool in a circular arc at the feed rate to the “end
point.” The center dimensioning is incremental. Direction of rotation
(see help graphic):
G2: In clockwise direction
G3: In counterclockwise direction
Example: G2, G3
. . .
N1 T3 G95 F0.25 G96 S200 M3
N2 G0 X0 Z2
N3 G42
N4 G1 Z0
N5 G1 X15 B-0.5 E0.05
N6 G1 Z-25 B0
N7 G2 X45 Z-32 R36 B2
N8 G1 A0
N9 G2 X80 Z-80 R20 B5
N10 G1 Z-95 B0
N11 G3 X80 Z-135 R40 B0
N12 G1 Z-140
N13 G1 X82 G40
. . .
Parameters
X
End point (diameter)
Z
End point
R
Radius (0 < R <= 200 000 mm)
I
incremental center point (distance from starting point to center
point; radius)
K
Incremental center point (distance from starting point to
center)
Q
Point of intersection. End point if the circular arc intersects a
line segment or another circular arc (default: 0):
Q=0: Near point of intersection
Q=1: Far point of intersection
B
Chamfer/rounding. Defines the transition to the next contour
element. When entering a chamfer/rounding, program the
theoretical end point.
No entry: Tangential transition
B=0: No tangential transition
B>0: Rounding radius
B<0: Chamfer width
E
Special feed factor for chamfer/rounding arc (default: 1)
Special feed rate = active feed rate * E (0 < E <= 1)
Programming X, Z: Absolute, incremental, modal or “?”
Danger of collision!
If V variables are used for calculating the address
parameters, a limited contour check is carried out. Ensure
that the variable values produce a circular arc.