Configuring vlans, Overview, Configuration guidelines – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 180
159
Configuring VLANs
Overview
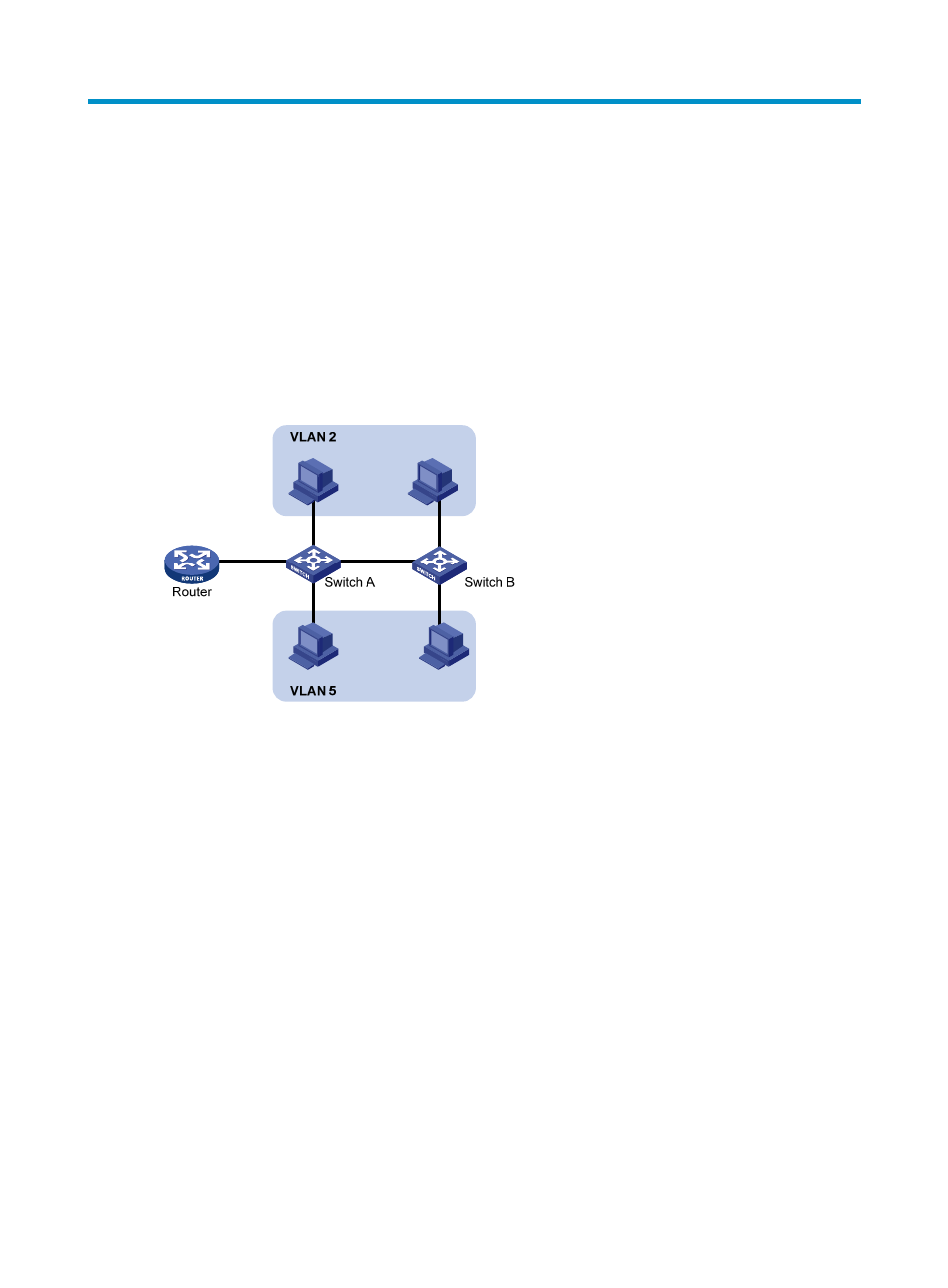
Ethernet is a network technology based on the Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detect
(CSMA/CD) mechanism. The medium is shared, so collisions and excessive broadcasts are common on
an Ethernet. To address this issue, virtual LAN (VLAN) was introduced to break a LAN down into
separate VLANs. VLANs are isolated from each other at Layer 2. A VLAN is a bridging domain, and all
broadcast traffic is contained within it, as shown in
Figure 123 A VLAN diagram
You can implement VLANs based on a variety of criteria. However, the Web interface is available only
for port-based VLANs, which group VLAN members by port. A port forwards traffic for a VLAN only after
it is assigned to the VLAN.
For more information about VLAN, see "
About the H3C Access Controllers Web-Based Configuration
Configuration guidelines
When you configure VLAN, follow these guidelines:
•
VLAN 1 is the default VLAN, which cannot be manually created or removed.
•
Some VLANs are reserved for special purposes. You cannot manually create or remove them.
•
Dynamic VLANs cannot be manually removed.
•
By default, an access port is not a tagged member of a VLAN, and a hybrid or trunk port is a
tagged member of VLAN 2 to VLAN 4049.